* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Human Body Project
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
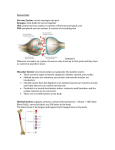
2013 The Human Body Project Miss Ward Turnford School The Human Body Project The human body project is designed to build upon your BTEC First knowledge from the Anatomy & Physiology Unit. In this project we will be looking at assessment criteria across two main units: Unit 1 Anatomy & Physiology of Sport and Unit 2 Physiology of Fitness. The Human body is an amazing piece of machinery it allows sports performers to participate in a huge range of sporting activities. There are a number of body systems that work together to enable the machine to function at peak performance. To understand how these levels of performance are achievable it is important to understand the human body human body and its responses to exercise. The project is broken down into two main sections that will take roughly a half term to complete. The first half term will focus on the skeletal, muscular and energy systems The second half term will focus on the cardiovascular and respiratory systems Within your work we will look at the structure and function of each of these areas of the body and how they respond to exercise. Section 1 Section 2 Date Set: Date Set: Date Due: Date Due: Project Scenario You have been appointed as a Trainee Sports Therapist working with the Sixth Form Football Teams. As part of your role you need to work with players from the teams to ensure that all the players in the squad stay in top condition and look at the effects that exercise has on their bodies. You will need to have an in-depth knowledge of the different systems in the human body and look at the effects of exercise in both the short and long term. Section 1: Skeletal, Muscular and Energy Systems TASK A – THE SKELETAL SYSTEM DESCRIBE the STRUCTURE and FUNCTION of the SKELETAL SYSTEM(P1) DESCRIBE the different CLASSIFICATIONS of joints (P2) GRADING CRITERIA PASS P1:DESCRIBE the STRUCTURE and FUNCTION of the SKELETAL SYSTEM PASS P2:DESCRIBE the different CLASSIFICATIONS of joints USE OF KEY VERBS VERB Describe PLAIN ENGLISH Try to “Paint a picture” in words. Assume that the person that you are Describing to does not know anything about the subject that you are describing. Tell them what you have learned. CONTENT 1. Know the structure and function of the skeletal system Structure of skeletal system: axial skeleton; appendicular skeleton; types of bone (long bones, short bones, flat bones, irregular bones, sesamoid bones); location of major bones (cranium, clavicle, ribs, sternum, humerus, radius, ulna, scapula, ilium, pubis, ischium, carpals, metacarpals, phalanges, femur, patella, tibia, fibula, tarsals, metatarsals, vertebral column – cervical, thoracic, and lumbar vertebrae, sacrum, coccyx) Function of skeletal system: support; protection; attachment for skeletal muscle; source of blood cell production; store of minerals Joints: fixed; slightly moveable; synovial/freely moveable (types, structures, movement at each joint) N O . 1 Learner Checklist(Steps to Success) TICK WHEN COMPLETE Learner Assesso r Label a diagram of the SKELETON. Include the following Labels: Axial Skeleton, Appendicular Skeleton, Cranium, Clavicle, Ribs, Sternum, Humerus, Radius, Ulna, Scapula, Ilium, Pubis, Ischium, Carpals, Metacarpals, Phalanges, Femur, Patella, Tibia, Fibula, Tarsals, Metatarsals, Vertebral Column-Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacrum, Coccyx 2 Paint a picture of the different types of bone: Long, Short, Flat, Irregular and Sesamoid bones. (E.G.) Long bones are found in the limbs. They have a central shaft(diaphysis) and expanded ends(epiphysis). An example of a long bone is the femur. 3 Paint a picture of where each bone is located and what type of bone it is (E.G)Humerus is located in the Upper arm. It is a Long Bone, one end of the humerus articulates with the scapula and the other with the radius and ulna. 4 Paint a picture of the following FUNCTIONS of the skeletal system: Support, Protection, Attachment for Skeletal muscle, Blood Cell Production, Store of minerals. (E.G.)Protection –Bones surround some vital organs and tissues. For example, the cranium protects the brain. Vertebral Column protects the spinal cord 5 Paint a picture of each of the following categories of joints: Fixed, Slightly Moveable, Synovial/Freely Movable. Where appropriate, paint a picture of other types of joint in that category. (E.G.) Slightly Movable joints are also known as Cartilaginous joints. The ends of the bones are covered in hyaline cartilage which stops the bones from rubbing……..An example is the Vertebral Column 6 Paint a picture of the types of movement possible at each joint.