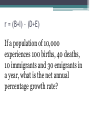* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Rust Science
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
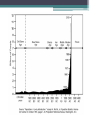
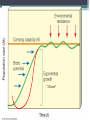
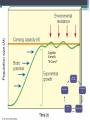
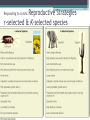
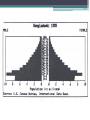
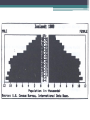
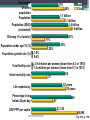
Population Dynamics Unit 2 APES Why study Human Population? • The World may or may be soon overpopulated. • Environmental Problems of Overpopulation: ▫ Resource Depletion ▫ Environmental Degradation Essential Questions • What is the history of human population growth, and how many people are likely to be here by 2050? • How is population size affected by birth, death, fertility, and migration rates? • How is population size affected by percentages of males and females at each level? • How can we slow population growth? • What success have India & China had in slowing population growth? • What are major impacts of human activities on the world’s natural ecosystems? Is the World Overpopulated? • World pop is projected to increase from 6.6 billion to 8.9 billion between 2006 & 2050. • The debate over interactions between population growth, economic growth, politics, and moral beliefs is one of the most important and controversial issues in environmental science. • Much of the world’s population growth is occurring in developing countries like China & India. Is the World Overpopulated? • Some people argue that the planet has too many people. • Some feel that the world can support billions of more people due to technological advances. • There is a constant debate over the need to reduce population growth. ▫ However, moral, religious, and personal freedoms must be considered. Brief History of Human Population Growth • Grew slowly at first but has grown rapidly recently because of the expansion of agriculture and industrial production (Industrial Revolution) AND lower death rates from improvements in hygiene and medicine. • In 2006, the population of developed countries grew exponentially at 0.1% per year, while, developing countries grew at 1.5% per year (15x faster) Where is the World Population Headed? • We do not know how long we can continue to increase the Earth’s capacity for human before the environment breaks down. ▫ There are likely to be between 7.2-10.6 billion people of Earth by 2050. ▫ 97% of the population growth will come from people in developing countries living in acute poverty (< $2 USD/day ~12 Yuan/day) UN Projections for Pop Growth Projections based on high, medium, or low world average fertility rates (# of children/woman). •High 2.5 •Medium 2.0 •Low 1.5 Opposite Views Of Population Growth & Issues • Thomas Malthus Human Pops grow exponentially until disease or famine, or social conditions reduced fertility rates. Opposite Views Of Population Growth & Issues Pop Growth results from • Karl Marx poverty and social ills. Pop Growth would slow if all people were treated justly. Population Dynamics ~ The Basics • Biotic Potential: reproductive rate of an organism if resources were unlimited & conditions were ideal. • For example the common housefly can lay 120 eggs in each generation (56 days). If nothing hurt the eggs or the flies, in 7 generations (1 year) there would be 5.6 trillion flies from 1 proud parent! • However, there are of course limiting factors. ▫ Scarcity of resources, competition, predation, disease, accidents, etc. “J Curve” Environmental Resistance • Exponential growth can only with unlimited resources, but factors usually limit growth (environmental resistance). • Carrying Capacity (K): Number of organisms that an area can support without depleting Rapid resources Growth Pop Rise Below K Overshoot K Pop Crash Adapting to Environmental Resistance • Over time species may increase their carrying capacity by developing adaptations. • Some species maintain their carrying capacity by migrating to other areas. • So far, technological, social, and other cultural changes have extended the earth’s carrying capacity for humans. Growth Patterns: • EXPONENTIAL GROWTH: pop growth increases at a constant rate per unit of time. • 2-4-8-16-32-64-…. • LOGISITIC GROWTH: pop growth is slowed as it approached carry capacity due to scarcity of resources, etc. Logistic Growth “S Curve” Rapid Growth Pop Rise Below K Overshoot K Pop Crash Population Density • Number of organisms in a defined space • Density Dependent: growth rate depends on the population density. ▫ Disease, stress, predation, etc. ▫ Logistic Growth is density dependent • Density Independent: population control factors not dependent on population density. ▫ Drought, fire, habitat destruction, weather Reproductive Strategies r-selected & K-selected species Responding to Limits: Survivorship Curves Late loss Early