* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Supply notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
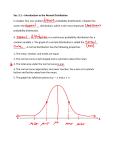
SUPPLY Take some time and read pages 148-151 in the textbook Identify all vocabulary terms Draw figure 13.1 on page 149 in your notes SUPPLY REVIEW QUESTIONS What is the law of supply? Price goes up, supply goes up What is the law of demand? Price goes up, demand goes down What are the determinants of demand? Buyers (#), income, tastes, expectations, related goods SUPPLY Consider this: you produce eggs and milk at your farm. Would you produce more eggs or milk if: You could get higher prices for eggs (market surged)? Easter is next week? Eggs are found to reduce heart disease? The government offered subsidies (cash back) to increase milk production? You buy a new machine that cleans eggs twice as fast? NY places a large tax on milk production The cost of chickens doubles SUPPLY Supply: various quantities of a good or service that producers are willing to sell at all market prices Law of Supply: Producers will produce more goods and services when prices are high, less when low Direct relationship INTRODUCTION TO SUPPLY A supply schedule is a table that shows the quantities producers are willing to supply at various prices Price per Widget ($) Quantity Supplied of Widget per day $5 10 $4 8 $3 6 $2 4 $1 2 GRAPHING SUPPLY Just like demand, Price is always on the vertical axis, Quantity is always on the horizontal The line that connects the points from a supply schedule are called a supply curve Supply Curve for Widgets $6 $5 Price per Widget $4 $3 Supply Curve $2 $1 $0 0 2 4 6 Quantity Supplied of Widgets 8 10 What do you notice about the supply curve? How would you describe the slope of the supply curve? Do you think that price and quantity supplied tend to have this relationship? 12 CHANGES IN SUPPLY •Change in the quantity supplied due to a price change occurs ALONG the supply curve •At $3 per Widget, the Quantity •If the price of Widgets fell of widgets is 6. supplied to $2, then the Quantity Supplied would fall to 4 Widgets. Supply Curve for Widgets $6 $5 Price per Widget $4 $3 Supply Curve $2 $1 $0 0 2 4 6 Quantity Supplied of Widgets 8 10 12 DETERMINANTS The following factors make supply shift in an economy: Resource Costs/Cost of inputs Expectations about future prices Number of firms (includes weather and natural disasters) Technology Subsidies, taxes, and regulations (government) FINAL V. INTERMEDIATE Final goods: The goods that consumers actually purchase, finished products (ie: cupcakes) Intermediate goods: goods that are needed to make the finished product (ie: Flour for cupcakes) RESOURCE COSTS If the costs of your intermediate goods increase so does the cost of final product Example: cost of cheese went up, so did the price of a double cheeseburger at McDonalds EXPECTATIONS Just like consumers have expectations (Ie; black Friday), so do producers If prices are expected to increase, producers produce more. If they are expected to decrease, producers may store their inventory for later release Does not necessarily apply to firms that produce perishable products (ie: bananas) NUMBER OF FIRMS When another Taco Bell opens in Binghamton, our supply of Tacos just increased overall If Sweet Frog went out of business, there would be a decrease in supply of frozen yogurt overall This determinant applies to the market as a whole, rather than individual production choices (weather and natural disasters) TECHNOLOGY Technology that allows you to increase your product faster and cheaper will result in an increase in supply. The opposite is also true. If your technology fails, you aren’t producing anything SUBSIDIES, TAXES, REGULATIONS Subsidy: The government gives you money to produce something (always leads to increase in supply) Taxes: Government takes your money when you produce something (leads to decrease in supply) Regulations: Varies. If there are lots of regulations there will be decrease in supply. Less regulation, more output. GRAPHING AN INCREASE SHIFT IN SUPPLY •Several factors will change the demand for the good (shift the entire demand curve) Supply Increase Curveinfor Supply Widgets $6 $5 $5 $4 $4 Price per Widget Price per Widget $6 $3 $3 Original Supply Curve Supply Curve $2 $2 $1 $1 $0 •As an example, suppose that there is an improvement in the technology used to produce widgets. New Supply Curve $0 0 2 0 42 4 6 6 8 Quantities Quantity Supplied Supplied of of Widgets Widgets 8 10 10 1212 14 GRAPHING A DECREASE IN SUPPLY •Supply can also decrease due to factors other than a change in price. $6 $6 $5 $5 $4 $4 Price per Widget Price per Widget Decrease in Supply Supply Curve for Widgets $3 •As an example, suppose that a large number of Widget producers go out of business, decreasing the number of suppliers. $3 Supply Curve $2 $2 $1 $1 $0 $0 0 2 0 2 4 4 6 6 Quantity Supplied of Widgets Quantity Supplied of Widgets 8 8 10 10 12 12 Original Supply Curve New Supply Curve Price THE GOVERNMENT OF PAGO-PAGA ADDS A SUBSIDY TO BOOMERANG PRODUCTION. S S1 Quantity Price THE GOVERNMENT OF PAGO-PAGA ADDS A NEW TAX TO BOOMERANG PRODUCTION. S1 S Quantity Price BOOMERANG PRODUCERS EXPECT AN INCREASE IN THE POPULARITY OF BOOMERANGS WORLDWIDE. S S1 Quantity Price THE PRICE OF PLASTIC, A MAJOR INPUT IN BOOMERANG PRODUCTION, INCREASES. S1 S Quantity Price WORKERS ARE INTRODUCED TO COFFEE AND THEIR PRODUCTIVITY INCREASES DRASTICALLY. S S1 Quantity YOUR TURN Complete the worksheet on supply shifts