* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download the shoulder
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
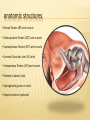
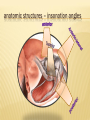
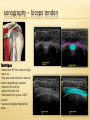
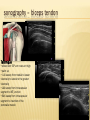
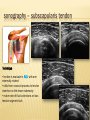
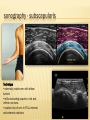
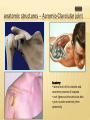
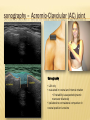
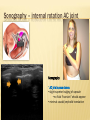
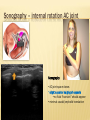
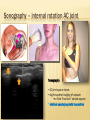
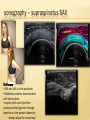
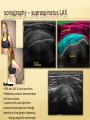
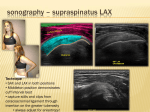
Patrick R Meyers, BS, RDMS, RVT, RDCS Musculoskeletal Ultrasound of SE Wisconsin, LLC the shoulder what’s included • palpable landmarks • anterior, anteriolateral, superior & posterior views • anatomic relationships • dynamic maneuvers • patient positions • bone landmarks • ipsilateral to contralateral comparisons • manual techniques to adjust for anisotropy anatomic structures • Biceps Tendon (BT) and muscle • Subscapularis Tendon (SCT) and muscle • Supraspinatus Tendon (SST) and muscle • Acromio-Clavciular Joint (AC Joint) • Infraspinatus Tendon (IST) and muscle • Posterior Labrum (Lab) • Spinoglenoid groove or notch • Superior Labrum (optional) anatomic structures – insonation angles anterior anatomic structures Biceps Tendon • attached to the supraglenoid tubercle • lies between the greater and lesser tuberosity of the humeral head • covered by transverse humeral ligament at tuberosities Sonography • tendon is evaluate in SAX & LAX • follow biceps tendon from the intracapsular segment through the insertion of the pectoralis on humerus • clip in SAX from intracapsular segment through pectoralis insertion • clip from medial to lesser tuberosity through bicipital groove through greater tuberosity sonography – biceps tendon Technique • elbow bent 900 arm rests on thigh • palm up • may use some internal or external rotation depending on patient • stills of LAX with clip • stills in SAX with clip • LAX sweep from groove to M/T junction • use power Doppler hypoechoic areas sonography – biceps tendon Technique • elbow bent 900 arm rests on thigh • palm up • LAX sweep from medial to lesser tuberosity to lateral to the greater tuberosity • LAX sweep from intracapsular segment to MT junction • SAX sweep from intracapsular segment to insertion of the pectoralis muscle anatomic structures - subscapularis tendon Subscapularis Tendon/Muscle • tendon insertion on lesser tuberosity of humerus and anterior scapula proximally • bone landmarks lesser tuberosity and coracoid process of scapula Sonography • tendon is evaluate in SAX & LAX • dynamic maneuver with elbow tucked and arm externally rotated • evaluate tendon, bursa and lesser tuberosity slip • SAX of tendon from coracoid to tendon insertion on lesser tuberosity • LAX superior to inferior sonography – subscapularis tendon Subscapularis tendon and muscle • tendon insertion on lesser tuberosity of humerus and anterior scapula proximally • bone landmarks lesser tuberosity and coracoid process of scapula Technique • tendon is evaluate in LAX • superior, middle and inferior segment • note any loss of mass between segments sonography – subscapularis tendon Technique • tendon is evaluate in SAX with arm externally rotated • stills from coracoid process to tendon insertion on the lesser tuberosity • make note of fluid collections or loss tendon segment bulk sonography - subscapularis Technique • externally rotate arm with elbow tucked • stills evaluating superior, mid and inferior sections • capture clip of arm in FULL internal and external rotations anatomic structures – Acromio-Clavciular joint Anatomy • lateral end of the clavicle and acromion process of scapula • cart ligneous intra articular disk • joint is wider anteriorly then posteriorly sonography – Acromio-Clavciular (AC) joint Sonography • LAX only • evaluated in neutral and internal rotation • if instability is suspected dynamic maneuver bilaterally • ipsilateral to contralateral comparison in neutral position is routine Sonography – internal rotation AC joint Sonography • AC joint space closes • slight superior bulging of capsule • no fluid “fountain” should appear • minimal caudal/cephalid translation Sonography – internal rotation AC joint Sonography • AC joint space closes • slight superior bulging of capsule • no fluid “fountain” should appear • minimal caudal/cephalid translation Sonography – internal rotation AC joint Sonography • AC joint space closes • slight superior bulging of capsule • no fluid “fountain” should appear • minimal caudal/cephalid translation anatomic structures -supraspinatus Supraspinatus Tendon/Muscle • muscle arises from the supraspinatus fossa of the scapula • passes beneath the acromion and attaches to the greater tuberosity of the humerus • slides beneath the subdeltoid subacromial bursa (SDSA) • responsible for abduction of the arm Crass Sonography Crass Modified Crass Middleton • tendon is evaluate in SAX & LAX • two positions Crass and modified Crass or Middleton •SAX & LAX of tendon and muscle sweeps from M/T junction through insertion point in both Crass and Middleton position • superior margin is the coracoacromial ligament sonography – supraspinatus SAX Technique • SAX and LAX in both positions • Middleton position demonstrates cuff interval best • capture stills and clips from coracoacromial ligament through insertion on the greater tuberosity • always adjust for anisotropy! sonography – supraspinatus LAX Technique • SAX and LAX in both positions • Middleton position demonstrates cuff interval best • capture stills and clips from coracoacromial ligament through insertion on the greater tuberosity • always adjust for anisotropy! modifications to Crass position Technique • patients with rotator cuff disease have trouble with Crass position • minimal position is to get arm with dorsal hand resting on lower back