(E.G.)A Hinge Joint allows Flexion and Extension. Flexion is bending a limb, like bending the elbow joint which may happen when performing a bicep curl. USE IMAGES TO MAKE YOUR WORK INTERESTING BUT THEY MUST NOT BE COPIED TASK B – THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM IDENTIFY the LOCATION of the MAJOR MUSCLES in the human body (P3) DESCRIBE the FUNCTION of the MUSCULAR SYSTEM and the different FIBRE TYPES(P4) EXPLAIN the FUNCTION of the MUSCULAR SYSTEM and the different FIBRE TYPES (M1) ANALYSE the FUNCTION of the MUSCULAR SYSTEM and the different FIBRE TYPES (D1) GRADING CRITERIA PASS MERIT DISTINCTION P3: IDENTIFY the LOCATION of the MAJOR MUSCLES in the human body P4: DESCRIBE the FUNCTION of the MUSCULAR SYSTEM and the different FIBRE TYPES M1: EXPLAIN the FUNCTION of the MUSCULAR SYSTEM and the different FIBRE TYPES D1: ANALYSE the FUNCTION of the MUSCULAR SYSTEM and the different FIBRE TYPES USE OF KEY VERBS VERB PLAIN ENGLISH Describe Try to “Paint a picture” in words. Assume that the person that you are Describing to does not know anything about the subject that you are describing. Tell them what you have learned. Create a List of KEY FEATURES.(e.g) Steven Gerrards Strengths are: Aerobic Endurance, Goal scoring ratio etc…. Once you have Described the subject, often you will need to give further details and reasons why. (e.g) Once you have described England’s poor performance in the World Cup, you may also give some Identify Explain Analyse reasons why the players did not perform as well as they could. You need to SELECT the KEY POINTS and EXPLAIN each point providing REASONS for each point and also looking at POTENTIALIMPACTS.(e.g.) If you were looking at the performance of Barcelona you may pick out the key points in their success – Money, Lionel Messi, Iniesta etc.. You would then explain the contribution of each player and also look at what the club could do to regain the Champions league next season CONTENT 2. Know the structure and function of the muscular system Muscular system: major muscles (biceps, triceps, deltoids, pectoralis major, rectus abdominis, rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius, semimembranosus, semitendinosus, biceps femoris, gastrocnemius, soleus, tibialis anterior, erector spinae, teres major, trapezius, latissimus dorsi, obliques, gluteus maximus); function; location; types of muscle (cardiac, skeletal, smooth) Function of the muscular system: movement – antagonistic pairs (agonist, antagonist); fixator; synergist; types of contraction (isometric, concentric, eccentric, isokinetic) Fibre types: Type 1; Type 2a; Type 2b; characteristics; types of sports each are associated with N O . Learner Checklist(Steps to Success) 1 2 Assignment Title : The Muscular System Label thefollowing muscles on a diagram(s): Bicep, Tricep, Deltoids, Pectoralis Major, Rectus Abdominus, Rectus Femoris, VastusLateralis, VastusMedialis, VastusIntermedius, Semimembranosus, Semitendinosus,Biceps Femoris, Gastrocnemius, Soleus, Tibilialis Anterior, Erector Spinae, Teres Major, Trapezius, LatissimusDorsi, Obliques, Gluteus Maximus. Paint a picture of the position of each muscle. (e.g.) Bicep muscle is located in the upper arm. It enables flexion of the elbow joint when contracted. It’s origin is the Scapula and point of insertion is the Radius. The Bicep will contract during a bicep curl Paint a picture of the types of muscle: Skeletal, Smooth and 3 4 TICK WHEN COMPLETE Learner Assesso r Cardiac. (E.G.)Skeletal muscle is stripy in appearance when looked at under the microscope. It is Voluntary which means that you must think before you use it. All of the muscles on the exterior of the body are classed as Skeletal. For example, the Triceps are a Skeletal muscle. 