* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download fertilization details - Fall River Public Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
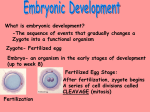
FERTILIZATION DETAILS 1. Review a. Sperm are deposited in the vagina b. Eggs are released by the ovary, one ovary at a time c. The sperm swims to meet the egg i. Passes through cervix (many get trapped in vagina) ii. Crosses uterus iii. Swims up fallopian tubes (may be wrong tube) d. Many sperm arrive at the egg at the same time e. Enzymes in the head of the sperm loosen the protective layer of cells around the egg f. Head of sperm enters egg and fuses with genetic information inside the egg g. Protective shield goes around the egg so no more sperm can get through h. Sperm (haploid) fuse with egg (haploid) to form a diploid zygote (23 chromosomes each – zygote with 46 chromosomes) 2. Travel of Zygote (draw page 1055) a. Newly fertilized egg is called a zygote b. Begins mitotic division (cleavage) after 30 hours (embryo) i. These cells don’t increase in size ii. Cleavage produces a ball of cells called a morula (not much larger than zygote) iii. Cells of the morula divide and form a blastocyst (ball of cells with a fluid filled cavity) c. Travels through fallopian tubes down to uterus as divides d. 4-5 days, the embryo reaches the uterus and is made up of 100 or more cells; e. By the time it reaches the uterus, the morula becomes a blastocyst f. When it reaches the uterus, the morula embeds itself in the thick uterine lining; implantation g. If doesn’t implant in correct location can be ectopic pregnancy h. Implantation: HCG is produced so lining isn’t shed (no period) and can be detected on home pregnancy kit i. Pregnancy begins at implantation (6 days after fertilization) Pregnancy 1. After implantation, the blastocyst slowly takes on human features; this nine month period is called gestation or pregnancy a. First Trimester i. For first 2-3 weeks, the embryo looks like embryo of other animals ii. The embryo develops from the mass of cells on the inner surface of the blastocyst iii. At first, all of the cells look alike but then they organize into three major layers: ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. iv. Different parts of the body develop from these different layers 1. Ectoderm; nervous tissue and skin 2. Mesoderm: muscle, connective tissue, organs 3. Endoderm: linings of digestive, respiratory and urinary tract; also liver, glands, pancreas, thyroid and thymus v. Membranes that help the embryo also form during this time 1. Amnion: amniotic fluid cushions the embryo 2. Yolk sac: where first blood cells and reproductive cells originate 3. Allantois: forms near yolk sac 4. Chorion: surrounds other membranes; one side has chorion villi that extend into the uterine lining vi. Placenta 1. made of chorion villi and part of the uterine lining. 2. 6-8 “ in diameter and 1” thick 3. nutrients, gasses, pathogens, drugs pass from mother to fetus through placenta 4. Developing fetus is attached to placenta by umbilical cord which has arteries and veins that carry blood between fetus and placenta 5. Blood between mother and fetus never mixes; materials are exchanged through diffusion 6. Developing placenta secretes a hormone calle HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) early in second week after fertilization. 7. HCG stimulates production of sex hormones which keeps uterine lining and embryo 8. As placenta grows, its secretes large amounts of estrogen and progesterone which maintain the uterus and prevents ovulation 9. If the egg is not fertilized: no more sex hormones would be made, and menstruation would follow vii. Organogenesis: process that forms the organs 1. Cell determination: organize according to function 2. Cell differentiation: get special structures 3. Morphogenesis: produces shape and structure of body regions viii. Brain, nervous system and spinal cord form in third week ix. Heart beats at 21 days and is smooth beating at 28 days x. By fifth week: arms, legs, eyes, ears, and digestive system develop xi. By 6th week: fingers and toes and some brain activity; embryo begins to move b. c. d. e. xii. From 8 weeks to birth: the embryo is called a fetus xiii. By End of first trimester, it is only 2 inches long, but organ systems have begun to form Second Trimester i. Mother’s abdomen begins to swell as uterus enlarges ii. Fetuses heartbeat can be heard and skeleton begins to form iii. Layer of soft hair grows over skin iv. Fetus begins to wake and sleep v. Can feel fetus moving around: swallows, hiccups, sucks its thumb and makes a fist; kicks feet and curls toes vi. By end of second trimester, it is about 32 cm long and eyes are open Third trimester i. Fetus grows quickly and undergoes changes so it can survive outside the mother ii. Can see light and darkness through abdominal wall, and can react to music and loud sounds iii. During last half of the trimester, the fetus develops fat under its skin to insulate the body for a steady temperature. Miscarriage: i. Spontaneous abortion occurs in more than 20% of all conceptions (1st trimester usually) ii. Usually because there is a genetic abnormality that prevents normal fetal development Birth i. Birth occurs 270 days after fertilization ii. Three stages: 1. Contractions dilate the cervix to about 10 centimeters; 5 fingers a. Hormones initiate childbirth causing smooth muscles lining uterus to contract b. Amniotic sac breaks and fluid falls through vagina (breaking water) c. Muscles in cervix and vagina relax allowing them to enlarge for fetus to pass through. d. Muscular contractions are called labor 2. Birth of the fetus a. Usually less than 2 hours b. Pushing 3. Afterbirth: a. fluid, blood, placenta are pushed out of the body with contractions; umbilical cord is severed b. Afterbirth (placenta, amnion and uterine lining) come out of the body about 10 minutes after the baby is born. iii. Baby’s lungs expand as the baby cries for the first time and breathes on its own. iv. Umbilical cord is cut and tied; baby’s circulatory system closes off and is now independent of the mother. v. Soon the respiratory and excretory systems become fully functional. 2. Vulnerability of Early Growth and Trauma of Birth a. So much growing and developing in embryonic stage, makes it a vulnerable time for the infant. b. Spontaneous abortions i. Trauma ii. Inherited defects (select against defective genotypes – natural selection and evolution) iii. Usually so early that mother is not aware that she was even pregnant – less costly, mother can become pregnant again c. Right after birth, fetus must make many physiological adjustments in a short amount of time: i. Lungs fill with air ii. Umbilical veins and arteries are lost iii. More work on heart 3. Maternal Health a. Nutrition i. Need good nutrition (carbs, proteins, fats) ii. Need more calories (not eating for two!) iii. Need to get folic acid or neural tube defects iv. Gain 20 – 35 pounds v. If poor nutrition right before birth brain function suffers b. Infections i. Antibodies help prevent all but the most serious infections ii. Teratogens (agents that cause birth defects) iii. Measles during the 1st six weeks can cause 50% chance of organs not forming properly or deafness c. Prescription Drugs i. In the 1960s tranquilizer thalidomine missing or deformed arms and legs ii. Anti-acne drugs can cause facial and cranial deformities iii. NO IBUPROFEN d. Alcohol i. Fetal alcohol syndrome ii. Common cause of mental retardation iii. Smaller than normal brain and head, facial deformations, poor motor coordination, heart defects iv. 60 – 70 % of alcoholic women have babies with FAS e. Cocaine i. Prevents nervous system from developing normally ii. Chronically irritable and abnormally small f. Cigarette Smoke i. Smoking reduces vitamin C in the blood and fetus ii. May disrupt other nutrients iii. Harms the growth and development (underweight newborn) iv. Risk is higher for stillbirth, miscarriage and premature delivery 4. First Four Weeks – Neonatal Life a. Reflexes: i. newborn is helpless but has some helping reflexes ii. sucking, rooting: breastfeeding iii. Moro reflex (arms embrace when lost support of head) iv. Babinski reflex: big toe curls down when foot is stroked v. Grasping vi. Blink, smile, sneeze, cough and gag b. Human Newborns are helpless compared to other animals i. Main way of helping self is to cry ii. Humans are the slowest maturing primate iii. Parents are in demand but more learning period iv. Human