loss Age Factors that Affect Population Growth • r = (B+I) – (D+E) • • • • • rate of growth B = births I = immigration D = deaths E = emigration Demographics • Vital statics about people such as ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ Births, Deaths, Immigration Emigration Where they live Population size, Etc. The Young, Poor, & Growing Countries • Asia, Africa, & Latin America • 80% of the world population, 90% of projected growth • Highest growth “hot spots” ▫ Sub-Saharan Africa, Middle East ▫ Economics, politics, religion, civil unrest, ▫ High birth rates, low contraceptive use) • Highest growth rates ▫ United Arab Emirates @ 6.8% The Older, Rich, Relatively Stable Countries • N. America, W. Europe, Japan, Australia, & New Zealand • Italy, Germany, Hungary & Japan have declining growth rates. ▫ Average age = 40, Life expectancy = 90, women are choosing to not have children ▫ Japan is currently around 127 million and expected to decrease to 100 million in 2050 1) Fertility/Birth Rates • Crude Birth Rate (B): number of births in a year per 1000 people • Total Fertility Rate (TFR): number of children born to an average woman in her reproductive life. • Replacement Level Fertility (RLF): number of children needed to replace the parents. ▫ About 2.1 children in developed countries ▫ Higher in other countries with a high infant mortality rate 1) Fertility/Birth Rates Cont. • Rates have declined in every region except for Africa ▫ Thailand reduced their TFR from 7.0 in 1979 to 1.64 in 2009 ▫ China went from a TFR 6.0 in 1970 to 1.8 in 1990 to 1.6 in 2009 due to the one-child policy ▫ Macao has lowest TFR in the world with 0.9 • World Average TFR = 2.6 Factors Affecting Fertility & Birth Rates • • • • • • • • • Cost of raising & educating the children Availability of pensions Urbanization Education & employment opportunities Infant deaths Marriage age Availability of contraception & abortion Women’s Rights within a culture Cultural beliefs, traditions, & cultural norms 2) Mortality (Death) Rates • Crude Death Rate: number of deaths per 1000 people in year ▫ Less Developed countries, such as Africa, see death rates of 20+/1000. ▫ Wealthier countries see about 10/1000 • Infant Mortality Rate: Number of child/infant deaths. • Natural Increase = crude birth rate – crude death rate Factors Affecting Mortality Rates • Increased food supplies and distribution. • Better nutrition • Medical & public health technology (immunizations/antibiotics) • Improved sanitation & personal hygiene • Safety of water supplies 2006 3) Immigration & Emigration • Immigration (I): people migrating into a population • Emigration (E): people migrating out of a population • Net Migration (I-E): Total number of people moving in and out of a population r = (B+I) – (D+E) • Total Growth rate (r): calculate using crude rates (per 1000) and divide by 10 = percentage • Zero Population Growth (ZPG): when B+I = D+E • Doubling time: amount of time it takes for a population to double ▫ Rule of 70s: Divide 70 by annual natural increase equal the approximate doubling time r = (B+I) – (D+E) If a population of 10,000 experiences 100 births, 40 deaths, 10 immigrants and 30 emigrants in a year, what is the net annual percentage growth rate? Doubling Time • If a population of a country grows at a rate of 5% a year, the number of years required for the pop to double is what? • The world’s 10 most populous countries in 2006 with projections in 2025. U.S. Trends • Nearly 2.9 million people added to the US in 2006. ▫ 59% occurred because of births outnumbering deaths. ▫ 41% came from illegal and legal immigration. • Sharp Rise in US birth rates during 1946-1964 called the Baby boom. ▫ Economic success & Men returning home from war. US Trends • The baby bust that followed the baby boom was largely due to delayed marriage, contraception, and abortion. Case Study: Fertility and Birth Rates in the United States • In 2006, the total fertility rate in the United States was slightly > 2.0 U.S. Trends Since 1820, the U.S. has admitted almost twice as many immigrants and refugees as all other countries combined. U.S. Trends • U.S. infant mortality is higher than it could be (ranked 46th world-wide) due to: ▫ Inadequate pre- and post-natal care for poor. ▫ Drug addiction. ▫ High teenage birth rate. 4) Life Expectancy (LE) • Age that a newborn infant can be expected to live to (average age of death) • Most population growth is due to a decline in death rates b/c of longer life expectancy. • General Trends: ▫ More developed countries have higher LE ▫ Women tend to have higher LE than men ▫ More money, longer life Implications of Longer Lives on Populations • Increased dependency ratio: ▫ Number of non-working compared to working individuals in a population. ▫ Countries, such as US & Japan, are seeing the number in the working force decline as the number of retiring individuals