5 Paint a picture of the function of the muscles: Movement – Antagonistic Pairs(Agonist/Antagonist), Fixator, Synergist, Contractions(Isometric, Concentric, Eccentric, Isokinetic). (e.g.)Concentric is when the muscle shortens when under tension. For Example holding the javelin before the arm is withdrawn and fully extended before its release. The Brachialis and Bicep shorten here closing the elbow joint 6 Paint a Picture of Muscle Fibre Types: Type 1, Type 2A, Type 2B. Include the Characteristics of each type and sports that they may be associated with. (e.g.)Type 2A Fibres are also called Fast Twitch or Fast Oxidative Fibres. They contract quickly and don’t tire easily. They would be used during a 1500m race. 7 Select the Key points about the muscular system that you wish to discuss further. Show that you have a deeper level of understanding. Use some sporting examples and diagrams to support your analysis. (e.g.)During a Press-Up, when lowering the body to the floor, the bicep is undergoing a concentric contraction-It is shortening under tension. This brings the humerus, radius and ulna closer together, flexing the elbow joint. The Bicep is acting as the agonist muscle. The triceps are relaxed at this time- antagonistic muscle action. Both the Bicep and Tricep are Skeletal muscles. USE IMAGES TO MAKE YOUR WORK INTERESTING BUT THEY MUST NOT BE COPIED FROM THE INTERNET TASK C – THE ENERGY SYSTEMS DESCRIBE the THREE different ENERGY SYSTEMS and their use in sport and exercise activities(P7) EXPLAIN the THREE different ENERGY SYSTEMS and their use in sport and exercise activities(M4) ANALYSE the THREE different ENERGY SYSTEMS and their use in sport and exercise activities(D2) GRADING CRITERIA PASS MERIT DISTINCTION P7: DESCRIBE the THREE different ENERGY SYSTEMS and their use in sport and exercise activities M4: EXPLAIN the THREE different ENERGY SYSTEMS and their use in sport and exercise activities D2: ANALYSE the THREE different ENERGY SYSTEMS and their use in sport and exercise activities USE OF KEY VERBS VERB PLAIN ENGLISH Describe Try to “Paint a picture” in words. Assume that the person that you are Describing to does not know anything about the subject that you are describing. Tell them what you have learned. Once you have Described the subject, often you will need to give further details and reasons why. (e.g) Once you have described England’s poor performance in the World Cup, you may also give some reasons why the players did not perform as well as they could. You need to SELECT the KEY POINTS and EXPLAIN each point providing REASONS for each point and also looking at POTENTIALIMPACTS.(e.g.) If you were looking at the performance of Barcelona you may pick out the key points in their success – Money, Lionel Messi, Iniesta etc.. You would then explain the contribution of each player and also look at what the club could do to regain the Champions league next season Explain Analyse CONTENT 5. Know the different types of energy systems Energy systems: phosphocreatine; lactic acid system; aerobic energy system; amount of ATP produced by each system; sports that use these systems to provide energy; recovery time N O . Learner Checklist(Steps to Success) 1 2 Title Page: Energy Systems Paint a picture of each of the following THREE energy systems: Phosphocreatine, Lactic Acid System and Aerobic Energy system. Include: the AMOUNT OF ATP produced, Sports that may use the system and Recovery time. (e.g.) The Phosphocreatine(PC) System provides immediate energy during sports performance. Phosphocreatine can release a high amount of energy. During activities that are short and require a burst of energy this system will be used. For Example. Throwing the javelin. The breakdown of Phosphocreatine allows ATP to be resynthesized. The system lasts for up to 10 seconds. This system can be recovered and restored within seconds so that it is ready to use again. Create a Table outlining different sports and when they may use each system. Give further details regarding how each system may be used during the same sporting activity.(e.g.) Football. Tackling, Shooting, Heading are all quick activities that happen instantaneously during the game. They are fuelled by the PC system as they happen within a few seconds or split seconds. This energy needs be readily available. The Aerobic System is also vital during the game as the players need to last 90 minutes. The Aerobic system has enough time to begin to work and to continue to work due to the length of the game. You need to SELECT the KEY POINTS and EXPLAIN each point providing REASONS for each point. Expand your selection of sporting activities. Use a wide range of sporting activities to allow you to do this.