* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Coverage by year
Human ecology wikipedia , lookup
History of cartography wikipedia , lookup
Royal Geographical Society wikipedia , lookup
Cartography wikipedia , lookup
Military geography wikipedia , lookup
Cartographic propaganda wikipedia , lookup
Counter-mapping wikipedia , lookup
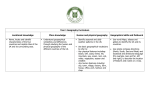
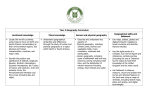
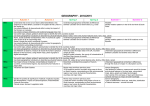
New National Curriculum Geography subject knowledge broken down into year groups. Key Stage 1. Pupils should develop knowledge about the world, the United Kingdom and their locality. They should understand basic subject-specific vocabulary relating to human and physical geography and begin to use geographical skills, including first-hand observation, to enhance their locational awareness. Subject Content. Pupils should be taught to: Year 1 Locational knowledge name and locate the world’s seven continents and five oceans Year 2 N. America, S. America, Africa, Europe, Asia, Oceania & Antarctica Pacific, Atlantic (North and South) India , Arctic, Southern Ocean Locational knowledge name, locate and identify characteristics of the four countries and capital cities of the United Kingdom and its surrounding seas Place knowledge England (London) Scotland (Edinburgh) Wales (Cardiff) N. Ireland (Belfast) Surrounding seas (North Sea, English Channel, Irish Sea) Local study of the school area extending to learn about Hucknall. understand geographical similarities and differences through studying the human and physical geography of a small area of Physical features include rivers, the United Kingdom, and of a small area in forests, hills and mountains. a contrasting non-European country Human features include towns, cities, train and tram tracks and roads. Vocabulary to include village, town and city. Recapping local area of Hucknall and extend to learn about Nottingham and Nottinghamshire, eg Sherwood Forest. Physical features include rivers, forests, hills and mountains. Human features include towns, cities, train and tram tracks and roads. Plus a small area of a Non-European country, eg Australia. Pupils should be taught to: Year 1 Human and physical geography Hucknall weather diary over 2 weeks Learn about seasons, days of week and months of the year. identify seasonal and daily weather patterns in the United Kingdom and the location of hot and cold areas of the world in relation to the Equator and the North and South Poles Human and physical geography use basic geographical vocabulary to refer to: key physical features, including: beach, cliff, coast, forest, hill, mountain, sea, ocean, river, soil, valley, vegetation, season and weather Beach, cliff, coast, forest, hill, mountain, sea, ocean, river, valley, seasons, weather City, town, village, farm, house, office, shop key human features, including: city, town, village, factory, farm, house, office, port, harbour and shop Use in context as part of a unit of work. Geographical skills and fieldwork Use globes, UK maps to identify UK and its countries. use world maps, atlases and globes to identify the United Kingdom and its countries, as well as the countries, continents and oceans studied at this key stage Year 2 Identify the Equator, North Pole(Arctic), South Pole (Antarctic) as cold areas and Africa and Australia as hot areas. Keep a comparative weather diary of Hucknall and the non-European country they study. Use a globe and world map As for Y1 and extend to include: Ocean, vegetation, soil, factory, port and harbour Use in context as part of a unit of work. Use globes and atlases to identify Non-European Country, oceans, continents and other specific areas studied in this key stage. Pupils should be taught to: Year 1 Year 2 Geographical skills and fieldwork Vocabulary to include left, right, near and far. Vocabulary north, south, east and west when reading a compass. use simple compass directions (North, South, East and West) and locational and directional language [for example, near and far; left and right], to describe the location of features and routes on a map Geographical skills and fieldwork use aerial photographs and plan perspectives to recognise landmarks and basic human and physical features; devise a simple map; and use and construct basic symbols in a key Geographical skills and fieldwork use simple fieldwork and observational skills to study the geography of their school and its grounds and the key human and physical features of its surrounding environment. Describe simple routes on a map such as how to travel from Hucknall to Nottingham. Devise a simple birds eye view of the school and its grounds that includes a simple key. Use an aerial photo of Hucknall to recognise the human and physical features. Create their own map of Hucknall or add the physical and human features to a blank map. This should include a key that clearly identifies these features. Fieldwork to observe the school grounds including playground, buildings, paths, wildlife areas and other key features. Fieldwork to observe features of the area around school including shops, houses, roads, use of land and other human and physical features. Link this to creating a birds eye view as outlined above. Link this to creating a map of the surrounding area as outlined above. Other activities could include carrying out a traffic survey, travelling to Nottingham on a tram and recording the route taken