* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SALIVARY GLANDS
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
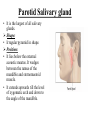
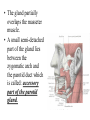
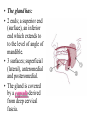
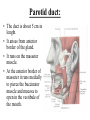
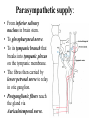
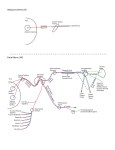
Parotid Salivary gland • It is the largest of all salivary glands. Shape: • Irregular pyramid in shape. Position: • It lies below the external acoustic meatus. It wedges between the ramus of the mandible and sternomastoid muscle. • It extends upwards till the level of zygomatic arch and down to the angle of the mandible. • The gland partially overlaps the masseter muscle. • A small semi-detached part of the gland lies between the zygomatic arch and the parotid duct which is called: accessory part of the parotid gland. • The gland has: • 2 ends; a superior end (surface), an inferior end which extends to to the level of angle of mandible. • 3 surfaces; superficial (lateral), anteromedial and posteromedial. • The gland is covered by a capsule derived from deep cervical fascia. Main structures within the substance of the gland: • From superficial to deep, they are: 1. Facial nerve and branches. 2. Retromandibular vein and its two divisions, maxillary vein, superficial temporal vein.. 3. External carotid artery and its two terminal branches. Facial nerve • It is the most superficial structure. • It enters the gland through its posteromedial surface. • It breaks within the gland into terminal branches that leave it through; upper end, lower end and anteromedial surface. • These terminal branches are 5; Temporal, zygomatic, buccal, marginal mandibular and cervical. Other structures within the gland: 1. Auriculotemporal nerve. 2. Posterior auricular artery. 3. Preauricular lymph nodes. Parotid duct: • The duct is about 5 cm in length. • It arises from anterior border of the gland. • It runs on the masseter muscle. • At the anterior border of masseter it runs medially to pierce the buccinator muscle and mucosa to open in the vestibule of the mouth. • Opening of parotid duct: It opens in the vestibule of the mouth opposite the upper second molar tooth. • Surface anatomy: The duct is represented by the middle 1/3 of the line between a point on the lower border of tragus of ear and a point midway between the ala of nose and red margin of the upper lip. Blood supply: • Arterial: External carotid artery and its terminal branches within the gland. • Venous: Into the retromandibular vein. • Lymph drainage: Into Preauricular (parotid), superficial cervical and deep cervical lymph nodes. Nerve supply: • Sensory supply: From Auriculotemporal nerve. • Sympathetic supply: From the plexus around external carotid artery. • Parasympathetic supply: Otic ganglion. Parasympathetic supply: • From inferior salivary nucleus in brain stem. • To glosspharyneal nerve. • To its tympanic branch that breaks into tympanic plexus on the tympanic membrane. • The fibres then carried by lesser petrosal nerve to relay in otic ganglion. • Postganglionic fibers reach the gland via Auriculotemporal nerve.