* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 17
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
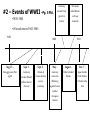
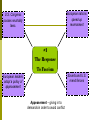
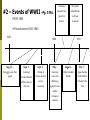
Chapter 17 The Road to War 1. What foreign policy did the US follow after World War I? • Isolationism- a withdrawal from foreign affairs during the 20’s and 30’s • The U.S. Government did not want to get involved in another World War. • Did NOT join the League of Nations, Permanent Court of International Justice, or World Court 2. What were the major postwar peace initiatives? • Disarmament- reduce the size of a country’s military • Washington Conference: organized by Charles Evans Hughes • He proposed the 5 Power Naval Treaty • Ordered countries to retire some of their warships to equal out naval strength. 3. How did war debts and reparations affect European nations after World War I? • The Allies owed the U.S. over $10 billion. • Britain, France, and Italy wanted their debts canceled • Germany owed $32 billion • Dawes Plan: gave Germany more time to pay reparations, also provided more loans 4. What role did the U.S. play in Nicaraguan politics? • 1926, Marines were sent to protect American interests • Henry Stimson negotiated a peace treaty to end Nicaragua’s civil war • 1933, Hoover withdrew all troops because of the high costs 5. How did U.S. relations with Latin America change in the 1930s? • Coolidge, Hoover, and Roosevelt all tried to improve Latin America relations • FDR and the “Good Neighbor Policy” • The U.S. invested in banana, coffee, and sugar plantations. “United Food Company” • Mexico nationalized their oil fields, this strained relations with the U.S. and Britain 6. How did the Great Depression affect Latin American countries? • Crop prices went down (bananas, coffee) • It created a huge gap between rich and poor • Caudillos- military leaders who used force to maintain order The Rise of Militarism Chapter 17 – Section 3 Page 512 What you need to know… 1) How did Mussolini create a fascist state in Italy? 2) Explain Stalin’s power in the Soviet Union. 3) Explain Hitler’s rise to power in Germany. 4) Causes of the Spanish Civil War. 5) Actions of Japan’s military during the 1930’s. The publishers of a new children’s encyclopaedia have asked young people to define what the term ‘democracy’ means today. With your partner discuss a short definition of this word. Write your answer on Page 3 in packet. Only one political party is allowed to exist - the Dictator is the leader of this party, and the party helps him to run the country One person - the ‘Dictator’ holds all of the power in the country So no elections are held because the Dictator does not allow people to choose who they want to run their country What is a Dictatorship Dictators rely upon a large, strong and loyal army to help them to maintain their power ???? Education and the media (newspapers, radio, film etc) are strictly controlled by the Government Anyone who is considered to be an enemy of the Dictator and his political party would be persecuted What is the difference between a democracy and a dictatorship? #1 - Benito Mussolini - ITALY Fascist Party – 1921 •Military dominated government •Blackshirts •Italian king appointed Mussolini prime minister and granted him dictatorial powers!! #1 – Why did Italy become a fascist state? • High unemployment • Fascists beat Communists • Widespread opposition to Socialists and Communists Play Video 2:26 minutes #2 – Joseph Stalin – Soviet Union • After Lenin’s death in 1924 – Stalin emerged as the nation’s leader. • Created a TOTALITARIAN STATE • Government controls COMPLETELY • Sent 15 Million to later camps by 1933 • Stalin felt he could loose control, so he purged all perceived enemies from Communist Party and the Red Army. • Approx. 30 Million died as a result of policies. #3 – Adolf Hitler – GERMANY Play Video (9:09 Min) •Mein Kampf (My Struggle) won supporters •Electoral success by Nazi Party led to Hitler becoming chancelor in 1933. •Third Reich (Third Empire) - - Nazi government #4 Francisco Franco - SPAIN • Causes of Civil War • A constitution was created that limited military power and reformed universal suffrage, nationalized public utilities and gave land to peasants. • Military men were threatened by this and Franco led them. • Franco fascists tried to overthrow the government. Germans and Italians helped Franco take over • Soviet Union allied with loyalists • Popular Front – Americans and others against fascism #5 – Japan’s Military Hideki Tojo Japanese Prime Minister 1920’s – Military grew and did not want to rely on foreign imports, wanted to reduce western influence and expand in Eastern Asia and the Pacific. 1931 – Invaded Manchuria 1934/1935 – Began a naval build-up 1937 – Went to war with China and occupied northern China. NAME THAT FAVORITE DICTATOR... Write down: a) The name of the Dictator. b) The name of the country that the Dictator is from. - For the following slides (after Charlie Chaplin!). 