* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CBSE/12th Class/2010/PHYSICS S.No Questions Answers
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
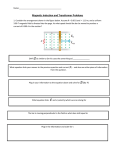
CBSE/12th Class/2010/PHYSICS S.No Questions Q.1 In which orientation, a dipole placed in a uniform electric field is in (i) stable, (ii) unstable equilibrium? Q.2 Q.3 Which part of electromagnetic spectrum has largest penetrating power? A plot of magnetic flux () versus current (I) is shown in the figure for two inductors A and B. Which of the two has larger value of self inductance? Q.4 Figure shows three points charges, +2q, -q and +3q. Two charges +2q and –q are enclosed within a surface ‘S’. What is the electric flux due to this configuration through the surface ‘S’? Q.5 A glass lens of refractive index 1.45 disappears when immersed in a liquid. What is the value of refractive index of the liquid? What is the ratio of radii of the orbits corresponding to first excited state and ground state in a hydrogen atom? Q.6 Answers Ans.1 (i) In stable equilibrium the dipole moment is parallel to the direction of electric field (i.e., q = 0). (ii) In unstable equilibrium dipole moment is perpendicular to the electric field. Ans.2 Gamma rays (-rays) have largest penetrating power. Ans. 3 Since flux is given as Larger is the slope of the graph between vs. I, more will be the value of self inductance L of the coil. It is clear from graph, Slope of A > slope of B. So , A will represent coil of higher L therefore B will represent coil of lower L. Ans.4 Electric flux is given by, Ans.5 For disappearance of glass lens in liquid, refractive index of liquid= refractive index of lens = 1× 45 Ans.6 Radius of the nth orbit is given by For I excited state, n = 2 For ground state, n =1 Therefore, = Q.7 A wire of resistance 8R is bent in the form of a circle. What is the effective resistance between the ends of a diameter AB Ans.7 The effective resistance between the ends of a diameter AB 1 1 1 1 + = 4 4 2 So, Reff = 2R = POORNIMA UNIVERSITY CBSE/12th Class/2010/PHYSICS Q.8 State the conditions for the phenomenon of total internal reflection to occur. Q.9 Explain the function of a repeater in a communication system. Q.10 . (i) Write two characteristics of a material used for making permanent magnets. (ii) Why is core of an electromagnet made of ferromagnetic materials? OR Draw magnetic field lines when a (i) diamagnetic, (ii) paramagnetic substance is placed in an external magnetic field. Which magnetic property distinguishes this behavior of the field lines due to the two substances? Q.11 Draw the circuit diagram of an illuminated photodiode in reverse bias. How is photodiode used to measure light intensity? Ans.8 There are two conditions for the phenomenon of total internal reflection to occur: 1.The index of refraction must decrease across the boundary in the direction of light refraction. 2.The angle of incidence of the light ray must exceed the critical angle of the interface. Ans.9 A repeater is a combination of a receiver and a transmitter. It picks up the signal from the transmitter, amplifies and retransmits it to the receiver sometimes with a change in carrier frequency. Repeaters are used to extend the range of a communication system. Ans.10 (i) Two characteristics of a material used for making permanent magnets: 1. High retentivity and 2. High coercivity (e.g.,steel) so that the magnetisation is not erased by stray magnetic fields, temperature fluctuations or minor mechanical damage. (ii) Ferromagnetic materials has the effect of concentrating the magnetic flux making it more concentrated and dense and amplifies the magnetic field created by the current in the coil and ensures that heating losses are minimum as they will have narrow Hystersis curve. Thus, core of an electromagnet is made of ferromagnetic materials. OR Following figures show the magnetic field lines for a (i) diamagnetic, (ii) paramagnetic substance placed in an external magnetic field The magnetic susceptibility distinguishes this behavior of the field lines due to the two substances. For diamagnetic substance, it is small and negative but for paramagnetic substance, it is small and positive. Ans.11 The circuit diagram of an illuminated photodiode in reverse bias is shown below: It is a reversed biased p-n junction, illuminated by radiation. The magnitude of the POORNIMA UNIVERSITY CBSE/12th