* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Blood vessels and nerves of thoracic wall 胸壁的血管和神经The
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
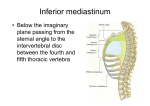
Regional anatomy Thorax Ling Shucai Contents Ⅰ. Summarization 概述 Ⅱ. Thoracic wall 胸壁 Ⅲ. Blood vessels and nerves in thoracic cavity 胸腔内的血管和神经 Ⅳ. Lungs 肺 Ⅴ. Mediastinum 纵隔 Ⅰ. Summarization Summarization 1. Boundary 境界 2. Surface landmark 表面标志 3. Lines of orientation on the thorax 胸部标 志线 1. Boundary 2. Surface Landmarks Jugular notch 颈静脉切迹 Sternal angle (of Louis) 胸骨角 Xiphoid process剑突 Costal margin (costal arch) 肋弓 Infrasternal angle 胸骨下角 Clavicle 锁骨 Inferior angle of scapula Nipple 乳头 肩胛骨下角 Surface Anatomy of the Anterior Thoracic Wall Jugular Notch (T2 Vertebral Level) Clavicle Sternal Angle (T4 Vertebral Level) Surface Anatomy of the Posterior Thoracic Wall C7 Spinous Process (Veterbra Prominens) Vertebral Border of Scapula Inferior Angle of Scapula 12th Rib 3. The Lines of Orientation on the Thorax Anterior median line 前正中线 Sternal line 胸骨线 Midclavicular line 锁骨中线 Parasternal line 胸骨旁线 Anterior axillary line 腋前线 Midaxillary line 腋中线 Posterior axiltary line 腋后线 Scapular line 肩胛线 Posterior median line 后正中线 Ⅱ. Thoracic wall Thoracic wall 1. Superficial structures 浅层结构 2. Deep structures 深层结构 3. Clinical notes 1. Superficial structures ∆ Skin ∆ Superficial fascia – Thoracoepigastric v. – Supraclavicular n. – Anterior and lateral cutaneous branches of intercostal n. The segmental innervation of anterior surface of trunk • T2-sternal angle • T4- nipple • T6-xiphoid process • T8-costal arch • T10-umbilicus • T12-midpoint between umbilicus and symphysis pubis C4 T2 Lymphatic drainage of breast • Into pectoral ln. from lateral and central parts of breast • Into apical and supraclavicular ln. from superior part of breast • Into parasternal ln. from medial part of breast • Into interpectoral ln. from deep part of breast • The lymphatic capillaries of breast form an anastomosing network which is continuous across the midline with that of the opposite side and with that of the abdominal wall 2. Deep structures △ Muscles of thoracic wall 胸壁的肌肉 △ Deep fascia and fascial space 深筋膜及筋膜间隙 (见胸前外侧壁章节) △ Blood vessels and nerves of thoracic wall 胸壁的血管和神经 The muscles of thoracic wall Extrinsic muscles • Pectoralis major • Pectoralis minor • Serratus anterior Intrinsic muscles • • • • Intercostales externi 肋间外肌 Intercostales interni 肋间内肌 Intercostales intimi 肋间最内肌 Transverses thoracis 胸横肌 transverses thoracis Intercostales externi • Origin: lower border of rib) • Insertion: upper border of rib below origin • Action: elevate ribs adding in forced inspiration • Replaced anteriorly by external intercostals membrane. Intercostales interni • Origin: upper border of rib • Insertion: lower border of rib above origin • Action: depress ribs for forced expiration • Replaced posteriorly by internal intercostals membrane. internal intercostals membrane external intercostals membrane Diaphragm 膈 Shape and position: dome-shaped between thorax and abdomen, consists of a peripheral muscular part and a central tendon Origin • • • • Sternal part: xiphoid process Costal part: lower six and costal cartilages Lumbar part: arises by two crura from upper 2-3 lumbar vertebrae Insertion: central tendon Weak areas: • • triangular spaces without muscular tissue Lumbocostal triangle: between costal and lumbar parts. Sternocostal triangle: between costal and sternal parts. Openings in the diaphragm • • • Aortic hiatus 主动脉裂孔-lies anterior to the body of the 12th thoracic vertebra between the crura. It transmits the aorta, thoracic duct Esophageal hiatus 食管裂孔-for esophagus and vagus nerves at level of T10. Vena cava foramen 腔静脉孔-for inferior vena cava, through central tendon at T8 level T8 T10 T12 Action: • Contraction: the dome • Relaxation: the dome moving downward, increases the volume of thoracic cavity which