* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download - SCHHS Emergency Department
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
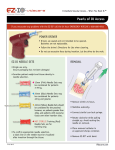
Intraosseous Access Drill (EZ-IO) Use Of Clinical Assessment Tool Practice Development CAT ID 052.01 CATs are criterion based assessment tools designed for diagnostic, formative and summative assessment applications. If a CAT is being used for summative assessment of competency it must be administered by a clinical coach, clinical educator or experienced assessor (e.g. Clinical Nurse Consultant or Nurse Practitioner). The CAT may also be used informally as a self directed learning tool or peer review tool. Successful CAT completion = 100% of criteria met. Observed Observed Performance Learning Opportunity Identified Identifies indications Describes risks/contra-indications Performs hand hygiene prior to and throughout the procedure; using a 40-60 second hand wash or 20 – 30 second 2 pump alcohol based hand rub and wears personal protective equipment (PPE) if patient on precautions or when at risk of contact with body fluids before touching the patient after touching the patient immediately before an invasive procedure immediately after an invasive procedure or potential exposure to body fluids after touching the patients surroundings Provides privacy Explains procedure to patient and patient is encouraged to raise questions Obtains consent Identifies correct site for insertion Checks for allergies if appropriate Identifies correct size EZ-IO needle: Pink – Paediatrics (3-39kg) 15mm length Blue – Adult (>40kg) 25mm length Yellow – Large Adult (>40kg with excessive tissue over insertion sites) 45mm length Collects equipment: EZ-IO Driver, appropriate EZ-IO needle, extension set, 10ml syringe, normal saline ampoule, EZ-IO stabilizing device or suitable dressing Assumes a position that facilitates safe ergonomic practice Primes extension set with 10mL normal saline Dons PPE, gloves and goggles Locates the correct target site Proximal Humerus, Proximal Fibula or Distal Fibula Cleans the insertion site using an 70% alcohol based skin preparation Assembles the EZ-IO drill and needle set Inserts EZ-IO needle by: The needle is maintained at 90° angle to the bone A constant downward pressure is maintained until a sudden decrease in resistance in the bone is observed Disconnects the drill from the needle set Removes the introducing stylet by twisting the stylet out of the needle in a counter-clockwise motion Discusses aspiration of marrow from Intraosseous (IO) for blood sampling, must be sent to Pathology and labelled as marrow aspirant Flushes IO with 10mL of Normal Saline Applies EZ-stabilizer dressing Connects EZ-IO extension tubing Describes on-going care with patient and encourages patient to raise questions Disposes of all waste Cleans and puts away all used equipment Reports and documents outcome of procedure and findings CAT ID 052.01 Page 1 of 3 Date approved: 19/05/2015 Intraosseous Access Drill (EZ-IO) Use of – Clinical Assessment Tool Assessment Result Competent Learning Opportunity Identified Assesse: Signature: Assessor: Signature Clinical Coach Educator CNC DATE: Entered into TREND Position: NP Other Plan for further learning if learning opportunity identified Indications An intraosseous device is indicated for patients who urgently require fluid or medication and have had failed or limited IV access. EZ-IO is a handheld, battery-operated device which drills the IO needle into the intraosseous space with a high-speed rotary motion. The EZ-IO can be used in both the proximal and distal tibia, as well as the humeral head. Intraosseous space: The IO space refers to the spongy, cancellous bone of the epiphysis and the medullary cavity of the diaphysis, which are connected. The vessels of the IO space connect to the central circulation by a series of longitudinal canals that contain an artery and a vein. The Volkmann’s canals connect the IO vasculature with the major arteries and veins of the central circulation. Intraosseous access device: A device placed in the IO space. Risk/Contra-indications Safe Ergonomic Practice includes positioning self, the patient and equipment to comply with best occupational health and safety practice to minimise risk to staff and patient with consideration to posture, time and force. 1. Obvious skin infection over insertion site 2. Known fracture at insertion site 3. Previous IO at the site within the past 48 hours 4. Previous orthopaedic surgery pinning/ plating at the site Anatomy or Graphics CAT ID 052.01 Page 2 of 3 Date approved: 19/05/2015 Intraosseous Access Drill (EZ-IO) Use of – Clinical Assessment Tool Figure one Figure two Figure three Figure one; Proximal humerus – approx. 1cm above the surgical neck Figure two; Proximal tibia – approx. 2cm below the patella and approx. 2cm medial to the tibial tuberosity Figure three; Distal tibia – approx. 3cm proximal to the medial malleolus Source: http://ccn.aacnjournals.org/content/31/2/76/F19.expansion.html http://www.vidacare.com/EZ-IO/Products-Needle-Sets.aspx Ongoing Care In non-emergency situations, local anaesthetic, such as 2% lignocaine, may be considered as an initial bolus injection. EZ-IO needles must be secured in situ to the skin either with the manufacturer’s dressing (preferred) or with another suitable dressing. Blood and marrow aspirate can be sent to pathology in paediatric collection tubes and labelled “Marrow Aspirant” or “Intraosseous sample”. This specimen is not suitable for use with istat. Infusions must be used in conjunction with a pressure infusion bag. Bolus fluids and medications are delivered via a three-way stopcock and 50ml syringe. Note: any bolus injection requires firm pressure to deliver via EZ-IO. The EZ-IO catheter can only stay in situ for up to 24 hours (manufacturer’s recommendation). The site should be monitored frequently for signs of erythema, swelling or evidence of extravasation. If these are noted, the device must be removed immediately. Removing the EZ-IO catheter involves disconnecting infusions, attaching a 10 ml luer-lock syringe to the catheter hub, then rotate the catheter clockwise-while pulling straight back, disposing of catheter in sharps container, and apply simple dressing. References Infusion Nurses Society,. (2009). Position Paper on Intraosseous Access Devices. Retrieved 8 September 2014, from http://www.ins1.org/files/public/4_20_09_Position_paper_Intraosseous.pdf Dolister, M., Miller, S., Borron, S., Truemper, E., Shah, M., Lanford, M., & Philbeck, T. (2013). Intraosseous vascular access is safe, effective and costs less than central venous catheters for patients in the hospital setting. The Journal Of Vascular Access, 14(3), 216-224. doi:10.5301/jva.5000130 Guthrie, K. (2014). Seizing and No Access!!!. Life in the Fast Lane. Retrieved 12 September 2014, from 2.3. http://lifeinthefastlane.com/seizing-and-no-access/ (Local Guideline or Procedure) Sunshine Coast Hospital and Health Service. (2013). Workplace Instruction: Pain Management Guidelines. Nambour: Sunshine Coast Hospital and Health Service World Health Organisation (2006). How to handwash. Document Approval/Review History Version 1 Document Custodian Nurse Educator Emergency Date of Approval 19/05/2015 Review Due 15/05/2017 Any feedback related to improving this CAT can be provided to Practice Development Team, via email [email protected]. Please ensure you reference the CAT ID in the subject line. CAT ID 052.01 Page 3 of 3 Date approved: 19/05/2015