Class/2010/PHYSICS Q.12 An electric lamp having coil of negligible inductance connected in series with a capacitor and an AC source is glowing with certain brightness. How does the brightness of lamp change on reducing the (i) capacitance, and (ii) the frequency? Justify your answer. Q.13 Arrange the following electromagnetic radiations in ascending order of their frequencies: (i) Microwave (ii) Radio wave (iii) X-rays (iv) Gamma rays Write two uses of any one of these. Q.14 The radii of curvature of the faces of a double convex lens are 10 cm and 15 cm. If focal length of the lens is 12 cm, find the refractive index of the material of the lens. photocurrent depends on the intensity of incident light as photocurrent incident light intensity A change in the photocurrent shows a change in the light intensity, if a reverse bias is applied. Thus photodiode can be used as a photodetector to detect optical signals. Ans.12 (i) As the capacitance is reduced, capacitive reactance = increases, hence impedance of circuit, = + increases and so current = decreases. As a result the brightness of the bulb is reduced. (ii) As frequency decreases; capacitive reactance = increases and hence impedance of circuit increases, so current decreases. As a result brightness of bulb is reduced. Ans.13 The range of frequencies are (i) Microwave : 3 x 1011 – 1 x 109 (ii) Radio wave : 3 x 107 – 3 x 104 (iii) X-rays : 3 x 1018 – 1 x 1016 (iv) Gamma rays : 3 x 1022 – 3 x 1018 Ascending order of the em waves in terms of frequencies Radio waves < Microwaves< X rays < Gamma rays uses: (i) -rays are highly penetrating. Due to high energy, they are used to produce nuclear reactions. In medicine, they are used to destroy cancer cells. (ii) X-rays are used in medical diagnostics to detect fractures in bones. They are used in engineering to check flaws in bridges. In physics X-rays are used to study crystal structure. (iii) Radiowaves are used for broadcasting programmes to distant places. Cell phones use radio waves to transmit voice communication (iv) Microwaves are used in microwave ovens and radar systems used in aircraft navigation. Ans.14 Given R1 =10 cm, R2 = -15 cm, f =12 cm Refractive index n =? Lens-maker’s formula is POORNIMA UNIVERSITY CBSE/12th Class/2010/PHYSICS Q.15 Q.16 Q.17 An electron is accelerated through a potential difference of 100 volts. What is the de-Broglie wavelength associated with it? To which part of the electromagnetic spectrum does this value of wavelength correspond? so, refractive index=1.5 Ans.15 Given: V=100 V Wavelength =? A heavy nucleus X of mass number 240 and binding energy per nucleon 7.6 MeV is split into two fragments Y and Z of mass numbers 110 and 130. The binding energy of nucleons in Y and Z is 8. 5 MeV per nucleon. Calculate the energy Q released per fission in MeV. =1×227 ´10-10 m = 1×227 Å This wavelength corresponds to X-ray region of electromagnetic spectrum. Ans.16 Given: For X, A=240, BE=7.6 MeV For Y, A=110, BE=8. 5 MeV For Z, A=130, BE=8.5 MeV (a) The bluish colour predominates in clear sky. (b) Violet colour is seen in the bottom of the spectrum when white light is dispersed by a prims. State reasons to explain these observations. Q85 240 MeV – 76 240 MeV Q(85 76) 240 MeV Q09 240 MeV = 216 MeV Ans.17 (a) The intensity of scattered light varies inversely as fourth power of wavelength. In visible light blue colour has minimum wavelength, so it is scattered most, that is why bluish colour predominates in a clear sky. (b) White light ranges from 400 nm (violet) to 750 nm (red).The refractive index of proton is maximum for violet and minimum for red; so prism separates constituent colours of white light and causes maximum deviation for violet colour. That is why violet colour is seen at the bottom of spectrum when white light is dispersed through a prism. POORNIMA UNIVERSITY CBSE/12th Class/2010/PHYSICS Q.18 . Plot a graph showing the variation of stopping potential with the frequency of incident radiation for two different photosensitive materials having work functions w1 and w2 (w1 > w2). On what factors does the (i) slope and (ii) intercept of the lines depend? Ans.18 The variation of stopping potential with the frequency of incident radiation for two different photosensitive materials is shown below: (i) Slope of graph tan = h/e and depends on h and e, which are constants. (ii) Intercept of lines depend on the work function. Q.19 A parallel plate