1 Mao 2 Stalin 3 Hitler 4 Hussein 5 Castro 6 Lenin 7 Mussolini Chapter 17 – Section 4 Page 518 What you need to know… 1. Response to Fascism 2. Early events of WWII 3. Why tensions between U.S. and Germany increased 4. Reasons Japan bombed Pearl Harbor It was the Allies vs. the Axis Powers… Allies (major powers) (major powers) Great Britain Germany Russia Italy United States Japan France (note: France surrendered to Germany in 1940 (after 6 weeks of fighting) 29 Axis Choose one of the following pictures and write a caption for it on Page 4 in your packet. European nations speed up rearmament U.S. Congress passes neutrality laws. #1 The Response To Fascism Soviets and U.S. mend fences European leaders adopt a policy of appeasement Appeasement – giving in to demands in order to avoid conflict #2 – Events of WWII –Pg. 5 Pkt. •1939-1945 Germany created Vichy govm’t in France Roosevelt aided Britain with war materials •US involvement 1941-1945 1939 Aug. 23 – Nonaggression Pact signed 1941 1940 Sept.1 Germany invades Poland (official start to the war) Sept. 3 Britain & France declare war on Germany May – August – Germany carried on Blitzkrieg against France & other European nations Hitler bombed Britain Dec. 7 – Japan bombs Pearl Harbor; US enters the War Stalin Hitler Non-Aggression Pact – Surprising!!! Hitler and Stalin were seen as natural enemies. When Hitler talked of taking over new land for Germany, many thought that he meant Russia. Hitler also hated Communism (Russia’s government) #3 - U.S. vs. Germany • Increase in U.S. aid to the Allies • German submarine attacks • Roosevelt’s “shoot-onsight” order So What Was Hitler Asking For? •Return of German Speaking Lands “Lebensraum” •Austria - Peacefully Annexed in 1938 German Troops Parade in Streets of Czechoslovakian Town, ca. 1939 35 So What Was Hitler Asking For? •Sudentenland - (now part of Czech Republic) •Munich Conference - Great Britain & France give to Hitler in return for peace •Hitler then invades the rest of Czechoslovakia German Troops Parade in Streets of Czechoslovakian Town, ca. 1939 36 So What Was Hitler Asking For? •Nonaggression Pact Russia stays out of the war in return for 1/2 of Poland •Great Britain & France finally declare war on Germany Hitler's triumphal entry into Danzig, Poland 1939 37 How Did Hitler Make War? •Blitzkrieg “Lightning War” 1939 Hitler invades: •Denmark •Norway • The Netherlands, •France 38 Hitler in Paris US Assistance •Roosevelt provided aid to the Allies: Lend-Lease - 1941 •US “lent” war materials to cash-strapped Great Britain Atlantic Charter •US secretly meets with England to commit to defeating Germany 39 London Firefighter Tackles an Air Raid Blaze Meanwhile … in the Pacific … #4 – Reason Japan bombed U.S. • Japan continuing expansion in China • Japanese assets in U.S. frozen & an embargo on Japan What? •Surprise attack by the Japanese on American forces in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii USS Arizona Sinking in Pearl Harbor Effect? •US declares war on Japan & other Axis powers Pearl Harbor: “a date which will live in infamy” Chapter 17 – Section 4 Page 518 What you need to know… 1. Response to Fascism 2. Early events of WWII 3. Why tensions between U.S. and Germany increased 4. Reasons Japan bombed Pearl Harbor It was the Allies vs. the Axis Powers… Allies (major powers) (major powers) Great Britain Germany Russia Italy United States Japan France (note: France surrendered to Germany in 1940 (after 6 weeks of fighting) 43 Axis Choose one of the following pictures and write a caption for it on Page 4 in your packet. European nations speed up rearmament U.S. Congress passes neutrality laws. #1 The Response To Fascism Soviets and U.S. mend fences European leaders adopt a policy of appeasement Appeasement – giving in to demands in order to avoid conflict #2 – Events of WWII –Pg. 5 Pkt. •1939-1945 Germany created Vichy govm’t in France Roosevelt aided Britain with war materials •US involvement 1941-1945 1939 Aug. 23 – Nonaggression Pact signed 1941 1940 Sept.1 Germany invades Poland (official start to the war) Sept. 3 Britain & France declare war on Germany May – August – Germany carried on Blitzkrieg against France & other European nations Hitler bombed Britain Dec. 7 – Japan bombs Pearl Harbor; US enters the War Stalin Hitler Non-Aggression Pact – Surprising!!! Hitler and Stalin were seen as natural enemies. When Hitler talked of taking over new land for Germany, many thought that he meant Russia. Hitler also hated Communism (Russia’s government) #3 - U.S. vs. Germany Increase in U.S. aid to the Allies German submarine attacks Roosevelt’s “shoot-on-sight” order So What Was Hitler Asking For? Return of German Speaking Lands “Lebensraum” •Austria - Peacefully Annexed in 1938 German Troops Parade in Streets of Czechoslovakian Town, ca. 1939 49 So What Was Hitler Asking For? •Sudentenland - (now part of Czech Republic) •Munich Conference - Great Britain & France give to Hitler in return for peace •Hitler then invades the rest of Czechoslovakia German Troops Parade in Streets of Czechoslovakian Town, ca. 1939 50 So What Was Hitler Asking For? •Nonaggression Pact Russia stays out of the war in return for 1/2 of Poland •Great Britain & France finally declare war on Germany Hitler's triumphal entry into Danzig, Poland 1939 51 How Did Hitler Make War? Blitzkrieg “Lightning War” 1939 Hitler invades: •Denmark •Norway • The Netherlands, •France 52 Hitler in Paris US Assistance Roosevelt provided aid to the Allies: Lend-Lease - 1941 •US “lent” war materials to cash-strapped Great Britain Atlantic Charter •US secretly meets with England to commit to defeating Germany 53 London Firefighter Tackles an Air Raid Blaze Meanwhile … in the Pacific … #4 – Reason Japan bombed U.S. Japan continuing expansion in China Japanese assets in U.S. frozen & an embargo on Japan What? •Surprise attack by the Japanese on American forces in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii USS Arizona Sinking in Pearl Harbor Effect? •US declares war on Japan & other Axis powers Pearl Harbor: “a date which will live in infamy”