* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Oral clinical examination
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
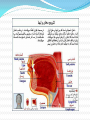
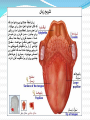
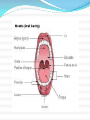
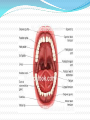
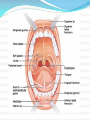
Lips and labial mucosa External portion of the lips: the vermilion border and the skin Vermilion border : the exposed red portion of the lip, covered by mucous membrane, no mucous glands Boundary: the moist labial mucosa in the mouth and the mucocutaneous junction on the skin Skin around the mouth: Lateral labial sulcus: begins at the ala of the nose and progresses downward and outward Mesial labial sulcus: begins at the corners of the mouth(commisures) and runs parallel to the lateral labial sulcus Mental labial sulcus: runs parallel to the mucoucutaneous junction of the lower lip Philtrum: a depression that divides the upper lip into right and left halves Upper and lower labial frenum: at the midline of the upper and lower lip Fibroepithelial polyp: small tag of tissue of the upper labial frenum Buccal mucosa Lining of the cheek Parotid papilla: near the second maxillary molar tooth on the buccal mucosa (opening of the stensen’ duct) Linea alba: hyperkeratotic line corresponding to the line of occlusion of the teeth Caliculus angularis: a small palpable nodule at the anterior termination of the linea alba Pterygomandibular raphe: a fold of tissue at the posterior boundary of the buccal mucosa Buccal frenum: attaches the buccal mucosa to both the maxilla and mandible at approximately the level of the premolar teeth Fordyce‘s granules: clusters of small, yellow nodules of ectopic sebaceous glands Leukoedema: wrinkled, whitish, opalescent appearance Mucogingival junction: junction of the attached gingiva and labial and buccal mucosa Hard palate Incisive papilla: anterior termination of the palatine raphe, in the midline just posterior to the maxillary central incisor teeth Palatine rugae: just behind the incisive papilla Palatine raphe: whitish band of tissue in the midline of the palate from the incisive papilla to the uvula Vibrating line or ahh line: the junction of the hard and soft palate Foveae palatinae: just anterior the vibrating line, on either side of the palatine raphe Soft palate: separates the mouth from the nose Uvula: posterior border of the soft palate in the midline Tonsillar fossae: the most anterior part of the lateral walls of the oropharynx Anterior pillar: anterior wall of the Tonsillar fossae (palatoglossus muscle) Posterior pillar: posterior wall of the Tonsillar fossae (palatopharyngeal muscle) Palatine tonsil: the space between these two pillars Nasopharynx: Anteriorly: choanae Posteriorly: pharyngeal wall Superiorly: first two cervical vertebrae Inferiorly: soft palate Waldeyer’s ring: The pharyngeal tonsils of the nasopharynx The palatine tonsils of the oropharynx The lingual tonsils of the tongue Tongue Dorsum of the tongue: 4 types lingual papillae Filiform papillae: the most, small, whitish hairlike projections Fungiform papillae: the second most, Mushroom-shaped, scattered among the filiform papillae, at the lateral border and the tip of the tongue Circumvallate papillae: posteriorly on the dorsum of the tongue Foliate papillae: on the posterolateral borders of the tongue, leaflike projections Median sulcus: a depression of the midline of the tongue Terminal sulcus: posterior end of the median sulcus Foramen cecum: a depression at the apex of the terminal sulcus Lingual tonsils: on the root of the tongue, posterior to the terminal sulcus Lingual frenum: on the ventral surface of the tongue and attaches to the genial tubercles of the mandible Plica fimbriata: a small line of tissue projection, on either side of the frenum Floor of the mouth Sublingual caruncles: two small projections on either side of the frenum, sites of openings of warton’s duct Sublingual fold: elevations running posteriorly from the caruncles Muscles of mastication: Temporalis, masseter, medial and lateral pterygoid Tepmoralis: Origin: fossa of the temporal bone Insertion: coronoid process and anterior border of the ramus Masseter Origin: lower portion of the zygomatic arch Insertion: lateral surfaces of the angle and coronoid process Medial pterygoid Origin: medial side of the lateral pterygoid plate and tuberosity of the maxilla Insertion: lower medial surface of the ramus Lateral pterygoid Origin: greater wing of the sphenoid bone and lateral surface of the pterygoid plate Insertion: neck of the condyle and the articular disc of the TMJ