increases. Age Structure • Percentage of people in young, middle, and older age groups determines how fast populations grow or decline. • Generation time: time it takes for one generation to pass • The number of people younger than age 15 is the major factor determining a country’s population growth. • Changes in the distribution of a country’s age groups have long-lasting economic and social impacts. Histograms • Graphs that shows the different age classes of a population ▫ Pre-reproductive age (14 and under) Not mature enough to reproduce ▫ Reproductive age (15-45) Able to reproduce ▫ Post-reproductive age (46 and older) To old to reproduce • Broken down by age. You can see the birth rate, maturity rate and death rate of an entire population. Usually broken down by country Histograms • Populations with a large proportion of its people in the reproductive ages 1-14 have a large potential for rapid population growth. • 32% of the people in developing countries were under 15 years old in 2006 versus only 17% in developed countries. • Today, baby boomers make up nearly half of all adult Americans and dominate the populations demand for goods and services. Expansive/rapid growth • Birth rate exceeds the death rate. Population is getting larger. Pyramid shaped histogram. • Ex’s. Kenya, Nigeria and Saudi Arabia. Stable/Slow Growth (Zero Growth) • Birth rate almost equals death rate. The population is not getting any larger or is growing very slowly. Histogram shape is straighter and more box-like until about age 45-85. • Ex. US, Australia & Canada has slow • Denmark, Austria and Italy has stable Declining (negative growth) • When the birth rate is smaller than the death rate. The pyramid bulges near the top or is inverted. • Ex. Germany, Bulgaria & Hungary. Declining (negative growth) • When the birth rate is smaller than the death rate. The pyramid bulges near the top or is inverted. • • Ex. Germany, Bulgaria & Hungary 5) Social & Economic Impacts • More Children ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ Needed to help with income & chores High infant mortality rates Societal status/pride Unmet need for contraceptives • Less Children ▫ Higher education ▫ Career women ▫ Cost of raising child Demographic Transitions • Increased economic development accompanies as decrease in death rates and birth rates. • • • • Stage 1: Stage 2: Stage 3: Stage 4: Pre-Industrial Transitional Industrial Post Industrial Demographic Transitions • Generalized model of demographic transition. ▫ Some developing countries may have difficulty making the demographic transition. Figure 9-14 Pre-Industrial • • • • • Kenya, Yemen, Libya, Jordan Food shortage Malnutrition Lack of sanitation Lack of medicine • High Death rate ~35/1000 • High birth rate • Little population growth Demographic Transitions • Generalized model of demographic transition. ▫ Some developing countries may have difficulty making the demographic transition. Figure 9-14 Transitional • • • • Better sanitation Economic development Better jobs Increase in medicine • Death rate rapidly declining • Birth rate increases (at first) • Rapid Increase in population Demographic Transitions • Generalized model of demographic transition. ▫ Some developing countries may have difficulty making the demographic transition. Figure 9-14 Industrial • Low birth rate ▫ better access to birth control ▫ decline in the infant mortality rate increased job opportunities for women ▫ Spend more resources on fewer children • Population grows due to population momentum ▫ More people in at the reproductive age Conditions Needed for Demo Transition • Improved standard of living • Confidence that children will survive to maturity • Improved social status of women • Increase availability of birth control Demographic Transitions • Generalized model of demographic transition. ▫ Some developing countries may have difficulty making the demographic transition. Figure 9-14 Postindustrial • • • • Low birth rate Low death rate Reaches ZPG - Stable but with more people Then birth rates fall below death rates and negative population growth occurs. • 37 countries have reached this stage. (mainly in W. Europe) • To most population experts, the challenge is to help the remaining 88% of the world to get to this stage. Demographic Transitions • Generalized model of demographic transition. ▫ Some developing countries may have difficulty making the demographic transition. Figure 9-14 Developing Countries• China is the largest but has taken drastic population control methods. • By 2050, India is predicted to pass it. Pakistan is projected to become 3rd with Iran and Ethiopia following. • However, Russia is losing 600,000 people a year, after being the 4th largest country in 1950. This is because of environmental pollution, hyperinflation, crime, corruption, disease and despair. Controlling Population Growth • Family Planning – allows