(e.g.)A Marathon runner will mainly rely on the Aerobic System during the race. As the runner will be running for several 3 4 TICK WHEN COMPLETE Learner Assesso r hours this system can provide the long-term energy that the runner needs. If the race was close at the end the runner may need to tap into the PC system to provide them with the high intensity energy needed for a Sprint finish. This can provide energy quickly for up to 10 seconds. USE IMAGES TO MAKE YOUR WORK INTERESTING BUT THEY MUST NOT BE COPIED FROM THE INTERNET TASK D – Bodies Acute Response to Exercise DESCRIBE the MUSCOSKELETAL and ENERGY systems response to acute exercise(P1) EXPLAIN the response of the MUSCOSKELTAL Systems to acute exercise ( M1 ) GRADING CRITERIA PASS P1:DESCRIBEthe MUSCOSKELETAL and ENERGY systems response to acute exercise MERIT M1: EXPLAIN the response of the MUSCOSKELTAL Systems to acute exercise USE OF KEY VERBS VERB Describe Explain PLAIN ENGLISH Try to “Paint a picture” in words. Assume that the person that you are Describing to does not know anything about the subject that you are describing. Tell them what you have learned. Once you have described the subject, often you will need to give further details and reasons why. (e.g.) Once you have described England’s poor performance in the World Cup, you may also give some reasons why the players did not perform as well as they could. CONTENT 1. Know the body’s response to acute exercise Musculoskeletal response: increased blood supply; increase in muscle pliability; increased range of movement; muscle fibre micro tears Energy systems: phosphocreatine; lactic acid; aerobic; energy continuum; energy requirements of different sport and exercise activities N O . Learner Checklist(Steps to Success) 1 2 TITLE : The Body’s acute response to exercise Paint a picture of theeffects that exercise has on the MUSCOSKELETAL system. Include the following: Increased Blood Supply, Increase in Muscle Pliability, Increased range of movement and Muscle Fibre Micro-Tears (e.g.) Blood Supply increases to the muscles during exercise , this allows more oxygen to be delivered through the blood capillaries to fuel the muscles. TICK WHEN COMPLETE Learner Assesso r Give further details and reasons why (where appropriate) for the effects on the MUSCOSKELTAL system.(e.g.)Dilation of the blood capillaries occurs this allows more blood to flow through the capillaries. This means that an increased amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide can be exchanged between the capillaries and skeletal muscle allowing energy production to increase and also to increase the speed at which waste is removed 3 Paint a picture of the effects that exercise has on the ENERGY systems. Include the following: Phosphocreatine, Lactic Acid and Aerobic Energy Systems, Energy Continuum and Energy requirement of different activities (e.g.) Increased movement during exercise increases the demands on the body for energy. The Creatine Phosphate system can provide energy for High intensity activities lasting up to 10 seconds. The supply of Creatine Phosphate will deplete after 10 seconds however. USE IMAGES TO MAKE YOUR WORK INTERESTING BUT DO NOT COPY THESE FROM THE INTERNET TASK E – Bodies Long Term Effects of Exercise DESCRIBE the LONG-TERM effects of exercise on the Muscoskeletal system and Energy Systems (P3) EXPLAIN theLONG-TERM effects of exercise on the Muscoskeletal and Energy Systems (M2) GRADING CRITERIA PASS P3:DESCRIBE the LONG-TERM effects of exercise on the Muscoskeletal system and Energy Systems MERIT M2:EXPLAIN the LONG-TERM effects of exercise on the Muscoskeletal and Energy Systems USE OF KEY VERBS VERB PLAIN ENGLISH Describe Try to “Paint a picture” in words. Assume that the person that you are Describing to does not know anything about the subject that you are describing. Tell them what you have learned. Once you have Described the subject, often you will need to give further details and reasons why. (e.g) Once you have described England’s poor performance in the World Cup, you may also give some reasons why the players did not perform as well as they could. Explain CONTENT 1. Know the long-term effects of exercise on the body systems Energy systems: increased aerobic and anaerobic enzymes; increased use of fats as an energy source Skeletal system: increase in bone calcium stores; increased stretch in ligaments; increased thickness of hyaline cartilage; increased production of synovial fluid Muscular system: hypertrophy; increase in tendon strength; increase in myoglobin stores; increased number of mitochondria; increased storage of glycogen and fat; increased muscle strength; increased tolerance to lactic acid N O . Learner Checklist(Steps to Success) 1 2 Assignment