* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Kristen Kodeski, MS, RD Fitness
Fat acceptance movement wikipedia , lookup
Body fat percentage wikipedia , lookup
Adipose tissue wikipedia , lookup
Abdominal obesity wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Human nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Diet-induced obesity model wikipedia , lookup
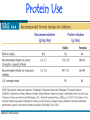
Fitness Physical Activity, Nutrients, And Body Adaptations Kristen Kodeski, MS, RD Fitness • Fitness • Sedentary • Physical activity –Exercise Copyright 2005 Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning Benefits Of Fitness •Restful sleep •Nutritional health •Optimal body composition •Optimal bone density •Resistance to colds and other infectious diseases •Low risks of some types of cancers •Strong circulation and lung function •Low risk of cardiovascular disease •Low risk of type 2 diabetes •Reduced risk of gallbladder disease in women •Low incidence and severity of anxiety and depression •Long life and high quality of life in the later years •Strong self-image Energy Balance Energy In = Energy Out weight maintenance Energy In > Energy Out Weight Gain Energy In < Energy Out Weight Loss A one-pound weight loss is equivalent to a calorie deficit of 3500 calories. Physical Activity Pyramid Developing Fitness Developing Fitness Flexibility Muscle strength and endurance Cardiorespiratory endurance Conditioning Training Overload principle Cardiorespiratory Endurance •Aerobic activity –VO2 max •Cardiorespiratory conditioning –Cardiac output •Muscle conditioning The Energy Systems Glucose Use •Diet affects glycogen storage and use • Exercise is the only way to deplete muscle glycogen • Carbohydrate is the main source of energy for high-intensity, short or intermittent duration activities – Competitive races, basketball, football, soccer, & swimming • Contributes to energy used in moderate intensity activites – Jogging, hiking, aerobic dancing, & gymnastics Glucose Use Intensity of activity affects glycogen use Lactic acid Duration of activity affects glycogen use Glucose Use •Glucose depletion –Carbohydrate loading •Glucose during activity •Glucose after activity •Training affects glycogen use Fat Use •Recommendations for endurance athletes –20% - 30% of energy intake from fat •Dietary fat vs. body fat stores Fat Use •Duration of activity affects fat use •Intensity of activity affects fat use •Training affects fat use Protein Use •Protein used in muscle building •Protein used as fuel •Diet affects protein use during activity Protein Use •Intensity and duration of activity affect protein use during activity •Training affects protein use Protein Use Vitamins And Minerals •Supplements •Vitamin E Vitamins And Minerals •Iron –Iron deficiency •Iron-deficiency anemia –Sports anemia –Iron recommendations for athletes Fluids And Electrolytes •Fluid losses via sweat •Hyperthermia –Heat stroke •Hypothermia Fluids And Electrolytes Fluids And Electrolytes •Electrolyte losses and replacement •Hyponatremia •Poor beverage choices –Caffeine –Alcohol Choosing A Diet •Water •Nutrient density •Carbohydrate •Protein Choosing A Diet Pregame meals Postgame meals Supplements •Ergogenic aids •Protein powders •Amino acid supplements Supplements •Carnitine •Chromium picolinate •Complete nutrition supplements Supplements •Creatine •Caffeine •Oxygenated water Supplements •DHEA and androstenedione •Human growth hormone = hGH What About…