pictorially. New National Curriculum Geography subject knowledge broken down into year groups. Key stage 2 Pupils should extend their knowledge and understanding beyond the local area to include the United Kingdom and Europe, North and South America. This will include the location and characteristics of a range of the world’s most significant human and physical features. They should develop their use of geographical knowledge, understanding and skills to enhance their locational and place knowledge. Pupils should be taught to: Locational knowledge locate the world’s countries, using maps to focus on Europe (including the location of Russia) and North and South America, concentrating on their environmental regions, key physical and human characteristics, countries, and major cities Year 3 / 4 Use maps to identify Europe (including Russia). Study physical geography including rivers, mountains, Study human geography including settlements, land use, water supply. Vocabulary Continent Border States/Countries EU Country Nationality & Ethnicity Year 5 / 6 Use maps to identify North and South America concentrating on their environmental regions Study physical geography including climate zones, biomes, vegetation belts, earthquakes and water cycle. Study human geography including economic activity, trade links and distribution of natural resources such as energy, food, minerals and water supply. Vocabulary Mountains Population Region Rivers Lakes Locational knowledge name and locate counties and cities of the United Kingdom, geographical regions and their identifying human and physical characteristics, key topographical features (including hills, mountains, coasts and rivers), and landuse patterns; and understand how some of these aspects have changed over time Pupils should be taught to: This could be a unit of work taught in Year 3/4 during the autumn term. Geographical regions could include distinct areas such as The Lakes, The Peak District, The Fens. The Yorkshire Dales etc…. This will give an opportunity to focus on topographical features. Year 3 / 4 Locational knowledge identify the position and significance of latitude, longitude, Equator, Northern Hemisphere, Southern Hemisphere, the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, Arctic and Antarctic Circle, the Prime/Greenwich Meridian and time zones (including day and night) This unit of work could compare a understand geographical similarities and region of the United Kingdom (not the local area) and a region in Europe differences through the study of (probably a country or a region within a human and physical geography of a country). region of the United Kingdom, a region Or it could be 2 separate units of work, in a European country, and a region one studying an area of the UK and the within North or South America other an area of Europe. Place knowledge Year 5 / 6 This could be a unit of work taught in Year 5/6 during the autumn term. Understand latitude, longitude, Equator, hemispheres, tropic, polar circles and time zones. This unit of work could compare a region of the United Kingdom (not the local area) and a region in North or South America (probably a country or a region within a country). Or it could be 2 separate units of work, one studying an area of the UK or Europe and the other an area of North or South America. Pupils should be taught to: Year 3 / 4 Year 5 / 6 Human and physical geography Study physical geography including rivers, mountains, Study physical geography including climate zones, biomes, vegetation belts, earthquakes and water cycle. describe and understand key aspects of: physical geography, including: climate zones, biomes and vegetation belts, rivers, mountains, volcanoes and earthquakes, and the water cycle human geography, including: types of settlement and land use, economic activity including trade links, and the distribution of natural resources including energy, food, minerals and water Pupils should be taught to: Geographical skills and fieldwork use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied Study human geography including settlements, land use, water supply. Vocabulary Village Town City Farm Factory Office Shop House Hospitals Year 3 / 4 These resources should be used across the key stage. Study human geography including economic activity, trade links and distribution of natural resources such as energy, food, minerals and water supply. Year 5 / 6 These resources should be used across the key stage. Geographical skills and fieldwork use the eight points of a compass, four and six-figure grid references, symbols and key (including the use of Ordnance Survey maps) to build their knowledge of the United Kingdom and the wider world Geographical skills and fieldwork use fieldwork to observe, measure, record and present the human and physical features in the local area using a range of methods, including sketch maps, plans and graphs, and digital technologies. North, East, South and West on a compass. 4 figure grid references map to identify position of landmarks in Nottinghamshire or as a link to PE for orienteering around the school grounds. All 8 points of the compass. 