couples to determine the number & spacing of their children ▫ Women tend to have fewer children if they are educated, holding a paying job, do not have their rights suppressed. • Birth control: method used to reduce birth • China Vs India’s Family Planning Programs ▫ India has tried to slow their population growth with only little success ▫ Since 1970, China has had the 1 child policy to cut its birth rate in half and sharply reduce its fertility rate. Percentage of world population Population 20% 1.1 billion 1.3 billion 1.4 billion 1.6 billion Population (2050) (estimated) Illiteracy (% of adults) Total fertility rate Infant mortality rate 47% 17% 36% Population under age 15 (%) Population growth rate (%) 20% 1.6% 0.6% 2.9 children per women (down from 5.3 in 1970) 1.6 children per women (down from 5.7 in 1972) 58 27 62 years 70 years Life expectancy Percentage living below $2 per day GDP PPP per capita India China 17% 80 47 $3,120 $5,890 Fig. 9-15, p. 186 China’s Family Planning Program • 1 child policy • TFR ~ 1.6 children/woman • Moved 300 million people out of poverty • Problems: ▫ Male preference = gender imbalance ▫ Average population age is increasing ▫ Not enough resources to support aging population China’s Family Planning Program • Couples who pledge to have only 1 child can receive: ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ Extra food Larger pensions Better housing Free medical care Salary bonuses Free school tuition for their 1 child Preferential treatment in employment for their child ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ Increase fees/ taxes Eliminating tax deductions Loss of health care benefits Loss of job options • More than 1 child? • Boys vs. Girls ▫ Girls are aborted at a higher rate than boys ▫ Some infant girls are killed ▫ Male children are sometimes fed better than female children India’s Family Planning Program • • • • • • • Failing Poor Planning Bureaucratic inefficiency Low status of women Extreme poverty Lack of administrative financial support Disagreement over the best ways to slow population growth Environmental Impact • Paul Ehrlich Formula • Environmental Impact = population X affluence X technology • I=PAT Environmental Impact: Developed Countries • High rate of resource use • Results in high levels of pollution & environmental degradation per person • Estimated that US citizens consume 35X as much as the average citizen of Indian and 100X as much a person in the poorest countries. ▫ Poor parents in a developing country would need to have 70-200 kids to have the same environmental impact as 2 US kids. Environmental Impact: Urbanization • Urbanization leads to slums, fecal snow, disease • Must import its food, water, energy, minerals, & other resources • Produce large amount of waste that pollutes air, land, and water. • 44% of world pop lives in urban areas that only occupy 5% of the worlds land & consume 75% of the world’s resources Natural Capital Degradation Altering Nature to Meet Our Needs Reduction of biodiversity Increasing use of the earth's net primary productivity Increasing genetic resistance of pest species and disease-causing bacteria Elimination of many natural predators Deliberate or accidental introduction of potentially harmful species into communities Environmental Impact: Natural Degradation Using some renewable resources faster than they can be replenished Interfering with the earth's chemical cycling and energy flow processes Relying mostly on polluting fossil fuels Fig. 9-17, p. 188 Environmental Impact: World Hunger • • • • Unequal distribution of available food Loss of arable land Increasing pop growth Increasing poverty in developing countries Strategies for ensuring adequate nutrition for a growing population: • Increase the number of new food crops from a diversity of plant species • Distribute food more equitably • Increase land are that is dedicated to grain production rather than meat production • Assist developing countries in efficient crop irrigation systems. SOLUTIONS: INFLUENCING POPULATION SIZE • The best way to slow population growth is a combination of: ▫ Investing in family planning. ▫ Reducing poverty. ▫ Elevating the status of women. 1994 Global Summit on Population Development • Cairo, Egypt • Encouraged action to stabilized the world’s population at 7.8 billion by 2050, instead of the projected 11-12.5 billion The major goals are to: • Provide universal access to family-planning services. • Improve the health care of infants, children & pregnant women • Encourage development of national population policies • Improving the status of women by expanding education & job opportunities Major goals continued: • Increase access to education for girls • Increase men’s involvement in childrearing responsibility & family planning • Take steps to eradicate poverty • Reduce & eliminate unsustainable patterns of production & consumption.