* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 39-1 The Endocrine System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
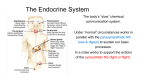
Biology Slide 1 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 and 2 The Endocrine System Slide 2 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System 39-1 The Endocrine System What is the function of the endocrine system? Slide 3 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System 39-1 The Endocrine System 1. made up of: a. glands that release their products into the bloodstream b. products deliver messages throughout the body. c. chemicals released can affect almost every cell in the body. Slide 4 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System Hormones 2. Hormones: a. chemicals released in one part of the body that travel through the bloodstream b. affect activities of cells in other parts of the body. c. bind to specific chemical receptors on cells. 1. If a cell doesn’t have receptors or receptors don’t respond to a hormone, that hormone has no effect on it. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall Slide 5 of 44 39-1 The Endocrine System Glands 3. Glands: organ that produces and releases a secretion. A. 2 kinds of glands: 1. Exocrine glands: release secretions directly to organs that use them. 2. Endocrine glands: release secretions directly into the bloodstream. Slide 6 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System 4. 7 major glands in the endocrine system: A. Hypothalmus B. Pituitary gland C. Parathyroid glands D. Thyroid glands E. Adrenal glands F. Pancreas G. Reproductive glands Slide 7 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System Hypothalamus Hypothalamus Pituitary gland Slide 8 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System Glands 5. Hypothalamus A. makes hormones that control the secretions of pituitary gland. B. Influenced by hormone levels and sensory information Slide 9 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System Glands 6. Pituitary gland A. Secretes 9 hormones regulate body functions B. Controls other endocrine glands C. Divided into 2 parts Slide 10 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System Pituitary Gland The Pituitary Gland Hypothalamus Anterior Posterior pituitary pituitary Pituitary gland Slide 11 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System Pituitary Gland Pg 1004 Slide 12 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System Pituitary Gland Slide 13 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System Pituitary Gland Slide 14 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System Glands 7.Thyroid a. Regulates body’s metabolism b. Produces thyroxine Slide 15 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System Thyroid Gland (Thyroid Disorders Hyperthyroidism: the body produces too much thyroxine. It is characterized by elevated temperature and metabolic rate, increased blood pressure, and weight loss. Hypothyroidism: the body produces too little thyroxine. It is characterized by lower temperature and metabolic rate, lack of energy, and weight gain. Goiter: enlargement of thyroid gland. Caused by an iodine deficiency.) Slide 16 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System Thyroid Gland Thyroid Gland Larynx Thyroid gland Esophagus Trachea Slide 17 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System Glands 8. Parathyroid glands a. release parathyroid hormone b. regulates the level of calcium in the blood. Slide 18 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System Parathyroid Gland Parathyroid Glands Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands Slide 19 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System Glands 9. Thymus a. During childhood, releases thymosin b. stimulates T cell development and proper immune response. Slide 20 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System Glands 10. Adrenal glands a. release epinephrine and norepinephrine b. helps body respond to stress. Slide 21 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System Glands 11. Pancreas a. produces insulin and glucagon b. regulates level of glucose in blood. Slide 22 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System Pancreas c. Diabetes Mellitus •When the pancreas fails to produce or properly use insulin, diabetes mellitus occurs. Slide 23 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System Glands 12. Pineal gland a. releases melatonin involved in rhythmic activities, such as daily sleep-wake cycles. Slide 24 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System Reproductive Glands 13. What are the functions of gonads (reproductive glands)? a. production of gametes b. secrete sex hormones. 14. 2 types of gonads: a. female-ovaries b. male-testes Slide 25 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System Glands 15.Testis a. produce testosterone b. responsible for sperm production and the development of male secondary sex characteristics. Slide 26 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System Glands 16. Ovary a. produce estrogen and progesterone. b. Estrogen is required for the development of female secondary sex characteristics and for the development of eggs. c. Progesterone prepares the uterus for a fertilized egg. Slide 27 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System Hormone Action 17. Hormone Action a. classified as: 1. Steroid hormones: * produced from a lipid called cholesterol. *can easily cross cell membrane 2. Nonsteroid hormones: * include proteins, small peptides, and modified amino acids. *can’t pass through cell membrane *bind to chemical receptor Slide 28 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System Prostaglandins 18.Prostaglandins a. Hormone like substance b. Produced in small amounts by all cells (except red blood cells) c. affect nearby cells and tissues, known as “local hormones.” Slide 29 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System Control of the Endocrine System 19.Control of the Endocrine System: regulated by feedback mechanisms (that function to maintain homeostasis) Slide 30 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System Control of the Endocrine System Controlling Metabolism Slide 31 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System Control of the Endocrine System Example: Controlling Metabolism Thyroxine, a hormone of the thyroid gland, affects the activity of cells throughout the body, increasing their rate of metabolism. A drop in thyroxine decreases the metabolic activity of cells. Slide 32 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 The Endocrine System Control of the Endocrine System If thyroxine is low, the hypothalamus secretes thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), which stimulates the anterior pituitary to secrete thyroidstimulating hormone (TSH). TSH stimulates the release of thyroxine. High levels of thyroxine in the blood inhibit secretion of TRH and TSH, which stops the release of additional thyroxine. Slide 33 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 Click to Launch: Continue to: - or - Slide 34 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 Cells that have receptors for a particular hormone are called a. nerve cells. b. target cells. c. exocrine cells. d. endocrine cells. Slide 35 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 Chemicals that travel through the bloodstream and affect the activities of other cells are known as a. hormones. b. receptors. c. enzymes. d. messengers. Slide 36 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 Melatonin, which is involved in rhythmic activities such as sleep-wake cycles, is released by the a. gonads. b. pineal gland. c. prostate gland. d. thyroid gland. Slide 37 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 Which group of hormones act on target cells by binding directly to DNA in the nucleus? a. steroids b. nonsteroids c. proteins d. second messengers Slide 38 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 39-1 Metabolism is maintained by feedback loops involving the a. hypothalamus, gonads, and adrenal glands. b. hypothalamus, anterior pituitary, and thyroid gland. c. anterior pituitary, pancreas, and thyroid gland. d. thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, and pancreas. Slide 39 of 44 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall END OF SECTION