results in inspiration, at the same time the intra-abdominal pressure is increased assists in defecation, vomiting or child birth. returns to the former position, reduces the volume to the thoracic cavity, resulting in expiration. The blood vessels and nerves of thoracic wall Anatomy of Intercostal space Posterior intercostal v. Posterior intercostal a. Intercostal n. The innervation of thoracic wall Anterior branches of thoracic nerves • Intercostal nerves 肋间神经 (anterior rami of T1- T11): • Subcostal nerve 肋下神经 (anterior ramus of T12): follows inferior border of T12 rib and passes into abdominal wall • Distribution: distributed to intercostales and anterolateral abdominal muscles, skin of thoracic and abdominal wall, parietal pleura and peritoneum Internal thoracic vessels • Internal thoracic a.&v. 胸廓内动脉和静脉 • Parasternal ln. 胸骨旁淋巴结 Endothoracic fascia 胸内筋膜 Internal thoracic artery 胸廓内动脉 -descends into thorax 1.2cm lateral to edge of sternum, and ends at the sixth costal cartilage by dividing musculophrenic (肌膈动脉 )and superior epigastric arteries (腹壁 上动脉) 心包膈动脉 胸廓内动脉 腹壁上动脉 Azygos vein 奇静脉 • Begins as continuation of right ascending lumbar vein • Ascending along the right side of vertebral column • Joins superior vena cava by aching above right lung root at level of T4 to T5 • Receives right posterior intercostals and subcostal veins plus some of bronchial, esophageal and pericardial veins, and hemiazygos vein • Tributaries-hemiazygosv.半奇静脉 and accessory hemiazygos v. 副半奇 静脉, which receive most left posterior intercostals vein and left bronchial veins Veins of vertebral column Vertebral venous plexus 椎静脉丛 • External vertebral venous plexus • Internal vertebral venous plexus Ⅲ. Blood vessels and nerves in thoracic cavity Arteries of thorax Pulmonary trunk • • • Arises from right ventricle Runs up, back ,and to the left Bifurcates inferior to aortic arch into right and left pulmonary arteries, one for each lung Pulmonary arteries • • Right pulmonary artery-passes posterior to ascending aorta and superior vena cava to hilum of right lung Left pulmonary artery-passes anterior to descending aorta and left main bronchus to hilum of left lung Ascending aorta 升主动脉 • Runs upward, forward and to the right, • Extends to level of second right sternocostal joint • Branches: right and left coronary arteries Aortic arch 主动脉弓 • Curves upward, to the left and posteriorly, then downward, arching over left principal bronchus and pulmonary trunk to lower border of T4 level, to become descending aorta • Branches (from right to left ) – Brachiocephalic trunk – Left common carotid artery – Left subclavian artery • Aortic isthmus-baroreceptor • Aortic glomera-chemoreceptor Arterial ligament 动脉韧带- remnant of ductus arteriosus, connects bifurcation of pulmonary trunk to inferior border of aortic arch Triangule of ductus arteriosus 动脉导管三角 • • Bounded by phrenic n., left vagus n. and left pulmonary a. Contents- arterial ligament , left recurrent n. and superficial cardiac plexuses Thoracic aorta 胸主动脉 Main branches Parietal branches • Nine pairs posterior intercostals arteries • One pair subcostal artery • For lower nine intercostals spaces and upper part of abdominal wall; superior phrenic arteries supply the superior surface of the diaphragm. Visceral branches • Bronchial branches: one or two for each lung • Esophageal branches • Pericardial branches Veins of thorax Brachiocephalic veins • Formed by union of internal jugular and subclavian veins posterior to the sternoclavicular joint • Angle of union is termed venous angle Superior vena cava • Formed by union of right and left brachiocephalic veins behind the right sternocostal synchorndrosis of first rib • Runs vertically down on right of ascending aorta • Joined by azygos vein at level of sternal angle • Enters right atrium at lever of lower border of third right sternocostal joint • Collects blood from veins of upper half of body Lymph