* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Newton`s first law of mechanics: An object moves at the same
Nanogenerator wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Inertial navigation system wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
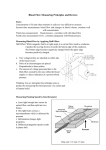
EGN 100 Essential Concepts Secret to success, in this course as in life, is to show up, on time, prepared. When you are here, be here. Newton’s first law of mechanics: An object moves at the same velocity, including zero, unless acted upon by external forces that add up to be something other than zero. Newton’s second law of mechanics: F = ma Mass attracts mass. Opposite charges attract. Like charges repel. What are the following: displacement, velocity, acceleration, mass, force, voltage, current, resistance, charge, work, energy, power? Ohm’s law: V = IR Krichoff’s voltage law: In a circuit, the sum of the voltage rises equals the sum of the voltage drops. A voltage rise occurs when there is a source of energy, such as the chemical energy of a battery or the mechanical energy of a generator. Work and energy have the same units: Joules Power is the rate at which work is done or energy is used. Mechanical work: Work = Fd Joules Mechanical power: P = Fd/t = Fv, F is force in Newtons, v is velocity in m/s and t is time in seconds. Mechanical energy is Pt = F(d/t)t = Fd Joules Electrical work: Work = QV, where Q is the charge in Coulombs and V is the voltage in Volts. Not always a useful measure since we don’t actually move charge around except as current. Electrical Power: P = IV, were I is current in Amperes and V is voltage in Volts. Electrical energy it Pt Joules First law of thermodynamics: Energy is not created or destroyed but is converted from one form to another. Second law of thermodynamics: When constraints are removed, energy goes from a higher level to a lower level. A battery contains chemicals that react with the battery electrodes with the result that electrons are added to one electrode and taken from the other, producing a voltage difference between the electrodes. If we connect the terminals with an electrical circuit, the charges will flow through the circuit, doing useful work and/or producing heat. A radian is a measure of angle defined as the angle subtended by and arc of length equal to the radius of the circle. Angular velocity is measured in radians per second. v = r where v is the velocity of a point on the circumference, is the angular velocity, and r is the radius. When two gears or two pulleys interact, the larger gear (or pulley) has an angular velocity smaller than the smaller gear and a torque greater than the smaller gear. Without losses, the power is the same in two interacting gears. P = T where T is torque and is angular velocity If P1 = P2, then T11 = T22 or T1/T2 = 2/1 Efficiency is Power out / Power in multiplied by 100 to express it in percent. Because of the second law of thermodynamics, it is impossible for efficiency to be greater than 100%. There is a magnetic field around a current. We can create an electromagnetic by forming the wire through which a direct current flows into a coil. According to the right hand rule, the direction of the magnetic field inside the coil is in one direction, creating a north and a south pole of the magnet. We can increase the strength of the electromagnet by increasing the current. We can change the magnetic polarity of the electromagnet by changing the direction of the current. The principles of an electromagnet can be put to good use in a dc motor. The armature is the part of the motor that is connected to the shaft and has coils of wire around it and placed between magnets. When a voltage is applied to the ends of the coil wires a current flows and the armature is magnetized. The interaction of the armature magnetic field and the other magnetic fields creates torque which causes the armature and the shaft to rotate. As the motor speeds up, the counter electromotive force (voltage) increases in proportion to the speed. Since the electrical polarity of the counter emf is opposite to that of the applied voltage, the net voltage decreases and the current decreases and a steady state or equilibrium voltage, current and angular velocity are maintained. The relationship between angular velocity and the torque to maintain that angular velocity is portrayed as the performance curve of the motor driven system. An example of such a curve is shown on the next page. Angular Velocity, rad/s Performance Curve 64:1 25.0 20.0 15.0 10.0 5.0 0.0 0.00 w= -244T + 21.7 0.02 0.04 0.06 0.08 Torque, n-m Since power is the product T, we can plot mechanical power as a function of torque (load) and find the maximum power at a torque equal to one-half the “stall” torque, i.e. one-half the torque at which the angular velocity drops to zero. We want to design and build our system to achieve maximum output power in order to maximize the performance of the system. Mechanical Power Curve Power, W 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 -0.2 0 0.02 0.04 0.06 Torque, N.m 0.08 0.1