* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 20: Mountain Building
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
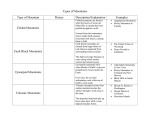
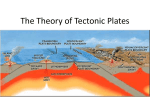
Chapter 20: Mountain Building I. Convergent Boundary Mountains A. Orogeny 1. processes that form all mountain ranges 2. orogenic belts occur frequently at plate boundaries B. Oceanic-Oceanic Convergence 1. Creates a subduction zone 2. The end of one plate melts 3. Magma from melted plate rises to form volcanic mountains C. Oceanic-Continental Convergence 1. Subduction Zone a) ocean plate sinks & melts 2. Volcanic mountains form on the continent 3. Sediments from the ocean are scraped of the ocean plate a) extreme pressure b) creates severely folded rocks (metamorphic) D. Continental-Continental Convergence 1. Creates the Earth’s tallest mountain Ranges a) K2 b) Mount Everest 2. Plates do not sink under each other a) crumple up to form faults b) crust is pushed up and over the faults II. Early Appalachian Mountains (Blue Ridge) A. Read pages 532-534 B. Answer the following: 1. When did the formation of the Appalachians begin? 2. When did the plate movements reverse in forming the Appalachians? 3. According to Figure 20-11, when did the fragment that was to become the Blue Ridge Province attached to N. America? 4. According to Figure 20-11, what does the island arc that attached 400300 m.y.b.p. eventually become? 5. According to Figure 20-11, how long ago did ancestral Africa collide with ancestral N. America? III. Other Types of Mountains A. Divergent Boundary Mountains 1. Occurs at mid-ocean ridges 2. High temperature magma is less dense a) low density causes the crust to rise and form mountains b) mountains are gently sloping 1 3. Mid-ocean ridge rocks a) igneous b) vertical dikes c) pillow basalt B. Non-boundary Mountains 1. Uplifted Mountains a) less folding and faulting b) form when the crust is heated c) lower density causes the entire section to rise d) ex. Adirondack Mountains in NY 2. Fault Block Mountains a) form when large pieces of crust are tilted, uplifted, or dropped downward 3. Volcanic Peaks *You must also know your vocabulary * The test will contain several application style questions. *There will be some open-ended questions also for completion (these are worth more) 2