nodes of the thoracic contents • Pulmonary lymph nodes 肺淋巴结 lie in the angles of bifurcation of branching lobar bronchi • Bronchopulmonary hilar lymph nodes 支气管肺门淋巴结 lie in the hilus of the lung • Tracheobronchial lymph nodes 气管支气管淋巴结 situated above or below the bifurcation of trachea • Paratracheal lymph nodes 气管旁淋巴结 along each side of the trachea • Anterior mediastinal lymph node 纵隔前淋巴结 lies anterior to the large blood vessels of thoracic cavity and pericardium; the efferents unite with those of paratracheal lymph nodes, to form the right and left bronchomediastinal trunks 支 气管纵隔干. The left bronchomediastinal trunk terminates in thoracic duct, and right in the right lymphtic duct • Posterior mediastinal lymph nodes 纵隔后淋巴结 lie along the esophagus and thoracic aorta Thoracic duct 胸导管 • Begins in front of L1 as a dilated sac, the cisterna chyli 乳糜池, which formed by joining of left and right lumbar trunks and intestinal trunk • Enter thoracic cavity by passing through the aortic hiatus of the diaphragm and ascends along on the front of the vertebral column, between thoracic aorta and azygos vein • Travels upward, veering to the left at the level of T5 • At the roof of the neck, it turns laterally and arches forwards and descends to enter the left venous angle • Just before termination, it receives the left jugular, subclavian and bronchomediastinal trunks • Drains lymph from lower limbs, pelvic cavity, abdominal cavity, left side of thorax, and left side of the head, neck and left upper limb Right lymphatic duct 右淋巴导管 • Formed by union of right jugular, subclavian, and bronchomediastinal trunks • Ends by entering the right venous angle • Receives lymph from right half of head, neck, thorax and right upper limb Innervation of thorax Phrenic nerve 膈神经 • Accompanied by pericardiophrenic vessels and passes anterior to lung roots between mediastinal pleura and pericardium to supply motor and sensory innervation to diaphragm • Sensory fibers supply to pleurae, pericardium and peritoneum of diaphragm; usually right phrenic nerve may be distributed on live, gallbladder and biliary system. Left vagus nerve 左迷走神经 • Enter thoracic inlet between left common carotid and left subclavian arteries, posterior to left brachiocephalic vein • Crosses aortic arch where left recurrent laryngeal nerve branches off • Passes posterior to left lung root • Forms anterior esophageal plexus • Forms anterior vagal trunk at esophageal hiatus(食管裂孔) where it leaves thorax and passes into abdominal cavity , then divides into anterior gastric and hepatic branches Right vagus nerve 右迷走神经 • Enter thoracic inlet on right side of trachea • Travels downward posterior to right brachiocephalic vein and superior vena cava • Passes posterior to right lung root • Forms posterior esophageal plexus • Forms posterior vagal trunk at esophageal hiatus where it leaves thorax and passes into abdominal cavity, then divides into posterior gastric and celiac branches Recurrent laryngeal nerves 喉返神经 • Right one hooks around right subclavian artery, left one hooks aortic arch • Both ascend in tracheo-esophageal groove • Nerves enter larynx posterior to cricothyroid joint, the nerve is now called inferior laryngeal nerve • Innervations: laryngeal mucosa below fissure of glottis , all laryngeal laryngeal muscles except cricothyroid Bronchial and esophageal branches Thoracic sympathetic trunk 胸交感干 • Branches of sympathetic trunk to thoracic plexuses • Greater splanchnic nerve 内脏大神经 formed by preganglionic fibers from T5~T9 ganglia, and relay in celiac ganglion. • Lesser splanchnic nerve 内脏小神经 formed by preganglionic fibers from T10~T12 ganglia, and relay in aorticorenal ganglion. • The postganglionic fibers supply the liver, spleen, kidney and alimentary tract as far as the left colic flexure. Ⅳ. Lungs The hilum and root of the Lungs ② ① ③ 右肺(前→后 ) : V. A. B ② ③ ① 左肺(前→后 ) : V. A. B The hilum and root of the Lungs ② ① ③ 右肺(上→下 ) : B.A.V. ② ③ ① 左肺(上→下 ) : A. B. V Ⅴ. Mediastinum 纵隔 Mediastinum 1. Position and bounderies 位置及界限 2. Subdivisions and contents of mediastinum 分区及内容 3. Relationships 毗邻 4. Mediastinal spaces 纵隔间隙 1. The position and bounderies -all of organs between the left and right mediastinal pleurae is called mediastinum. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the thoracic inlet above to the diaphragm below. Left side of mediastnum Right side of mediastnum 2. Subdivisions and contents of mediastinum • Superior mediastinum 上纵隔 • Inferior mediastinum 下纵隔 – Anterior mediastinum 前纵隔 – Middle mediastinum 中纵隔 – Posterior mediastinum 后纵隔 Superior mediastinum 上纵隔 Location-from inlet of thorax to plane extending from level of sternal angle anteriorly to lower border of T4 vertebra posterioly Contents • Superficial layer – Thymus – Three veins • Left brachiocephelic v. • Right brachiocephelic v. • Superior vena cava • Middle layer – Aotic arch and its three branches – Phrenic n. – Vagus n. • Posterior layer – Trachea – Esophagus – Thoracic duct Relations of aortic arch • Anteriorly and to the left - pleura, lung,phrenic n., pericardiacophrenic vessels and vagus n. • Posteriorly and to the right- trachea, esophagus, left recurrent n., thoracic duct, deep cardiac plexus • Superiorly-its three branches, left brachiocephalic v. and thymus • Inferiorly-pulmonary a., arterial ligament, left recurrent n., left principal bronchus and superficial cardiac plexus Inferior mediastinum 下纵隔 • • Anterior mediastinum 前纵隔 Location-posterior to body of sternum and attached costal cartilages, anterior to heart and pericardium Contents-fat, remnants of thymus gland, anterior mediastinal lymph nodes • • Middle mediastinum 中纵隔 Location-between anterior mediastinum and posterior mediastinum Contents: heart and pericardium, beginning or termination of great vessels, phrenic nerves, pericardiacophrenic vessels and lymph nodes • • Posterior mediastinum 后纵隔 Location-posterior to heart and pericardium, anterior to vertebrae T5- T12 Contents: esophagus, vagus n., thoracic aorta, azygos system of veins, thoracic duct, thoracic sympathetic trunk, posterior mediastinal lymph nodes 3. Relationships Left subclavian a. Thoracic duct Left vagus n. Left recurrent n. Phrenic n. & pericardiacophrenic a. Aortic arch Thoracic aorta Sympathetic trunk Root of lung Pericardium Esophagus Greater splanchnic n Relationships of the root of left lungs Trachea Left vagus n. Arch of azygos v. Azygos v. Sympathetic trunk Esophagus Superior vena cava Phrenic n. & pericardiacophrenic a. Root of lung Pericardium Inferior vena cava Relationships of the root of right lungs 以肺根为标志观察纵隔的毗邻 左 肺 根 右 肺 根 上方 主动脉弓(自前→后) 奇静脉弓(自后→前) 下方 肺韧带 肺韧带 后方 左迷走神经,胸主动脉 右迷走神经,奇静脉 右膈神经 前方 左膈神经 心包膈血管 心包膈血管 上腔静脉 右心房 部分心包 Relations of esophagus • Anteriorly-trachea, bifurcation of trachea, left principal branchus, left recurrent n., right pulmonary a., anterior esophageal plexus, pericardium, left atrium, diaphragm • Posteriorly-posterior esophageal plexus, thoracic aorta, thoracic duct, azygos v., hemiazygos v.,accessory hemiazygos v., right posterior intercostal v. • Left-left common carotid a., left subclavian a., aortic arch, thoracic aorta, superior part of thoracic duct • Right-arch of azygos v. Relations of thoracic aorta • Anteriorly-left root of lung, pericardium and esophagus • Posterior- hemiazygos v., accessory hemiazygos v., • Right-azygos v. and thoracic duct • Left-mediastinal pleura 4. Mediastinal spaces 纵隔间隙 • Retrosternal space 胸骨后间隙 -lies beween sternum and endothoracic fascia • Pretracheal space 气管前间隙 -lies within superior mediastinum, between trachea, bifurcation of trachea and aortic arch • Retroesophagus space 食管后间隙 - lies within superior mediastinum, beween esophagus and endothoracic fascia 思考题 试述肺根内结构由上而下,从前向后的排列。 上纵隔内由前向后有哪些结构? 分别试述左右肺根的毗邻。 试述纵隔境界与分区。、 试述食管前方的毗邻结构。 试述后纵隔内走行的结构。 试述膈肌中的裂孔与走行结构。 试述胸导管在上纵隔内经过的毗邻结构。 试述锁胸筋膜的构成及经过结构。