* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 6 - EARTH NOTES
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Meteorology wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
History of climate change science wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
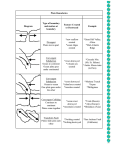
Earth Science Unit Ch 6 I. ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE a. b. POLLUTION = i. ii. iii. iv. Chemical Nature Concentration Persistence Pollution Prevention vs. Pollution Cleanup… Which is cheaper?? c. Goals of Environmental Science i. Establish principles about how the natural world functions ii. Develop viable solutions to environmental problems iii. Make recommendations to elected officials iv. Identify, understand, and solve environmental problems that we have created v. ECOLOGY = vi. Use ecology to address human population growth & consequences of that growth d. ENVIRONMENTAL SUSTAINABILITY i. 1. Ecological Resource 2. Economic resource 3. Renewable resources (perpetual resources) 4. Potentially Renewable resources ii. Based on… 1. What are the effects of our actions on the environment? 2. Resources are limited, and we must live within those limits. 3. Understand all the costs to the environment & society 4. We all share the responsibility for environmental sustainability iii. Solar Capital vs. Earth Capital iv. Why aren’t we sustainable? v. Why can’t we just stop? vi. Challenge = meet immediate needs AND protect the environment in the long term II. Gaia Hypothesis = Planet Earth behaves like a living organism (Earth’s organisms adjust the environment to keep it habitable for life). a. Proposed by ________________________________ in the early 1970s. b. Feedback Loops POSITIVE EX: NEGIATIVE EX: III. 5 Biogeochemical Cycles: CONSTRUCTIVE EX: DESTRUCTIVE EX: nutrients are recycled through the ecosystem a. ________________________: Nutrient is present, but temporarily unavailable b. ________________________: Primary source of nutrients c. ________________________: Consists of the organisms through which nutrients pass. BIOGEOCHEMICAL CARD ACTIVITY (separate note pages) __________________________________– can move over large distances (can be gaseous) ______________________ – local cycling because it does NOT form gaseous compounds. IV. Solar Radiation a. Basics: i. Provides heat, determines climate, allows photosynthesis. ii. Powers the water, carbon, and other biogeochemical cycles iii. Created by _______________________________ iv. 31% of the solar radiation that hits Earth is immediately reflected by clouds, land, snow, ice, and the ocean. 1. Albedo = v. Remaining 69% is absorbed & eventually lost as ________________ to space. b. Temperature Changes w/ Latitude c. Temperature Changes w/ Season V. The Atmosphere a. Composition: b. Layers: i. Troposphere ii. Stratosphere iii. Mesosphere iv. Thermosphere v. Exosphere c. Atmospheric Circulation i. Convection Currents: ii. Winds affected by: 1. ________________ & _______________ gradients (greater gradient = stronger wind) 2. Coriolis Effect = Earth’s rotation causes wind to be deflected toward the west near the equator. Global Winds: Trade Winds, Prevailing Westerlies, Polar Easterlies Convection Cells: Hadley Cell, Ferrell Cell, Polar Cell VI. Weather & Climate a. Weather (day-to-day changes in atmosphere) b. Climate (average weather conditions over a period of years) i. 2 factors influencing climate: __________________ & ______________________ ii. Wladimir Koppen : separated climates into 6 climate zones. c. Precipitation i. Caused by moisture-laden air rising & cooling. ii. Cool air holds _________ water than warm air 1. So… as air cools, it gets _____________ to the saturation point (when precipitation can form). iii. Rain Shadow d. Tornadoes i. Powerful, rotating funnel of air associated with severe thunderstorms. ii. Vary greatly in their strength, size, and speed. iii. How they form: e. Tropical Cyclones (hurricanes, typhoons, or cyclones) i. Giant, rotating tropical storms with winds btwn 119–250km/h (74–155 mph) ii. Most common during summer months… why??? iii. Damage mostly due to __________________________= waves up to 25ft high. iv. How they form: f. Pressure Centers LOW (Cyclone) HIGH (Anticyclone) DIAGRAM CHARACTERISTICS (in