capacitor is charged by a battery. After sometime the battery is disconnected and a dielectric slabs its thickness equal to the plate separation is inserted between the plates. How will (i) the capacitance of the capacitor. (ii) Potential difference between the plates and (iii) the energy stored in the capacitor be affected? Justify your answer in each case. Ans.19 ∝ (i) The capacitance of capacitor increases to K times, since = (ii)The potential difference between the plates becomes 1/K times. (iii) As, E=V/d and V is decreased; therefore, electric field decreases to 1/K times. Q.20 Write the principle of working of a potentiometer. Describe briefly, with the help of a circuit diagram, how a potentiometer is used to determine the internal resistance of a given cell. Energy stored by the capacitor, U= . As Q = constant, C is increased, and so energy stored by capacitor decreases to 1/K times. Ans.20 Principle: If constant current is flowing through a wire of uniform area of cross-section at constant temperature, the potential drop across- any portion of wire is directly proportional to the length of that portion i.e., V µl Potentiometer can also be used to determine the internal resistance of a cell. For this a cell whose internal resistance is to be determined is connected to terminal A of the potentiometer across a resistance box through a key K2. First close the key K1 and obtain the null point. Let l1 be the length of this null point from terminal A then E=Kl1 When key K2 is closed, the cell sends current through resistance Box (R).If E2 is the terminal Potential difference and null point is obtained at length l2(AJ2) then V=Kl2 Thus E/V=l1/l2 But E=I(R+ r) and V=IR This gives E/V=(r+R)/R So (r+R)/R=l1/l2 giving r=R(l1/l2-1) Using above equation we can find internal resistance of any given cell POORNIMA UNIVERSITY CBSE/12th Class/2010/PHYSICS Q.21 Write the expression for the magnetic moment ⃗ due to a planer square loop of side ‘l’ carrying a steady current I in a vector form. In the given figure this loop is placed in a horizontal plane near a long straight conductor carrying a steady current I1 at a distance l as shown. Give reasons to explain that the loop will experience a net force but no torque. Write the expression for this force acting on the loop. Ans.21 Magnetic moment due to a planar square loop of side l carrying current I is ⃗ = ⃗ For square loop A l2 The net torque on the loop will be = ⃗ × ⃗, the angle between vector m and B = zero so, =0 Force experienced by the nearer parallel side of the loop Q.22 (a) Depict the equipotential surfaces for a system of two identical positive point charges placed a distance ’d’ apart. (b) Deduce the expression for the potential energy of a system of two point charges q1 and q2 brought from infinity to the points ⃗ and ⃗respectively in the presence of external electric field ⃗ . = Force experienced by the farther parallel side of the loop = . F1 is attractive and F2 is repulsive force. − . = . Net force on the loop towards the wire = Ans.23 (a) Equipotential surfaces due to two identical charges is shown below (b) Potential energy of a system of two charges in an external electric field. Suppose q1 and q2 are two charges brought from infinity at locations ⃗ and ⃗ respectively in an external electric field. Let be the potentials ( )⃗ and ( ⃗) at positions ⃗ and ⃗ due to external electric field ⃗ . In this case work is done in bringing charges q1 and q2 against their own electric fields and external electric fields. POORNIMA UNIVERSITY CBSE/12th Class/2010/PHYSICS Q.23 What is an unpolarized light? Explain with the help of suitable ray diagram how an unpolarized light can be polarized by reflection from a transparent medium. Write the expression for Brewster angle in terms of the refractive index of denser medium. Ans.23 Unpolarised light: The light having vibrations of electric field vector in all possible directions perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation is called the ordinary (or unpolarised) light. When unpolarised light is incident on the boundary between two transparent media, the reflected light is polarised with its electric vector perpendicular to the plane of incidence when the refracted and reflected rays make a right angle with each other. When Un-polarized light is incident at the angle called Brewster’s angle or angle of polarization (P), the light that is reflected