* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Syllabus for Algebra IB File
Perturbation theory wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Computational fluid dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Routhian mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Computational electromagnetics wikipedia , lookup
Least squares wikipedia , lookup
Inverse problem wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Flux balance analysis wikipedia , lookup
Multi-objective optimization wikipedia , lookup
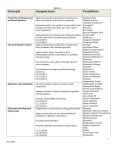
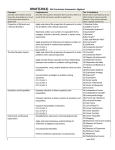
Algebra I B Syllabus 2012-2013 Unit 1 – Function and Relations Objective 1– Define relation, function, domain, and range Objective 2– Be able to determine if a relation is a function given ordered pairs, a graph, or a table Objective 3– Be able to identify the domain and range of a relation given ordered pairs, a graph, or a table Objective 4– Analyze a set of data for the existence of a pattern by completing a table or a sequence Objective 5– Be able to express a pattern as an equation given a sequence or table Unit 2 – Graphing Linear Functions Objective 1 – Define linear equation, slope, x-intercept, y-intercept, slopeintercept form, and standard form Objective 2 – Identify the x-intercept and y-intercept Objective 3 – Determine the slope of a line given a graph, given two points, and given an equation Objective 4 – Identify, describe, and/or use constant rates of change Objective 5 – Graph an equation in slope-intercept form Objective 6 – Graph an equation in standard form Unit 3 – Writing an Equation of a Line Objective 1 – Define parallel, perpendicular, reciprocal, and opposite number Objective 2 – Convert between slope-intercept form, standard form, and other forms of a linear equation Objective 3 – Write or identify a linear equation given a graph Objective 4 – Write or identify a linear equation given the slope and point on the line (using point slope, then converting) Objective 5 – Write or identify a linear equation given two points on the line Objective 6 – Write the equations of parallel and perpendicular lines Objective 7 – Given a scatter plot, write the equation of a line of best fit Objective 8 – Model a situation with a linear equation Unit 4 – Inequalities Objective 1 – Identify inequality symbols Objective 2 – Graph an inequality on a number line Objective 3 – Solve linear inequalities and graph their solution Objective 4 – Solve compound linear inequalities and graph their solution Objective 5 – Model situations using linear inequalities Unit 5 – Absolute Value Objective 1 – Define and interpret absolute value Objective 2 – Evaluate absolute value expressions Objective 3 – Solve absolute value equations Objective 4 – Solve absolute value inequalities and graph their solution Unit 6 – Systems of Equations Objective 1 – Determine whether a point is a solution to a system of equations Objective 2 – Solve a system of equations by graphing (including infinite solutions, no solutions, and one solution) Objective 3 – Solve a system of equations using the substitution method Objective 4 – Solve a system of equations using the elimination method Objective 5 – Write, solve, and interpret systems of equations in the context of problem situations Unit 7 – Systems of Inequalities Objective 1 – Graph the solution to a linear inequality Objective 2 – Solve a system of inequalities by graphing Objective 3 – Determine whether a point is a solution to a system of inequalities Objective 4 – Write, solve, and interpret systems of inequalities in the context of problem situations Unit 8 – Exponents Objective 1 – Simplify exponents using the Product-of-Powers Property Objective 2 – Simplify exponents using the Power-of-a-Power Property Objective 3 – Simplify exponents using the Power-of-a-Product Property Objective 4 - Simplify exponents using the Quotient-of-Powers Property Objective 5 - Simplify exponents using the Power-of-a-Quotient Property Objective 6 – Simplify exponents using the Zero Exponent Property Objective 7 – Simplify exponents using the Negative Exponent Property Objective 8 – Simplify exponents using multiple properties Unit 9 – Radical Expressions Objective 1 – Estimate a radical without using a calculator Objective 2 – Simplify a radical expression (without variables) Objective 3 – Add and/or Subtract radicals (without having to simplify first) Objective 4 – Multiply radicals (without variables) Objective 5 – Simplify radical expression by rationalizing the denominator Unit 10 – Adding/Subtracting/Multiplying Polynomials Objective 1 – Classify a polynomial by degree and/or number of terms Objective 2 – Add polynomial expressions and express answer in simplest form Objective 3 – Subtract polynomial expressions and express answer in simplest form Objective 4 – Multiply polynomial expression by a monomial and express answer in simplest form Objective 5 – Multiply two binomials and express answer in simplest form Objective 6 – Multiply binomial by a trinomial and express answer in simplest form Unit 11 – Factoring Polynomials Objective 1 – Find the GCF of two monomials Objective 2 – Factor a polynomial using the GCF Objective 3 – Factor a difference of squares Objective 4 – Factor a polynomial in the form x2 + bx + c Objective 5 – Factor a polynomial in the form ax2 + bx + c, where a > 1 and a is prime Unit 12 – Factoring Polynomials Objective 1 – Factor a polynomial completely using multiple methods Objective 2 – Solve an equation by factoring Objective 3 – Solve word problems using factoring Unit 13 – Rational Expressions Objective 1 – Simplify a rational algebraic expression Objective 2 – Find the LCM of a set of monomials Objective 3 – Add/Subtract Rational expressions with monomial denominators Objective 4 – Multiply/Divide rational expressions Objective 5 – Solving equations with rational expressions