the N. Hemisphere) AIR PRESSURE CHANGES g. Winds i. ISOBARS! ii. Winds are influenced by two things: 1. ________________________________________________ a. Isobars are drawn at regular millibar intervals (e.g., 996 mb, 1000 mb, 1004 mb, etc.). b. Isobars can show wind speed the closer the lines, the ____________________ the wind 2. _____________________________________ a. Alters wind __________________ ~Fronts~ Front: ___________________________________________________________________________________ COLD FRONT STATIONARY FRONT WARM FRONT OCCLUDED FRONT KNOW: how the air masses move, direction the front moves, and associated weather VII. The Global Ocean a. 4 interconnected oceans (Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Arctic), Pacific is largest b. Patterns of Circulation in the Ocean i. __________________ = mass movements of surface ocean water 1. caused by ____________. ii. _____________ = circular currents 1. Earth rotates toward the __________, influencing the gyres… iii. Majority of ocean water is in ________________________, so circumpolar flow is virtually unimpeded by landmasses (West Wind Drift) NORMAL c. Vertical Mixing of Ocean Water i. Density ii. Ocean Conveyor Belt 1. Human activities may change the path of this conveyor belt, drastically changing the climate. d. Ocean Interactions with the Atmosphere i._______________________________________________________________ = periodic warming of surface waters of the tropical East Pacific that alters weather in local areas and elsewhere. The upwelling brings cool, nutrient-rich water normally. EL NINO Ocean Changes: Weather Changes: LA NINA Ocean Changes: Weather Changes: VIII. Internal Planetary Processes a. Earth Structure i. Three main sections: b. Plate Tectonics i. Continental Drift = continents have moved. Proposed by Alfred Wegner. 1. Supporting Evidence: ii. Plate Tectonics = movement of lithospheric plates carrying continents. iii. Plate Boundary = _______________________________________________________ 1. intense geologic activity here iv. Plates (____________________) float on the magma (______________________) v. Plate motion is created by convection currents in the asthenosphere 1. Boundary = plates move apart 2. Boundary = plates come together - 3 types: 1. 2. 3. a. 3. Zone: one plate is forced under another. Boundary = plates slide past one another c. Volcanoes i. Magma vs. Lava ii. Occur at 3 locations: 1. _________________________________ zones 2. spreading centers (like a ___________________________________) 3. above hot spots = rising plume of magma that flowed from an opening in the crust. a. AKA – “_________________________________” iii. “Ring of Fire” around the Pacific Ocean iv. Largest eruption of the 20th century: ____________________________________ VOLCANO EXPLORER WEBSITE: http://dsc.discovery.com/convergence/pompeii/interactive/interactive.html Volcano Type How are they built? Physical Characteristics Famous Examples STRATOVOLCANO CINDER CONE SHIELD Inside a Volcano: Three factors affect the size of the volcano and strength of the eruption: (1) _________________________ = resistance to flow, or “___________________” of the magma. (2) Amount of . (3) Amount of . (the more silica, the _______________ the viscosity!!) **Generally, stronger eruptions = __________ viscosity, __________ gas, & __________ silica. d. Earthquakes i. Elastic Rebound Hypothesis ii. Release Seismic Waves (vibrations) in all directions. 1. P-waves 2. S-waves 3. L-waves iii. Most occur along faults (usually near plate boundaries) iv. Focus = v. Epicenter = vi. Seismograph 1. Help determine where, when, and how long the quake occurred. vii. __________________________Scale = measures the size of earthquake waves viii. ____________________________Scale = calculates the total energy released. ix. More than 1million quakes occur each year x. Effects of Earthquakes: 1. landslides 2. tsunamis 3. liquefaction xi. San Andreas Fault xii. Quakes can occur at plate boundaries OR in the middle of a plate (the stress can build up anywhere!!) IX. Topographic Mapping One special kind of map is called a topographic map. It has contour lines to show the shape and elevation of the land. They are sometimes called "level lines" because they show points that are at the same level.