Title : The Long Term Effects of Exercise on the Body Paint a picture of the long-term effects of exercise on the Muscoskeletal system. Include: Hypertrophy, Increase in Tendon Strength, Increase in Myoglobin Stores, Increased Mitochondria, Increased Glycogen and Fat Stores, Increased Muscle Strength, Increased tolerance to Lactic Acid, Increased Bone Calcium, Increased Ligament Stretch, Increased thickness of Hyaline Cartilage, Increased production of Synovial Fluid. Learner (e.g.) Muscle Hypertrophy – The size and bulk of the muscles increases. Use of the muscles causes them to tear through stress. The muscle tissue repairs itself and makes the muscle tissue bigger as a result Give further details and provide reasons (Where appropriate).(e.g.) Muscles become more efficient at using oxygen as a result of training. More Mitochondria are produced in muscle cells. These are the site where energy is produced and if more sites are available then more energy can be produced and therefore the muscles are able to work for longer due to the increased energy that is available to them. 3 TICK WHEN COMPLETE Paint a picture of the long-term effects of exercise on the Energy systems. Include:Increased Aerobic and Anaerobic Enzymes, Increased use of Fats for energy.(e.g.)More Aerobic Enzymes are produced through aerobic exercise. These are able to breakdown glucose more effectively and efficiently Assesso r Give further details and provide reasons (Where appropriate).(e.g.)More Enzymes are also available to breakdown Fats. More body fat can be stored in muscles as a result of training. The enzymes mean that more fat can be used as an energy source, meaning that the athlete can compete for longer. USE IMAGES TO MAKE YOUR WORK INTERESTING BUT DO NOT COPY THEM FROM THE INTERNET Section 2: Cardiovascular and Respiratory Systems TASK A – CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM DESCRIBE the STRUCTURE and FUNCTION of the CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM(P5) EXPLAIN the FUNCTION of the CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM (M2) GRADING CRITERIA PASS P5: DESCRIBE the STRUCTURE and FUNCTION of the CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM MERIT M2: EXPLAIN the FUNCTION of the CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM USE OF KEY VERBS VERB PLAIN ENGLISH Describe Try to “Paint a picture” in words. Assume that the person that you are Describing to does not know anything about the subject that you are describing. Tell them what you have learned. Once you have Described the subject, often you will need to give further details and reasons why. (e.g) Once you have described England’s poor performance in the World Cup, you may also give some reasons why the players did not perform as well as they could. Explain CONTENT 3. Know the structure and function of the cardiovascular system Structure of the cardiovascular system: heart (atria, ventricles, bicuspid valve, tricuspid valve, aortic valve, pulmonary valve, aorta, vena cava – superior and inferior, pulmonary vein, pulmonary artery); blood vessels (arteries, arterioles, capillaries, veins, venuoles) Function of the cardiovascular system: delivery of oxygen and nutrients; removal of waste products; thermoregulation (vasodilation and vasoconstriction of vessels); function of blood (oxygen transport, clotting, fighting infection) N O . 1 2 Learner Checklist(Steps to Success) TICK WHEN COMPLETE Learner Assesso r Assignment Title: The Cardiovascular System Label the following features on a diagram of the human heart: Atria, Ventricles, Bicuspid Valve, Tricuspid Valve, Aortic Valve, Pulmonary Valve, Aorta, Vena Cava-Superior and Inferior, Pulmonary Vein, Pulmonary Artery. 3 Paint a pictureof each of the heart structures.(e.g.) The tricuspid valve is located in between the right atrium and ventricle. It controls blood flow between the atrium and ventricle 4 Paint a picture of each of the Blood Vessels: Arteries, Arterioles, Capillaries, Veins and Venuoles.(e.g.) Arteries carry blood away from the heart. The blood is oxygenated. They are elastic and are able to contract. Blood travels at high pressure in the arteries. They are able expand to allow more blood to flow through when needed….. 5 Paint a picture of the FUNCTIONS of the Cardiovascular System: Delivery of Oxygen and Nutrients, Removal of Waste products, Thermoregulation(Vasodilation and Vasoconstriction. (e.g.) Oxygen and nutrients are transported to the tissues through the blood. These provide the cells/tissues with energy that they need to survive. 6 Paint a picture of the FUNCTIONS of the blood: Oxygen Transport, Clotting, Fighting Infection.(e.g.)Blood contains Antibodies and White Blood Cells that help to fight against viruses and bacteria that can cause damage to the body. USE IMAGES TO MAKE YOUR WORK INTERESTING BUT THEY MUST NOT BE COPIED FROM THE INTERNET TASK B – RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DESCRIBE the STRUCTURE and FUNCTION of the RESPIRATORY SYSTEM (P6) EXPLAIN the FUNCTION of the RESPIRATORY SYSTEM(M3) GRADING CRITERIA PASS P6: DESCRIBE the MERIT M3: EXPLAIN the FUNCTION of the RESPIRATORY SYSTEM STRUCTURE and FUNCTION of the RESPIRATORY SYSTEM USE OF KEY VERBS VERB PLAIN ENGLISH Describe Try to “Paint a picture” in words. Assume that the person that you are Describing to does not know anything about the subject that you are describing. Tell them what you have learned. Once you have Described the subject, often you will need to give further details and reasons why. (e.g) Once you have described England’s poor performance in the World Cup, you may also give some reasons why the players did not perform as well as they could. Explain CONTENT 4. Know the structure and function of the respiratory system Structure of the respiratory system: nasal cavity; epiglottis; pharynx; larynx; trachea; bronchus; bronchioles; lungs (lobes, pleural membrane, thoracic cavity, visceral pleura, pleural fluid, alveoli); diaphragm; intercostal muscles (external and internal) Function: gaseous exchange; mechanisms of breathing (inspiration and expiration); lung volumes, eg tidal volume, vital capacity, residual volume; control of breathing (neural and chemical) N O . 1 2 Learner Checklist(Steps to Success) TICK WHEN COMPLETE Learner Assesso r Assignment Title: The Respiratory System Label the following parts on a diagram: Nasal Cavity, Epiglottis, Pharynx, Larynx, Trachea, Bronchus, Bronchioles, Lungs(Lobes, Pleural Membrane, Thoracic Cavity, Visceral Pleura, Pleural fluid, Alveoli), Diaphragm, Intercostal Muscles(Internal and External) 3 Paint a picture of the role of each part.(e.g.) Larynx is also called your voice box. It is made of muscle and cartilage. It contains your vocal chords that allow you to talk and links the pharynx to the trachea. Repeat this process for each of the named parts. 4 Paint a picture and give as much detail as possible regarding the following functions: Gaseous Exchange, Mechanisms of breathing( Inspiration and Expiration), Lung Volumes(e.g.)Tidal Volume, Vital Capacity, Residual Volume, Control of breathing(Neural and Chemical) (e.g.)During Inspiration, the Intercostal muscles contract lifting the Ribs up and outwards. The Diaphragm is forced down and the sternum is pushed forwards. This expands the Thoracic Cavity, pressure falls allowing air to flow into the lungs. Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide are exchanged. Repeat this process for each function that is listed. USE IMAGES TO MAKE YOUR WORK INTERESTING BUT DO NOT COPY THESE FROM THE INTERNET TASK C – Bodies acute response to exercise DESCRIBE the CARDIOVASCULAR and RESPIRATORY systems responses to acute exercise(P2) EXPLAIN the response of the CARDIOVASCULAR and RESPIRATORY Systems to acute exercise ( M1 ) GRADING CRITERIA PASS P2:DESCRIBE the CARDIOVASCULAR and RESPIRATORY systems responses to acute exercise MERIT M1: EXPLAIN the response of the CARDIOVASCULAR and RESPIRATORY Systems to acute exercise USE OF KEY VERBS VERB Describe PLAIN ENGLISH Try to “Paint a picture” in words. Assume that the person that you are Describing to does not know anything about the subject that you are describing. Tell them what you have learned. Once you have described the subject, often you will need to give further details and reasons why. (e.g.) Once you have described England’s poor performance in the World Cup, you may also give some reasons why the players did not perform as well as they could. Explain CONTENT 1. Know the body’s response to acute exercise Cardiovascular response: heart rate anticipatory response; activity response; increased blood pressure; vasoconstriction; vasodilation Respiratory: increase in breathing rate (neural and chemical control); increased tidal volume N O . Learner Checklist(Steps to Success) 1 Paint a picture of the effects that exercise has on the CARDIOVASCULARsystem. Include: Anticipatory Response, Activity Response, Increased Blood Pressure, Vasoconstriction, and Vasodilation. (e.g.) Heart Rate increases immediately as soon as you take part in physical activity. The heart beats more times each minute. This allows more blood containing oxygen to be delivered to skeletal muscles to allow them to create energy. 