from the surface is therefore perfectly polarized. From Snell’s law of refraction, we can say that Q.24 (i) Define 'activity' of a radioactive material and write its S.I. unit. (ii) Plot a graph showing variation of activity of a given radioactive This is Brewster’s law. Ans.24 (i) The activity of a radioactive substance is the rate of decay or the number of POORNIMA UNIVERSITY CBSE/12th Class/2010/PHYSICS sample with time. (iii) The sequence of stepwise decay of a radioactive nucleus is disintegrations per second of the substance. (ii) variation of activity of a given radioactive sample with time is shown below If the atomic number and mass number of D2 are 71 and 176 respectively, what are their corresponding values for D? (iii) Q.25 A long straight wire of a circular cross-section of radius 'a' carries a steady current 'I'. The current is uniformly distributed across the cross-section. Apply Ampere's circuital law to calculate the magnetic field at a point 'r' in the region for (i) r > a and (ii) r < a. OR State the underlying principle of working of a moving coil galvanometer. Write two reasons why a galvanometer cannot be used as such to measure current in a given circuit. Name any two factors on which the current sensitivity of a galvanometer depends. Ans.25 Let us consider an infinitely long cylinderical wire of radius a, carrying current I. Suppose that the current is uniformly distributed over whole cross-section of the wire. The cross-section of wire is circular. Current per unit cross-sectional area. = ……..(1) (i) r > a : We consider a circular path of radius r ( a) passing through external point P concentric with circular cross-section of wire. By symmetry the strength of magnetic field at every point of circular path is same and the direction of magnetic field is tangential to path at every point. So line integral of magnetic field ⃗ around the circular path Current enclosed by path = Total current on circular cross-section of cylinder = I By Ampere’s circuital law POORNIMA UNIVERSITY CBSE/12th Class/2010/PHYSICS This expression is same as the magnetic field due to a long current carrying straight wire. This shows that for external points the current flowing in wire may be supposed to be concerned at the axis of cylinder. (ii) r < a: Consider a circular path of radius r ( a), passing through internal point Q, concentric with circular cross-section of the wire. In this case the assumed circular path encloses only a path of current carrying circular cross section of the wire. Therefore current enclosed by path= current per unit cross-section cross section of assumed circular path By Ampere’s circuital law Clearly, magnetic field strength inside the current carrying wire is directly proportional to distance of the point from the axis of wire. OR Principle: When current (I ) is passed in the coil, torque acts on the coil, given by NIAB sin Where, is the angle between the normal to plane of coil and the magnetic field of strength B, N is the number of turns in a coil. When the magnetic field is radial, as in the case of cylindrical pole pieces and soft iron core, then in every position of coil the plane of the coil, is parallel to the magnetic field lines, so that 90and sin 901 Deflecting torque, NIAB A galvanometer cannot be used as such to measure current due to following two reasons: (i) A galvanometer has a finite large resistance and is connected in series in the circuit, so it will increase the resistance of circuit and hence change the value of current in the circuit. (ii) A galvanometer is a very sensitive device, it gives a full scale deflection for the POORNIMA UNIVERSITY CBSE/12th Class/2010/PHYSICS Q.26 What is space wave propagation? Give two examples of communication system which use space wave mode. A TV tower is 80 m tall. Calculate the maximum distance upto which the signal transmitted from the tower can be received. Q.27 In a meter bridge, the null point is found at a distance of 40 cm from A. If a resistance of 12 is connected in parallel with S, the null point occurs at 50.0 cm. from A. Determine the values of R and S. current of the order of microampere, hence if connected as such it will not measure current of the order of ampere. Current sensitivity of galvanometer depends on (i) Number of turns N: It increases with increase of number of turns. (ii) Area of coil A: It increases with increase of area of coil. Ans.26 Space wave