* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The End of World War II
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Berlin Blockade wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Containment wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Berlin Crisis of 1961 wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1962–1979) wikipedia , lookup
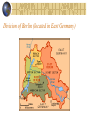
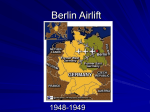
The End of World War II Chapter 14 Section 5 Costs of World War II While the Allies enjoyed their victory, the huge costs of WWII began to emerge As many as 50 million people had been killed The Allies learned of the extent of the horrors of the Holocaust as the concentration camps were liberated War crimes trials, such as those at Nuremberg in Germany, held leaders accountable for their wartime actions and crimes against humanity To ensure tolerance and peace, the Western Allies set up democratic governments in Japan and Germany with new constitutions Victims of the Holocaust Concentration Camp at Dachau, Germany The Holocaust Holocaust Ovens at Concentration Camp Barracks in Concentration Camp Nazi War Criminals on Trial at Nuremberg Defendants at Nuremberg The defendants at Nuremberg. Front row, from left to right: Hermann Göring, Rudolf Hess, Joachim von Ribbentrop, Wilhelm Keitel, Ernst Kaltenbrunner, Alfred Rosenberg, Hans Frank, Wilhelm Frick, Julius Streicher, Walther Funk, Hjalmar Schacht. Back row from left to right: Karl Dönitz, Erich Raeder, Baldur von Schirach, Fritz Sauckel, Alfred Jodl, Franz von Papen, Arthur Seyss-Inquart, Albert Speer, Konstantin van Neurath, Hans Fritzsche. United Nations In 1945, delegates from 50 nations convened to form the United Nations, an international organization established after WWII whose goal is to maintain peace and cooperation in the international community Under the UN charter, each member nation has one vote in the General Assembly Security Council of the United Nations A smaller Security Council has greater power within the United Nations (UN) The Security Council has five permanent members: the United States, Russia, Britain, France, and China The Security Council has 10 rotating members, for a total of 15 member countries Each has the right to veto any council decision Agencies of the UN have tackled many world problems, from disease to helping refugees Flag of the United Nations United Nations Headquarters New York City United Nations General Assembly Flags of Security Council Nations United Nations Security Council Cold War However, conflicting ideologies soon led to a Cold War This refers to a state of tension and hostility between the United States and the Soviet Union between 1946 and 1990 (democracy vs. communism) Soviet leader Stalin wanted to spread communism into Eastern Europe He also wanted to create a buffer zone of friendly countries as a defense against Germany By 1948, pro-Soviet communist governments were in place throughout Eastern Europe Truman Doctrine When Stalin began to threaten Greece and Turkey, the United States outlined a policy called the Truman Doctrine This policy meant that the USA would resist (and contain) the spread of communism throughout the world President Harry S. Truman Containment of Communism Marshall Plan To strengthen democracies in Europe and to rebuild Europe, the USA offered a massive aid package, called the Marshall Plan Marshall Plan money was even offered to the Soviets who rejected it Berlin Blockade Western attempts to rebuild Germany triggered a crisis over the city of Berlin The Soviets controlled East Germany, which surrounded Berlin To force the Western Allies out of Berlin, the Soviets blockaded West Berlin, but a yearlong airlift forced them to end the blockade Berlin Airlift Air Routes into Berlin Division of Berlin (located in East Germany) NATO and the Warsaw Pact Tensions between the USA and the USSR continued to mount In 1949, the United States and nine other nations formed a new military alliance called the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) The Soviets responded by forming the Warsaw Pact (1955), which included the Soviet Union and seven Eastern European satellite nations controlled by the USSR NATO Logo and Member Flags Warsaw Pact Countries NATO vs. Warsaw Pact Countries Current NATO Member Countries NATO membership Of the 28 member countries, two are located in North America (Canada and the United States) and 25 are European countries while Turkey is in Eurasia. All members have militias, although Iceland does not have a typical army. Three of NATO's members are nuclear weapons states: France, the United Kingdom, and the United States. NATO has 12 original founding member nation states and through April 2009 it has added 16 more member nations. Powerpoint Questions (17 points) 1. Where did the post-war war-crimes trials take place? 2. How many people (estimated) died during World War II worldwide? (military and civilians) 3. Define the United Nations. When was it established? (2 points) 4. How many total members form the UN Security Council? 5. Who are the five permanent members of the U.N. Security Council? (5 points) Powerpoint Questions (17 points) 6. Define Cold War. 7. What type of government did Stalin prefer for Eastern Europe? 8. What was the Truman Doctrine? 9. What was the name of the plan to help rebuild Europe? 10. How did the Western allies respond when the Soviets attempted to blockade entry and exit from Berlin? Powerpoint Questions (17 points) 11. What alliance did the USA and 9 other allies form in 1949? 12. What alliance did the Soviets form in 1955? The End