2 TICK WHEN COMPLETE Learner Assesso r Give further details and reasons why (where appropriate)for the effects on the Cardiovascular system. ( e.g.) Vasoconstriction occurs where some blood vessels redirect blood away from areas where it is not needed. The diameter of the blood vessels is temporarily reduced so less blood will flow to certain areas. For example, when Cycling less blood is needed in the upper body in comparison to the leg muscles Paint a picture of the effects that exercise has on the RESPIRATORYsystem. Include the following: Increase in Breathing Rate, Increased Tidal Volume. (e.g.)Breathing rate increases as an immediate response to exercise as more oxygen is needed by the body to produce energy. More breaths and deeper breaths are taken in order to achieve this. Give further details and reasons why (where appropriate)for the effects on the Respiratory system. ( e.g.)The immediate increase in breathing rate is partly due to receptors in the muscles and joints sensing the increase in activity in these parts of the body and sending messages to the brain to increase the rate of breathing so that more oxygen can be delivered to the muscles and more carbon dioxide can be removed. USE IMAGES TO MAKE YOUR WORK INTERESTING BUT DO NOT COPY FROM THE INTERNET TASK D – Bodies long term response to exercise DESCRIBE the LONG-TERM effects of exercise on the Cardiovascular and Respiratory Systems(P4) EXPLAIN the LONG-TERM effects of exercise on the Cardiovascular and Respiratory (M2) GRADING CRITERIA PASS P4:DESCRIBEthe LONG-TERM effects of exercise on the Cardiovascular and Respiratory Systems MERIT M2:EXPLAIN the LONG-TERM effects of exercise on the Cardiovascular and Respiratory USE OF KEY VERBS VERB PLAIN ENGLISH Describe Try to “Paint a picture” in words. Assume that the person that you are Describing to does not know anything about the subject that you are describing. Tell them what you have learned. Once you have Described the subject, often you will need to give further details and reasons why. (e.g) Once you have described England’s poor performance in the World Cup, you may also give some reasons why the players did not perform as well as they could. Explain CONTENT 1. Know the long-term effects of exercise on the body systems Cardiovascular system: cardiac hypertrophy; increase in stroke volume; increase in cardiac output, decrease in resting heart rate; capillarisation; increase in blood volume; reduction in resting blood pressure; decreased recovery time; increased aerobic fitness Respiratory system: increased vital capacity; increase in minute ventilation; increased strength of respiratory muscles; increase in oxygen diffusion rate N O . Learner Checklist(Steps to Success) 1 Give further details and provide reasons (Where appropriate)of the changes that happen to the Cardiovascular System. Include: Cardiac Hypertrophy, Increases in: Stroke Volume / Cardiac Output. Decrease in Resting Heart Rate, Capillarisation, Increase in blood volume, Reduced Resting Blood Pressure, Decreased recovery time and increased aerobic fitness. 2 TICK WHEN COMPLETE Learner Assesso r (e.g.)Cardiac Hypertrophy is when the heart muscle increases in size. The cardiac muscle in the Left Ventricle increases in thickness and is able to contract more forcefully. Like any other muscle, through stress from repeated training the heart responds by increasing in size. This affects Stroke Volume as the heart is able to pump more blood out with every beat at rest. In turn this affects Cardiac Output. Give further details and provide reasons (Where appropriate)of the changes that happen to the Respiratory System. Include: Increased -Vital Capacity/Minute Ventilation/Strength of Respiratory Muscles/Oxygen diffusion rate. (e.g.)Like the heart muscle the breathing muscles increase in size and become stronger through endurance training. The diaphragm and Intercostal muscles become stronger allowing the chest cavity to be able to expand more allowing more air and therefore oxygen to enter the lungs. Getting more oxygen into the lungs means that this can be converted into more energy. Therefore, endurance performers can last for longer USE IMAGES TO MAKE YOUR WORK INTERESTING BUT DO NOT COPY FROM THE INTERNET