propagation: Space wave propagation is a straight line propagation of electromagnetic wave from transmitting antenna to recieving antenna both installed in the ground. Space Waves, also known as direct waves, are radio waves that travel directly from the transmitting antenna to the receiving antenna. In order for this to occur, the two antennas must be able to “see” each other; that is there must be a line of sight path between them. Ans.27 In first case l1 40 cm POORNIMA UNIVERSITY CBSE/12th Class/2010/PHYSICS Q.28 Describe briefly, with the help of a labelled diagram, the basic elements of an A.C. generator. State its underlying principle. Show diagrammatically how an alternating emf is generated by a loop of wire rotating in a magnetic field. Write the expression for the instaneous value of the emf induced in the rotating loop. OR A series LCR circuit is connected to an source having voltage v = vm sint . Derive the expression for the instantaneous current I and its phase relationship to the applied voltage. Obtain the condition for resonance to occur. Define ‘power factor’. State the conditions under which it is (i) maximum and (ii) minimum. Ans.28 AC generator consists of the four main parts: (i) Field Magnet: It produces the magnetic field. In the case of a low power dynamo, the magnetic field is generated by a permanent magnet, while in the case of large power dynamo, the magnetic field is produced by an electromagnet. (ii) Armature: It consists of a large number of turns of insulated wire in the soft iron drum or ring. It can revolve round an axle between the two poles of the field magnet. The drum or ring serves the two purposes: (i) It serves as a support to coils and (ii) It increases the magnetic field due to air core being replaced by an iron core. (iii) Slip Rings: The slip rings R1 and R2 are the two metal rings to which the ends of armature coil are connected. These rings are fixed to the shaft which rotates the armature coil so that the rings also rotate along with the armature. (iv) Brushes: These are two flexible metal plates or carbon rods (B1 and B2) which are fixed and constantly touch the revolving rings. The output current in external load RL is taken through these brushes. Principle: When the armature coil is rotated in the strong magnetic field, the magnetic flux linked with the coil changes and the current is induced in the coil, its direction being given by Fleming’s right hand rule. The direction of current remains unchanged during the first half turn of armature. During the second half revolution, the direction of current is reversed. Thus, the direction of induced emf and current changes in the external circuit after each half rotation. If N is the number of turns in coil, f the frequency of rotation, A area of coil and B the magnetic induction, then induced emf POORNIMA UNIVERSITY CBSE/12th Class/2010/PHYSICS OR Suppose resistance R, inductance L and capacitance C are connected in series and an alternating source of voltage V V0 sin t is applied across it. On account of being in series, the current (i ) flowing through all of them is the same. Suppose the voltage across resistance R is VR , voltage across inductance L is VL and voltage across capacitance C is VC . The voltage VR and current i are in the same phase, the voltage VL will lead the current by angle 90° while the voltage VC will lag behind the current by angle 90°. Clearly VC and VL are in opposite directions, Therefore their resultant potential difference VC VL (if VC VC ). Thus VR and (VC VL ) are mutually perpendicular and the phase difference between them is 90°. As applied voltage across the circuit is V, the resultant of VR and (VC VL ) will also be V. From POORNIMA UNIVERSITY CBSE/12th Class/2010/PHYSICS Condition for resonance to occur in series LCR ac circuit: For resonance the current produced in the circuit and emf applied must always be in the same phase. Phase difference ( ) in series LCR circuit is given by Q.29 State Huygen’s principle. Show, with the help of a suitable diagram, how this principle is used to obtain the diffraction pattern by a single slit. Draw a plot of intensity distribution and explain clearly why the secondary maxima become weaker with increasing order (n) of the secondary maxima. OR Draw a ray diagram to show the working of a compound microscope. Deduce an expression for the total magnification when the final image is formed