* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
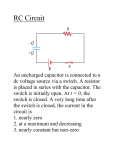
Download Score_____/38 pts( 2pts per question) Purpose: Use this simulation
Crystal radio wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup