* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 1 - Asbury Park School District
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
Rotation matrix wikipedia , lookup
Plane of rotation wikipedia , lookup
Rotation formalisms in three dimensions wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Compass-and-straightedge construction wikipedia , lookup
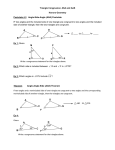
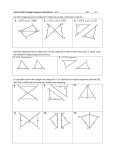
Asbury Park Name of Unit: Congruence, Proof & Constructions Content Area: HS Math - Geometry Big Idea: ● ● ● ● ● Unit #/Duration: Unit 1 / 45 days Grade Level: 10th Triangles are congruent if and only if pairs of corresponding sides and all corresponding angles are congruent Congruence can be defined in terms of rigid motions [ translations, rotations, reflections ]; Dilations do not maintain congruence Formal geometric constructions can be made with a variety of tools and methods (compass and straightedge, string, reflective devices, paper folding, dynamic geometric software) Geometric Proofs are comprised of theorems, postulates properties , definitions and demonstrate understanding of geometric concepts Essential Questions: ● How can you prove 2 triangles congruent? ● What are undefined notions in Geometry? Why do we refer to them as undefined? ● How are transformations and functions related? ● What is “Identity Symmetry”? ● What is the relationship between a rotation and a ● School District reflection? Can you explain why any point on the perpendicular bisector is equidistant from any pair of pre-image and image point? What is a correspondence Why does a congruence naturally yield a correspondence? What is a centroid, and how does it divide a median? What is the “protractor postulate? And why must it be used to prove vertical angles are congruent? I Can Statements: ● construct an equilateral triangle ● communicate mathematical concepts clearly and ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● concisely bisect an angle copy an angle construct a perpendicular bisector Define and identify two points of concurrencies Apply the definition of supplementary and complementary angles to determine unknown angles Identify congruent “special angles” formed when a transversal cuts parallel lines review formerly learned geometry facts ex: interior and exterior angles of a triangle, isosceles triangle, etc. Apply SMAT 180 ( sum of measures of angles inside a triangle =180 degrees)to find a missing interior angle write unknown angle proofs draw valid conclusions based upon observations and proven fact write unknown angle proofs involving auxiliary lines Describe parallel line theorems and their converses articulate what differentiates rigid motions from non-rigid motions identify the parameters needed to complete any rigid motion Manipulate rotations by each parameter: center of rotation, angle of rotation, and a point under the rotation construct the line of reflection of a figure and its reflected image construct the image of a figure when provided the line of reflection identify rotational symmetry within an individual ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● figure define translation and perform a translation by construction understand that any point on a line of reflection is equidistant from any pair of pre-image and image points in a reflection construct a line parallel to a given line through a point not on that line using a rotation by 180° prove the alternate interior angles theorem using the parallel postulate and a construction define congruence in terms of rigid motions state the correspondence that arises from a given congruence apply a sequence of rigid motions from one figure onto another figure in order to demonstrate that the figures are congruent prove SAS congruence using rigid motion transformations complete proofs involving properties of an isosceles triangle prove ASA or SSS congruence using transformations complete triangle congruency proofs requiring a synthesis of the skills prove properties of parallelograms Use the properties of midsegments to solve for the unknown value Construct a Square and a Nine-Point Circle ● Common Core State Standards: ● G.CO.1 ; G.CO.2 ; G.CO.3 ; G.CO.4 ; G.CO.5 ; G.CO.6 ; G.CO.7 ; G.CO.8 ; G.CO.9 ; G.CO.10 ; G.CO.11 ; G.CO.12 ; G.CO.13 Pre-requisite Standards: 8.G.1 ; 8.G.2 ; 8.G.3 ; 8.G.5 Mathematical Practices Highlighted: ● MP 3 ; MP 4 ; MP 5 ; MP 6 Interdisciplinary Connections: History : proofs without technology Symbol: **IC Technology Integration: (Standards included only if students will be demonstrating knowledge/understanding/skill.) 