at the near point. Ans.29 Huygen’s principle states that each point on a wave front behaves as a source of secondary wavelets. The secondary wavelets travel with the speed of light in that medium. The surface of tangency to the secondary wavelets in forward direction at any instant gives the new position of the wavefront at that time. Propagation of wavefront from a point source: When monochromatic light is made incident on a single slit, we get diffraction pattern on a screen placed behind the slit. POORNIMA UNIVERSITY CBSE/12th Class/2010/PHYSICS In a compound microscope, an object is placed at a distance of 1.5 cm from the objective of focal length 1.25 cm. If the eye piece has a focal length of 5 cm and the final image is formed at the near point, estimate the magnifying power of the microscope. The diffraction pattern contains bright and dark bands, the intensity of central band is maximum and goes on decreasing on both sides. Let AB be a slit of width ‘a’ and a parallel beam of monochromatic light is incident on it. According to Fresnel the diffraction pattern is the result of superposition of a large number of waves, starting from different points of illuminated slit. Let be the angle of diffraction for waves reaching at point P of screen and AN the perpendicular dropped from A on wave diffracted from B. The path difference between rays diffracted at points A and B, To find the effect of all coherent waves at P, we have to sum up their contribution, each with a different phase. At the central point C of the screen, the angle is zero. Hence the waves starting from all points of slit arrive in the same phase. This gives maximum intensity at the central point C. If point P on screen is such that the path difference between rays starting from edges A and B is, then path difference If angle is small, The intensity of secondary maxima decreases with increase of order n because with increasing n, the contribution of slit decreases. For n = 2, it is one-fifth, for n = 3, it is one-seventh and so on. OR POORNIMA UNIVERSITY CBSE/12th Class/2010/PHYSICS POORNIMA UNIVERSITY CBSE/12th Class/2010/PHYSICS Q.30 (a) Explain the formation of depletion layer and potential barrier in a p-n junction. (b) In the figure given below, the input waveform is converted into the output waveform by a device ‘X’. Name the device and draw its circuit diagram. Ans.30 (a) When a p-n junction is formed, there are more electrons on the n-side and more holes on the p-side. Because of this, electrons from n-side will diffuse towards the p-side and holes from the p-side will diffuse to the n-side. On crossing the p-n boundary, these electrons and holes may collide with each other and recombine. Hence, the donor or acceptor atoms get depleted of their associated electrons or holes and will be left with a charged ion core in the layer near the junction boundary. Hence, a layer called the depletion layer is formed at the junction. (c) Identify the logic gate represented by the circuit as shown and write its truth table. OR (a) With the help of the circuit diagram explain the working principle of a transistor amplifier as an oscillator. (b) Distinguish between a conductor, a semiconductor and an insulator on the basis of energy band diagrams An important consequence of formation of this depletion layer is the appearance of a junction potential. This is in a direction opposing any further diffusion of majority carriers from either side. This potential acts as a barrier and is hence, known as a ‘barrier potential’, VB. The potential barrier and the depletion layer width is directly proportional to the doping concentration on both sides. (b) The device X depicted in the figure represents a Full wave rectifier. (c) The given logic gate depicted in figure is an AND gate. The truth table for the Gate is OR Principle: (a) Principle: An oscillator converts dc into ac. A fraction of output voltage POORNIMA UNIVERSITY CBSE/12th Class/2010/PHYSICS or current is fed back to the input circuit in the same phase as the input signal and the oscillations produced in LC circuit are amplified. (b) If the valence and conduction bands overlap, the substance is referred as a conductor. If the valence and conduction bands have a forbidden gap more than 3 eV, the substance is an insulator. If the valence and condition bands have a small forbidden gap ( 1 eV), the substance is a semiconductor. POORNIMA UNIVERSITY