* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Shape of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Systolic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
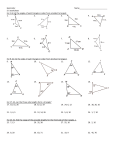
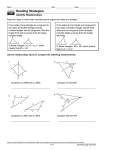
Indirect Proof Inequalities Indirect Proofand and Inequalities 5-5 5-5 ininOne Triangle One Triangle Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz HoltMcDougal GeometryGeometry Holt Indirect Proof and Inequalities 5-5 in One Triangle Objectives Apply inequalities in one triangle. Holt McDougal Geometry Indirect Proof and Inequalities 5-5 in One Triangle The positions of the longest and shortest sides of a triangle are related to the positions of the largest and smallest angles. Holt McDougal Geometry Indirect Proof and Inequalities 5-5 in One Triangle Example 2A: Ordering Triangle Side Lengths and Angle Measures Write the angles in order from smallest to largest. The shortest side is smallest angle is F. The longest side is , so the , so the largest angle is G. The angles from smallest to largest are F, H and G. Holt McDougal Geometry Indirect Proof and Inequalities 5-5 in One Triangle Example 2B: Ordering Triangle Side Lengths and Angle Measures Write the sides in order from shortest to longest. mR = 180° – (60° + 72°) = 48° The smallest angle is R, so the shortest side is . The largest angle is Q, so the longest side is The sides from shortest to longest are Holt McDougal Geometry . Indirect Proof and Inequalities 5-5 in One Triangle Check It Out! Example 2a Write the angles in order from smallest to largest. The shortest side is smallest angle is B. The longest side is , so the , so the largest angle is C. The angles from smallest to largest are B, A, and C. Holt McDougal Geometry Indirect Proof and Inequalities 5-5 in One Triangle Check It Out! Example 2b Write the sides in order from shortest to longest. mE = 180° – (90° + 22°) = 68° The smallest angle is D, so the shortest side is The largest angle is F, so the longest side is The sides from shortest to longest are Holt McDougal Geometry . . Indirect Proof and Inequalities 5-5 in One Triangle A triangle is formed by three segments, but not every set of three segments can form a triangle. Holt McDougal Geometry Indirect Proof and Inequalities 5-5 in One Triangle A certain relationship must exist among the lengths of three segments in order for them to form a triangle. Holt McDougal Geometry Indirect Proof and Inequalities 5-5 in One Triangle Example 3A: Applying the Triangle Inequality Theorem Tell whether a triangle can have sides with the given lengths. Explain. 7, 10, 19 No—by the Triangle Inequality Theorem, a triangle cannot have these side lengths. Holt McDougal Geometry Indirect Proof and Inequalities 5-5 in One Triangle Example 3B: Applying the Triangle Inequality Theorem Tell whether a triangle can have sides with the given lengths. Explain. 2.3, 3.1, 4.6 Yes—the sum of each pair of lengths is greater than the third length. Holt McDougal Geometry Indirect Proof and Inequalities 5-5 in One Triangle Example 3C: Applying the Triangle Inequality Theorem Tell whether a triangle can have sides with the given lengths. Explain. n + 6, n2 – 1, 3n, when n = 4. Step 1 Evaluate each expression when n = 4. n+6 n2 – 1 3n 4+6 (4)2 – 1 3(4) 10 15 12 Holt McDougal Geometry Indirect Proof and Inequalities 5-5 in One Triangle Example 3C Continued Step 2 Compare the lengths. Yes—the sum of each pair of lengths is greater than the third length. Holt McDougal Geometry Indirect Proof and Inequalities 5-5 in One Triangle Check It Out! Example 3a Tell whether a triangle can have sides with the given lengths. Explain. 8, 13, 21 No—by the Triangle Inequality Theorem, a triangle cannot have these side lengths. Holt McDougal Geometry Indirect Proof and Inequalities 5-5 in One Triangle Check It Out! Example 3b Tell whether a triangle can have sides with the given lengths. Explain. 6.2, 7, 9 Yes—the sum of each pair of lengths is greater than the third side. Holt McDougal Geometry Indirect Proof and Inequalities 5-5 in One Triangle Check It Out! Example 3c Tell whether a triangle can have sides with the given lengths. Explain. t – 2, 4t, t2 + 1, when t = 4 Step 1 Evaluate each expression when t = 4. t–2 4–2 2 Holt McDougal Geometry 4t 4(4) 16 t2 + 1 (4)2 + 1 17 Indirect Proof and Inequalities 5-5 in One Triangle Check It Out! Example 3c Continued Step 2 Compare the lengths. Yes—the sum of each pair of lengths is greater than the third length. Holt McDougal Geometry Indirect Proof and Inequalities 5-5 in One Triangle Example 4: Finding Side Lengths The lengths of two sides of a triangle are 8 inches and 13 inches. Find the range of possible lengths for the third side. Let x represent the length of the third side. Then apply the Triangle Inequality Theorem. x + 8 > 13 x>5 x + 13 > 8 x > –5 8 + 13 > x 21 > x Combine the inequalities. So 5 < x < 21. The length of the third side is greater than 5 inches and less than 21 inches. Holt McDougal Geometry Indirect Proof and Inequalities 5-5 in One Triangle Check It Out! Example 4 The lengths of two sides of a triangle are 22 inches and 17 inches. Find the range of possible lengths for the third side. Let x represent the length of the third side. Then apply the Triangle Inequality Theorem. x + 22 > 17 x > –5 x + 17 > 22 x>5 22 + 17 > x 39 > x Combine the inequalities. So 5 < x < 39. The length of the third side is greater than 5 inches and less than 39 inches. Holt McDougal Geometry Indirect Proof and Inequalities 5-5 in One Triangle Example 5: Travel Application The figure shows the approximate distances between cities in California. What is the range of distances from San Francisco to Oakland? Let x be the distance from San Francisco to Oakland. x + 46 > 51 x + 51 > 46 46 + 51 > x Δ Inequal. Thm. x>5 x > –5 97 > x Subtr. Prop. of Inequal. 5 < x < 97 Combine the inequalities. The distance from San Francisco to Oakland is greater than 5 miles and less than 97 miles. Holt McDougal Geometry Indirect Proof and Inequalities 5-5 in One Triangle Check It Out! Example 5 The distance from San Marcos to Johnson City is 50 miles, and the distance from Seguin to San Marcos is 22 miles. What is the range of distances from Seguin to Johnson City? Let x be the distance from Seguin to Johnson City. x + 22 > 50 x + 50 > 22 x > 28 28 < x < 72 x > –28 22 + 50 > x Δ Inequal. Thm. 72 > x Subtr. Prop. of Inequal. Combine the inequalities. The distance from Seguin to Johnson City is greater than 28 miles and less than 72 miles. Holt McDougal Geometry Indirect Proof and Inequalities 5-5 in One Triangle Lesson Quiz: Part I 1. Write the angles in order from smallest to largest. C, B, A 2. Write the sides in order from shortest to longest. Holt McDougal Geometry Indirect Proof and Inequalities 5-5 in One Triangle Lesson Quiz: Part II 3. The lengths of two sides of a triangle are 17 cm and 12 cm. Find the range of possible lengths for the third side. 5 cm < x < 29 cm 4. Tell whether a triangle can have sides with lengths 2.7, 3.5, and 9.8. Explain. No; 2.7 + 3.5 is not greater than 9.8. 5. Ray wants to place a chair so it is 10 ft from his television set. Can the other two distances shown be 8 ft and 6 ft? Explain. Yes; the sum of any two lengths is greater than the third length. Holt McDougal Geometry