* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Metals scheme
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
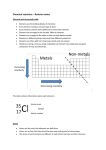
Y10 Science 9/05/2017 ATOMS AND METALS 2013 4 weeks Material World Achievement Objectives: Properties and changes of matter: Investigate the chemical and physical properties of different groups of substances, for example acids and bases, fuels and metals. Distinguish between pure substances and mixtures and between elements and compounds. The structure of matter: Describe the structure of the atoms of different elements. Distinguish between an element and a compound, and a pure substance and a mixture at particle level. Chemistry and society: Link the properties of different groups of substances to the way they are used in society or occur in nature. Focusing questions? What makes up an atom? What is the difference between a metal and a non-metal? What properties of metals make them useful? What causes corrosion? Why are alloys so useful? How do ions form? How are chemical formulae worked out? Key competencies focus: All key competencies are incorporated into this unit of work, however, in this unit there is particular emphasis on: Using language, symbols, and texts. Assessment focus: Nature of science: Communicating in science – Alloys Written test Literacy focus- keywords: Key words/terms: atom, nucleus, proton, neutron, electron, group, physical property, alloy, rusting, corrosion, formula, compound, reactant, product, equation, oxide, pop test, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, oxygen. Note: NOS = Nature of Science text NMS = New Millennium Science text KISS = Kiwi Integrated Science text WB = Science 10 workbook Learning Experiences Resources 1. Revision Issue Science 10 workbook. Complete revision activities. WB p1-6 Nature of science focus` Y10 Science 9/05/2017 Learning Experiences Resources 2. Atomic structure Pretest Show first 5min only of Video 22 on the history of the discovery of structure of atoms. Complete p13-14 of workbook ‘An atomic jigsaw’. Draw structure of the atom – label nucleus, protons, neutrons and electrons. Draw the electronic structure of a variety of different elements showing electron shells. Define atomic number, mass number and calculate numbers of different subatomic particles. 3. Periodic Table List and memorise symbols and names of first 20 elements plus other useful metals from elsewhere in Periodic Table (Ti, Cr, Fe, Ni, Cu, Zn, Ag, Sn, Pt, Au, Hg, Pb, U). Give out A5 size Periodic table – find the names of the shaded elements (using text). Put in the line that divides metals and non-metals List characteristics of different Groups on the table (Gp 1, Gp 2, halogens, inert gases. Students choose an element they don’t know much about and produce an A4 poster (atomic structure, discovery, properties, uses). 4. Comparing properties of metals and non-metals Revise physical vs chemical property. Compare the physical and chemical properties of a variety of metals and nonmetals e.g electrical conductivity, malleability, Mp, lustre, reaction with acid. Skill: Compare conductivity of metal with non-metal Summarise properties and relate properties to uses. Pretest in folder Video 22 ‘Atoms and their electrons’ NOS 2 p12-14 (Atoms again) NMS 2 p4-5 (Atoms again) WB An atomic jigsaw p13 KISS Bk 3 pg37 5. Physical properties: Measuring melting point ‘Think-pair-share’ physical properties of a slab of wax. Practical skill: Measure Mp of wax (melt wax and measure temp at point when all wax is melted. Do not continue heating. Average class results. 6. Applications of knowledge of properties of metals Teacher demo: Use the Ring and Ball (heating tray) to demonstrate expansion on heating and contraction on cooling) and relate to application of removing tight caps, putting steel wagon rims on wooden wheel etc Teacher demo: Compare heat conductivity of iron vs copper and relate to use of Cu as pot bases. Nature of science focus` Understanding NMS 2 p6-7 (Periodic trends) WB Symbols and formulae p12 WB Atoms and elements p14 WB Using the periodic table p15 WB Prac 14C p131 Periodic table song: http://www.privatehand.com/flash/elements.ht ml ‘Periodic Table’ video Communicating WB Prac 14C2 p132 WB Metal or non-metal p8 WB The structure of metals and non-metals Metals: Mg, Fe, Cu Non-metals: S (sulphur chunk), C(coal or graphite electrode), wax, sugar Use powerpack, wires and bulb to test Thermometer Paraffin wax Digital thermometers Investigating Investigating Communicating Investigating KISS Bk2 p44-45 KISS Bk2 p48-49 Hmwk: WB p18 -19 Y10 Science 9/05/2017 Learning Experiences Resources Practical: Heat a nail strongly and bend with tongs. Relate to blacksmith making horseshoes, twin towers collapsing on 9/11. Fitting steel tyr to wagon wheel: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JBM0RzElvRE &feature=related 7. Metals and technology: Alloys Define alloy. List some alloys, composition and use. Relate use of alloy to its properties. Practical: Make an alloy by coating copper with brass. See instruction sheet in folder. NOS 2 p42-45 NMS 2 p52-53 (Metals) Nature of science focus` Investigating Participating & contributing Aluminium alloys: http://videos.howstuffworks.com/discovery/3548 9-howstuffworks-show-episode-6-aluminumand-drag-racing-video.htm Hmwk: Find out the % composition of N.Z coins. 8. Assessment: Communicating in science - Alloys 9. Metal oxides and other compounds Practical: Burning magnesium Reactants, Product, Observations, Particle picture, word equation, symbol equation Define burning as fast oxidation. Teacher demo: Heat mixture of zinc powder and sulphur on tin lid over a Bunsen. Nice flash and mushroom cloud. Do in fume cupboard if possible or by open window. (Have a go prior to lesson) Write word, particle picture and symbol equation (zinc sulphide produced) 10. Ion formation Use previous day’s reactions to describe ion formation. Draw diagrams showing electron transfer. 11. Formulae of molecules and compounds Define compound. Using a variety of molymod molecules you have prepared earlier, write chemical formulae for molecules and compounds. Draw simple particle pictures of compounds from their formula. 12. Rusting Investigate conditions needed for rusting to occur. Practical: Start experiment “Rusting Away”. Use steel wool instead of nails. Observe daily over three days. Best set up on Friday and check on Monday. Write word equation for rusting and define rusting as slow oxidation = corrosion. Discuss how rusting/corrosion produce a compound that has different physical characteristics to the metal it came from. Assessment task in folder Communicating Investigating Mg ribbon and tongs NOS p15-17 WB Ex14.12 p17 Communicating NOS 2 p18-21 Molymods NMS 1 p98-99 (Formulae) NMS 2 p8-9 (Compounds) WB Counting atoms, Formula practise, Write a wrong p20-22 KISS Bk1 pg58-59 WB 14.05 & 14.06 p10-11 Steel wool, cooking oil Communicating Investigating Participating & contributing Y10 Science 9/05/2017 Learning Experiences Resources Nature of science focus` 13. 14. Steel wool, Mg ribbon Investigating Preventing rusting Check results of previous practical and write conclusions. Preventing rusting – read and summarise text (pg59),answer questions (pg58) Practical: Mg ribbon wrapped around steel wool. Unit test Test in folder