* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter Fifteen
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
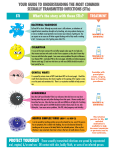
Chapter Fifteen Sexually Transmitted Infections Sexually Transmitted Infections • More than 25 sexually transmitted infectious organisms can be passed from person to person through sexual activities • Bacterial STIs are often curable • Viral STIs are not curable The STI Epidemic • STIs are the most common infections reported in the U.S. • STIs comprise 87% of the cases of infectious diseases reported to CDC • U.S. has the highest STI rates among industrialized nations • By age 24, 1 in 3 sexually active people has had an STI • Incidence • Prevalence Who Is Affected: Disparities Among Groups • Gender disparities • Age disparities • Racial and ethnic disparities Behavioral Factors Contributing to STI Transmission • • • • • • • • Early initiation of intimate sexual activity Numerous sex partners High-risk sex partners High risk sexual behavior Inconsistent and incorrect condom use Substance abuse Sexual coercion Lack of knowledge of and concern about STIs Social Factors Contributing to STI Transmission • Poverty and marginalization • Access to health care • Secrecy and moral conflict about sexuality Biological Factors Contributing to STI Transmission • Asymptomatic nature • Resistance to treatment or lack of a cure • Other: douching, immature cervix, uncircumcised penis Consequences of STIs • Women, men, and infants affected • Presence of STIs increases HIV risk • Untreated STIs have serious consequences – Infertility/ sterility • Untreated Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) causes 15% of women’s infertility • Ectopic pregnancy, miscarriage – Blindness – Cancer, heart disease Principal Bacterial STIs • Chlamydia – Responsible for 80% of women’s tubal infertility – Infects 2.8 million Americans each year • Gonorrhea – 700,000 Americans contract gonorrhea each year – Can cause sterility in both men and women • Syphilis – Infection has stages that indicate progression of infection – Can lead to brain damage and death in newborns • Urinary tract infections – Caused by several different bacteria Sexually Transmitted Infections • Bacterial STIs are often curable • Viral STIs are not curable Principal Viral STIs • Human Papillomavirus (HPV) – 20 million carriers, 5.5 million new cases yearly – Treatment and vaccine • Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) – 45 million Americans infected – Managing symptoms • Hepatitis A, B, C – Viral disease of liver – One third of Americans show evidence of past infection Other Infections • Bacterial vaginosis – Caused by overabundance of Gardnerella bacteria – Treat with antibiotics • Candidiasis: Yeast Infections – Many factors contribute to infection – Men and women can carry the organism • Trichomoniasis – Most common curable STI in young women – Men and women can carry the organism Other STIs • • • • • • Chancroid Cytomegalovirus Enteric infections Granuloma inguinale Lymphogranuloma venereum Molluscum contagiosum Parasites • Pubic lice: Phthirus pubis; commonly known as crabs • Scabies: mite Sarcoptes scabiei • Both can be transmitted non-sexually via clothes, towels, bedding STIs and Women • Women’s anatomy increases susceptibility • Pelvic inflammatory disease - PID – Infection of fallopian tubes spreads – One of the leading causes of female infertility – Caused by some types of STI bacteria • Cystitis: bladder infection – Often related to sexual activity; not an STI – Can create pain and damage kidneys Avoiding STIs • Practice abstinence • Practice sexual exclusivity • Reduce risk during sexual activity • Select partners carefully • Avoid multiple partners • Avoid injecting drugs • Get vaccinated • Protect babies • Be a good communicator Treating STIs • Recognize STI symptoms • Seek treatment • Get partners to treatment Summary • • • • • STIs are epidemic STIs are linked to behavior Principle STIs STIs and women Preventing STIs





















![itching and scratching guided notes [2/17/2017]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/005554232_1-fdcd1a11e73f76c0d26c4b298e3f53ab-150x150.png)