* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Location and Climate
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
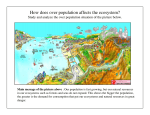
7th Grade Science Ecology Freshwater Ecosystems Facts and Information Description Streams and Rivers With three-fourths of the Earth being covered with water, it is not surprising that many organisms make their homes there. Water ecosystems can be either salty (marine) or fresh. Freshwater ecosystems include lakes, ponds, streams and rivers. Abiotic factors such as sunlight, temperature, oxygen and salt content affect all water ecosystems. Streams and rivers are freshwater ecosystems with moving water. These waters can either move fast or slow. Fast-moving water has a higher amount of oxygen then slow-moving water. Organisms that live here need the additional oxygen to survive. Most plants are not adapted to survive the moving water, so they grow mainly on the banks of the river or stream. Primary consumers that live in the moving waters of the river rely on leaves and seeds that fall in there for food. Animals of the moving-water ecosystems include: large-mouth bass, perch, fathead minnows, crayfish, leeches, trout and many species of insects Sunlight is especially important. Plants need energy from the sun in order to carry out their food-making process called photosynthesis. Since water absorbs sunlight, photosynthesis only occurs at the surface. For this reason, most of the plants in water ecosystem food chains are algae. Ponds and Lakes Freshwater ecosystems can have either still water or moving water. Ecosystems with still water are called ponds and lakes. Lakes are larger and deeper than ponds. Many ponds are small and shallow enough to allow sunlight all the way through to the bottom. These ponds have plant life all the way to the bottom. Many plants such as cattails, reeds, and other grasses grow along the edge of the lake where their roots can reach the soil. Animals that live in lakes and ponds must be adapted to the still water. In addition, the animal life changes, depending on where in the lake you are! Along the shore you would find animals such as frogs, snails and insects. In the open water, animals such as sunfish feed on the algae floating on the surface. At the bottom of the lake, animals such as catfish scavenge for bits of food left over from predators’ meals. SBISD As the fast-moving streams and rivers flow toward the ocean, they eventually join other flowing water ecosystems. As these moving waters join, the speed of the flow slows down. More soil circulates throughout the water and this slower water allows more plants and animals to make their homes here. Spring 2009