4/6 figure grid references on a map. Use Ordnance Survey maps of United Kingdom to identify position of famous landmarks or as a link to PE to orienteering on an Educational Visit to Derbyshire and the Peak District. These skills should be taught across the key stage. The fieldwork should be undertaken in the local area to observe, measure and record the human and physical features. These skills should be taught across the key stage. The fieldwork could be undertaken in the Derbyshire and the Peak District to record and explain the human and physical features. This could be linked to using compass and grid references on maps. Key Skills at each Key Stage. Key Stage 1. Map skills, continents, hot and cold areas, equator Devise a simple map with a key, use aerial photographs to recognise landmarks Knowledge of countries of UK Comparing local area with non-European place Daily weather patterns Key physical features and human features of places studied Knowledge of compass directions (4 points) Carry out field work in the school and its grounds noting key physical and human features Key Stage 2. Locate world countries using maps. Focus on continents of Europe, North America, South America Key physical features and human features of places studied (see new NC objectives) Name and locate counties and cities of UK, geographical regions, topographical features including hills, mountains, coasts, rivers Identify how land is used and how this has changed over time Map skills including latitude, longitude, Equator, Northern hemisphere, Southern hemisphere, Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, Arctic and Antarctic circle, GMT and time zones including day and night Study key human and physical features of a region of UK, region of Europe and region of North or South America Areas to be covered: Map skills UK knowledge World knowledge Local study European study (KS2) North or South America study (KS2) International study (KS1) Identifying key human and physical features of places Comparing human and physical features of places studied with local area Presenting findings in project form (KS2) Use maps, globes, atlases and computer mapping to locate countries and describe their features Knowledge of compass skills (8 points). 4 and 6 figure grid references, symbols and key including OS maps to build knowledge of UK and wider world Carry out fieldwork to observe, record, measure and present key human and physical features of the local area Key Stage 1. Key Stage 1. Key Stage 1. Name the four countries of the UK, their capitals and the surrounding seas. Use world maps, atlases and globes to identify these. Name and locate the 7 continents and the 5 oceans of the world. Use world maps, atlases and globes to identify these. Study the local area (Hucknall and Nottinghamshire). Physical and human features. See NC for list of features and vocabulary to be taught. Key Stage 1. Key Stage 1. Key Stage 1. Study a non-European contrasting country. Physical and human features. See NC for list of features and vocabulary to be taught. Identify seasonal and daily Fieldwork unit studying the weather patterns of the UK and human and physical features of location of Hot and Cold areas the school and its local area. of the world in relation to the Use aerial maps and photographs equator and the North and to recognise landmarks, devise a South Poles. simple map with a key that uses symbols. Use simple compass directions (NSEW) and associated vocabulary found in NC. Key Stage 2. Key Stage 2. Key Stage 2. Key Stage 2. Locate world countries using maps, focus on Europe (including Russia), North and South America. Concentrate of their environmental regions, key human and physical features, countries and major cities. Use 8 points of compass, 4 and 6 figure grid references, symbols and keys (including OS maps) to build their knowledge of the UK and the wider world. Name and locate counties and cities of the UK, identifying key human and physical features (including hills, mountains, coasts and rivers), geographical regions, land-use patterns including how these have changed over time. Use 8 points of compass, 4 and 6 figure grid references, symbols and keys (including OS maps) to build their knowledge of the UK and the wider world. Key Stage 2. Locational knowledge. Focus on latitude, longitude, Equator, Northern and Southern hemisphere, Tropics or Cancer and Capricorn, Arctic and Antarctic Circle, the Prime and Greenwich Meridian and time zones (including day and night). Use 8 points of compass, 4 and 6 figure grid references, symbols and keys (including OS maps) to build their knowledge of the UK and the wider world. Key Stage 2. Understand similarities and differences through the study of human and physical geographical features of a region of the UK (See NC for list of aspects to be studied). Use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied. Understand similarities and differences through the study of human and physical geographical features of a region within North or South America (See NC for list of aspects to be studied). Use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied. Use fieldwork to observe, measure, record and present the human and physical features in the local area using a range of methods, including sketch maps, plans and graphs, and digital technologies. Map skills. Use 8 points of compass, 4 and 6 figure grid references, symbols and keys (including OS maps) to build their knowledge of the UK and the wider world. Key Stage 2. Understand similarities and differences through the study of human and physical geographical features of a European country (See NC for list of aspects to be studied). Use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied. Key Stage 2.