newborns are helpless but ready to learn 5. Phases of Post Natal Growth a. Infancy: i. About 7.5 pounds and 20” long ii. Head and neck are 30% of the body (adults 10%) iii. Legs are only 15% of body (adults 50%) and weak iv. Body made of a lot more water v. Large brain early in life (cranial); doubles in size the first year and is adult size by age 10 vi. Brain grows in cell size, not cell number; make more connections, more fatty myelin sheaths vii. Other organs grow in first years of life; thymus 40% in first year; adult size by age 12; then shrinks; thymus is important at educating T cells in immune system viii. Length, chest circumference increase b. Childhood i. Rapid neurological development ii. Gradual increases in organ sizes, height and weight iii. Toddler, more neuromuscular control iv. Learn to speak v. Rate of neurological development varies a lot as does physical growth vi. Men do take longer for neurological development vii. Increased height and length of legs (epiphyseal growth) viii. By 10, skull is like that of an adult c. Adolescence and Puberty i. Childhood growth is slow and steady, then adolescent growth spurt ii. Hormones are secreted and secondary sex characteristics are now evident iii. Increase in weight and then height iv. Growth spurt usually over 2 years d. Menarche i. Girls become sexually mature with first menstrual period after height growth spurt declines ii. Need some body fat and fatter girls have periods first iii. Now seeing decline in age of first menarche 6. Reaction Norm a. Now that we see the biological basis of human development, we will see how the environment plays a role. b. Environment can play a part in shaping the adult organism c. Ie, the genotype may have potential to be 70 inches if environment is ideal. d. Sometimes growth is slowed and then there is catch up growth, but sometimes it cannot get back on track. e. Something may effect critical part of growth process (iodine deficiency), length of time that growth delayed was too long (malnutrition) f. Chronic mild undernutrition: body size reduced, adolescence delayed, sexual maturation delayed. 7. Factors that influence growth and nutrition a. Genetics i. Body shape and size, fat deposition, and growth patterns are more related to genetics ii. Body size is determined by many genes iii. Ossification and dental development are also genetically controlled iv. Racial differences in height, skeletal maturation v. Sex differences between males and femailes b. Neural control i. Growth center in the brain (hypothalamus) keeps growth on track genetically so if there is a problem (illness, some malnutrition) there can be catch up with growth. ii. Peripheral nervous system also helps c. Hormonal control i. Endocrine glands influence growth ii. Fetal hormones, and other hormones throughout the lifetime d. Nutrition i. Need food for essential growth e. f. g. h. i. j. k. ii. In post-war Germany, children lagged behind normal growth curves iii. Hard to test malnutrition (unethical); rats and mice iv. Nutritional needs vary throughout the life cycle of the child v. Need lots of nutrition, calcium, protein, vitamins, iron Secular trends i. People grow differently at different stages of history ii. People today grow faster than before Socioeconomic Class i. Higher socioeconomic class are taller ii. Size of family is also important Season and Climate i. Growth in height is faster in the spring ii. Weight is faster in autumn iii. Not necessarily weather, other conditions that go along with weather Exercise i. Adults and children can grow muscle mass with exercise ii. Reduce fat storages Disease i. Asthma can lead to delay in puberty ii. Tuberculosis and cystic fibrosis can influence height Antenatal insults i. Before birth while mother is pregnant ii. Alcoholic mothers can have children with fetal alcohol syndrome, retarded growth and development iii. Smoking leads to lower birth weight iv. Undernutrition Emotion i. Emotional factors influence growth, post war Germany ii. Stress can outweigh dietary supplement 8. Summary a. The advantage of slow growth and maturation is ability to learn and become enculturated b. Growth is a long time, but can delayed to prevent environmental damage. c. Can lead to permanent reduction in size.