8.1 educational Technology: all students will use digital tools to access, manage, evaluate and synthesize information in order to solve problems individually and collaboratively and to communicate knowledge Symbol: ***TI [ Use of TI-84’s and an Epson Brite Board are used daily in the math classroom, with the use of internet websites to enrich the learning experience when appropriate ] NOTE: Use of Geometer’s Sketch pad can be used for constructions & Geometric Shape features on Epson Briteboard should be used along with use of interactive pens for kinesthetic learners Texts ● Primary Text: Eureka math 10 [ Engage NY Geometry] ● ● Secondary/Supplemental Texts: Pearson Geometry HMH Geometry Suggested Instructional Activities/Strategies Topic A – Basic constructions: Lesson 1: Construct an Equilateral Triangle * **TI Lesson 2: Construct an Equilateral Triangle II ***TI Lesson 3: Copy and Bisect an Angle **TI Lesson 4: Construct a Perpendicular Bisector ***TI Lesson 5: Points of Concurrencies Topic B - Unknown angles: Lesson 6: Solve for Unknown Angles—Angles and Lines at a Point Lesson 7: Solve for Unknown Angles—Transversals ***TI Lesson 8: Solve for Unknown Angles—Angles in a Triangle Lesson 9: Unknown Angle Proofs—Writing Proofs Lesson 10: Unknown Angle Proofs—Proofs with Constructions Lesson 11: Unknown Angle Proofs—Proofs of Known Facts **IC Topic C – Transformations / Rigid motions : Lesson 12: Transformations—The Next Level **TI Lesson 13: Rotations ***TI Lesson 14: Reflections ***TI Lesson 15: Rotations, Reflections, and Symmetry ***TI Lesson 16: Translations Lesson 17: Characterize Points on a Perpendicular Bisector Lesson 18: Looking More Carefully at Parallel Lines Lesson 19: Construct and Apply a Sequence of Rigid Motions ***TI Lesson 20: Applications of Congruence in Terms of Rigid Motions Lesson 21: Correspondence and Transformations ***TI Mid-module assessment Topic D - Congruence : Lesson 22: Congruence Criteria for Triangles—SAS Lesson 23: Base Angles of Isosceles Triangles Lesson 24: Congruence Criteria for Triangles—ASA and SSS Lesson 25: Lesson 25: Congruence Criteria for Triangles—SAA and HL Lesson 26: Triangle Congruency Proofs—Part I Lesson 27: Triangle Congruency Proofs—Part II Topic E – Proving properties of geometric figures: Lesson 28: Properties of Parallelograms Lesson 29: Special Lines in Triangles Lesson 30: Special Lines in Triangles Topic F - Advanced constructions: Lesson 31: Construct a Square and a Nine-Point Circle ***TI Lesson 32: Construct a Nine-Point Circle ***TI Topic G – Axiomatic Systems: Lesson 33: Review of the Assumptions Lesson 34: Review of the Assumptions End-of-module assessment Teacher Resources ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Compass Protractors Straight edge Patty paper or tracing paper Geometer’s Sketchpad or Geoebra Document camera Epson Brite-board ( interactive) Communicators Vocabulary ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Domain Specific Academic Vocabulary (Tier 3) Isometry Transformations Translation Rotation Reflection Congruence Image Pre-image Chord Midsegment Median Centroid Inscribed Formative Assessments: ● Do Now’s ( class openers) ● Class work ● Homework ● Exit Tickets ● Reflections Type ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● General Academic Vocabulary (Tier 2) Rectangle Circle Triangle Bisect Construct Prove Rigid Motion Viable argument Assessments Summative Assessment: ● Mid-module assessment ● End-of-module assessment ● Teacher-prepared quizzes Differentiation/Scaffolding (for example ELL, students who are classified, struggling learners, etc.) Visual ● Auditory Kinesthetic Language Development ● ● ● Khan Academy and other math websites used presenting images of topics discussed ; use of communicators and templates to assist with marking up triangles to determine congruence; Geogebra ; Geometer’s Sketch pad ; Visual presentation of completed student constructions for comparison ; Use different colored markers/ pencils to mark congruent angles and sides Reading directions aloud and close-reading activities; khan Academy lessons Constructions ; patty paper folding , tracing to perform physical rotations of shapes Vocabulary rich integration in the classroom through use of diagrams and other graphic organizers to help process concepts and increase recall ; Historical reference to math conjecture and proof Appendix 1 (graphic organizers, rubrics, websites, activities, manipulatives, sample assessments, etc.) ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Kutasoftware.com Mathisfun.com Coolmath.com KhanAcademy.com video, Angles and Trim http://youtu.be/EBP3I8O9gIM video clip (Sherlock Holmes, Master of Deduction Does it Again, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o30UY_flFgM discuss the connection between Holmes’s process of identifying the attacker and the deduction used in geometry. Historical connection Eratosthenes: https://youtu.be/wnElDaV4esg Geogebra Geometer’s Sketch pad Mid-module assessment & rubric p. 175-188 Eureka Math ● ● ● ● ● End-of-module Assessment p. 280 – 297 Eureka Math Graphic organizer of geometric facts & properties p. 268-270 Eureka Math Copied angle and bisector rubric p. 35 Prior geometry key facts chart p. 58, 59, 60 Reference chart ( properties of real numbers & properties of equality ) Appendix 2 (Quad D Exemplar Lesson Plan) http://map.mathshell.org/lessons.php?unit=9315&collection=8 [ Evaluating conditions for congruency]