* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrine Changes in Pregnancy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
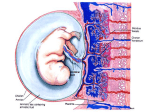
12-Mar-17 PLACENTA – Endocrine Functions Dr. Waqas Hameed • During pregnancy a woman’s body undergoes a variety of changes to prepare for the growth, nourishment, and birth of a child. • Health of developing fetus - closely tied to that of the mother PREGNANCY contd. • Pregnancy changes a woman’s normal hormone patterns • One of the first signs of pregnancy is a MISSED MENSTRUAL PERIOD 1 12-Mar-17 Maternal needs: Safe environment for the fetus Adequate nutrition for the fetus Maternal changes: ↑ in maternal hormones Production of new hormones for maternalfetal-placental unit Adequate environment for growth & Polypeptide hormones development of fetus Steroid hormones Disposal of fetal waste products Placenta – an endocrine organ Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin Estrogens Progesterone Human Chorionic Somatomammotropin ↑ in production of specific binding proteins by the liver Human Chorionic Gonadotropin ( hCG ) • From syncitial trophoblast cells • Measured in blood after 8 – 9 days of ovulation / fertilization ( shortly after implantation of blastocyst) 2 12-Mar-17 • Detectable in urine • Basis of pregnancy test • Morning Sickness hCG hCG contd. contd. hCG hCG contd. Prevents INVOLUTION of Corpus Luteum Causes Corpus Luteum to increase secretion of estrogen & progesterone Effect of hCG on Fetal Testis contd. Regulates development of fetal testes Stimulates Interstitial cells Results in increased testosterone secretion Causes fetus to grow male sex organs 3 12-Mar-17 ESTROGEN From Syncitial Trophoblast cells Towards end of pregnancy – Estrogen levels are 30 times the normal levels Estrogen FUNCTIONS contd. PROGESTERONE Enlargement of mother’s uterus Enlargement of mother’s breast & growth EARLY PREGNANCY - from Corpus Luteum of breast ductal structure Enlargement of mother’s female external genitalia Relaxes the pelvic ligaments LATER ON - tremendous quantities from palcenta - upto 10 fold increase 4 12-Mar-17 Functions of Progesterone Functions of Progesterone Development of Decidual cells in uterine contd. Helps estrogen to prepare mother’s breast endometrium – nutririon of early embryo ↓’s uterine contractions – prevents for lactation spontaneous abortion Inhibits prostaglandin formation ↑’s secretion of Fallopian tubes & Uterus Inhibits T-lymphocyte cell mediated – to provide nutritive matter for Morula rejection (prevents placental rejection) & Blastocyst 5 12-Mar-17 Human Chorionic Somatomammotropin From 5th week of pregnancy Secretion directly proportional to weight of placenta Chemically similar to Growth Hormone Weak actions similar to Growth Hormone Human Chorionic Somatomammotropin contd. Major effect on maternal glucose - providing adequate nutrition for fetus: Maternal Pituitary Changes Enlarges 2-3 fold and increases in vascularity Hyperplasia of lactotropes Stimulates insulin release Increase in prolactin secretion – increased Stimulates lipolysis & free fatty acid production and release estrogens stimulate prolactin release, but inhibit may lead to development of maternal insulin resistance – thought to be responsible for gestational diabetes lactation until after birth LH, FSH, & GH levels are low ACTH appears normal 6 12-Mar-17 Maternal Thyroid Changes Maternal Adrenal Changes Enlarges in 1st trimester ↑ Cortisol Total T4 & T3 increases significantly ↑ in binding globulins Increase in thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG) ↑ in production of free cortisol due to estrogens No signs of hypercortisolism Free T4 and Free T3 do not change Diurnal rhythm doesn’t change T4 and T3 do not cross the placenta Maternal Calcium Changes RELAXIN The mother must provide enough calcium for fetal bone formation • Ovary – Corpus Luteum Increased intake of calcium • Placental tissue Increased PTH levels Increased 1,25(OH)2D – maternal kidney responsible for production – placenta also produces & has specific receptors for 1,25(OH)2D 7 12-Mar-17 Maternal Body Response • Uterus – ↑ 50 gm to 1100 gm • Weight Gain – Average – 24 pounds • • • • • Fetus – 7 pounds Uterus – 2 pounds Breasts – 2 pounds Blood & ECF – 2 pounds Fat accumulation – 2 pounds Metabolism in Pregnancy • BMR – 15%↑ later half of pregnancy Nutrition IRON • Fetus requires 375 mg iron • Mother needs 600 mg iron • Vitamins • Upto 75 pounds ↑ possible !!! Blood Volume Respiration • At term – 30% above normal • 20% more oxygen requirement • ↑ minute ventilation by 50% • Progesterone - ↑ sensitivity of resp. centre Urinary System • Reabsobrptive capacity for sodium, chloride & water - ↑ by 50% • GFR - ↑ by 50% 8 12-Mar-17 PREECLAMPSIA & ECLAMPSIA • 5% women - ↑ blood pressure • Protein leakage in urine • Excess salt & water retention • Weight gain • Edema ECLAMPSIA • • • • • • Extreme degree of Preeclampsia Vascular Spasm Seizures Coma Death Termination of pregnancy – Cesarean section • Hypertension • Insufficient bld supply to placenta Exercise Jazak Allah 9