* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DC Resistivity: Modeling
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
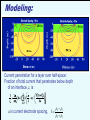
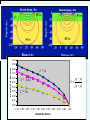
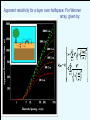
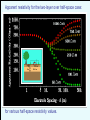
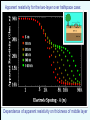
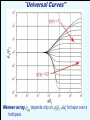
Geology 5660/6660 Applied Geophysics 6 Apr 2016 Last Time: Intro to DC Electrical Resistivity • DC Resistivity: inject electrical current across two (source & sink) electrodes, measure voltage across two others. • Governing equation derives from Maxwell’s equations to get Ohm’s Law: • Material property imaged is rock resistivity: Low for clays, shales, graphite; intermediate for soils/ unconsolidated seds; high for consolidated seds and crystalline rocks Sensitive to sulfides, temperature, pore fluids • Apparent resistivity (1&2 current; a&b voltage electrodes) For Wed 6 Apr: Burger 265-301 (§5.1-5.4) © A.R. Lowry 2016 Geology 5660/6660 Applied Geophysics Last Time Cont’d: DC Electrical Resistivity • Electrode Arrays: Wenner (constant spacing): Wenner-Lee (local voltage measurements) Schlumberger (move only current electrodes): Dipole-dipole Pole-dipole (simple approach for tunnels/karst) Modeling: 1 2 Current penetration for a layer over half-space: Fraction of total current that penetrates below depth of an interface, z, is a is current electrode spacing, r2 - r1 k= r2 + r1 1 2 1.00 Fraction of Current 0.90 0.80 z=a 0.70 0.60 0.50 r2 - r1 k= r2 + r1 z = 3a/2 0.40 0.30 z = 3a 0.20 0.10 0.00 -1.00 -0.80 -0.60 -0.40 -0.20 0.00 0.20 Resistivity Ratio k 0.40 0.60 0.80 1.00 Apparent resistivity for a layer over halfspace: For Wenner array, given by: array Apparent resistivity for the two-layer over half-space case: for various half-space resistivity values. Apparent resistivity for the two-layer over halfspace case: Dependence of apparent resistivity on thickness of middle layer “Universal Curves" Wenner array app depends only on 2/1, a/d1 for layer over a halfspace For 3+ layers: • Rule of thumb: if layer thickness < 0.1 the depth to top of layer, it cannot be resolved • But also depends on resistivity contrast (thicker layers may not be resolved if contrast is too small; transition of apparent resistivity versus a-spacing is much sharper for a resistive layer over a conductive layer than for the opposite). • When layer thickness is small relative to depth-to-top, solution from sounding can be highly non-unique Resist does either Wenner or Schlumberger array for vertical sounding only (horizontal layers); and is somewhat less adaptable than the other Burger programs = 100 m = 10 m = 500 m = 10000 m 10 m (Particularly because of 10 m forced logarithmic 10 m variation of a-spacing)