* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download APHG - Chapter 10 - Madison County Schools
Economic planning wikipedia , lookup
Criticisms of socialism wikipedia , lookup
Economic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Production for use wikipedia , lookup
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
World-systems theory wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
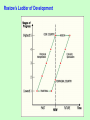
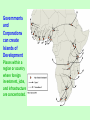
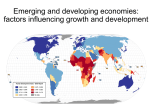
Development Chapter 10 GDP: Measure of Development Development • Commodity Chain: series of links connecting places of production, distribution, and consumption in a world market. • How does the location on the chain affect the wealth of the people involved? Commodity Chain Assignment • This assignment asks you to do some detective work to investigate the sources of the products you consume. • You’ll be asked to choose a specific product and trace it from source to consumption. This type of project is called “commodity chain analysis,” since it starts with a product (a commodity) and uncovers the chain of events, people, and materials that produced it. Stages of a Commodity Chain •When researching your commodity the stages of the commodity chain to focus on are (note: some commodities will : •Design and technology •Raw inputs and parts •Manufacturing/Production •Sales, distribution •Marketing Example: The iPod • When looking at each stage of the iPod commodity chain consider: – Design and technology – who made it, where, what are the wages/labor conditions, who owns the technology (patent)? – Raw inputs and parts – what is needed to make the iPod – metal, plastic, how many separate parts? – Manufacturing/Production – who assembles the iPod, where, what are the wages/labor conditions? – Sales, distribution – how does the iPod get to the stores it is sold in, who sells the product, who buys it? – Marketing – how is the iPod marketed, to whom is it marketed, how much are those in the advertisements paid? Choose Your Commodity • Some sample ideas: – Starbucks Coffee – iPod – Nike tennis shoes – Clothing – Prom Dress Key Question: How do you Define and Measure Development? Measuring Development Gross National Product (GNP) Measure of the total value of the officially recorded goods and services produced by the citizens and corporations of a country in a given year. Includes things produced inside and outside a country’s territory. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Measure of the total value of the officially recorded goods and services produced by the citizens and corporations of a country in a given year. Gross National Income (GNI) Measure of the monetary worth of what is produced within a country plus income received from investments outside the country. ** Most common measurement used today. Issues with Measuring Economic Development • All measurements count the: – Formal Economy – the legal economy that governments tax and monitor. • All measurements do not count the: – Informal Economy – the illegal or uncounted economy that governments do not tax or keep track of. Other Ways of Measuring Development • Occupational Structure of the Labor Force • Productivity per Worker • Transportation and Communications Facilities per Person • Dependency Ratio Differences in Communications Connectivity Around the World Dependency Ratio by Country, 2005 A measure of the number of people under the age of 15 and over the age of 65 that depends on each working-age adult. What does Development Mean? • Development implies “progress” – Progress in what? – Do all cultures view development the same way? – Do all cultures “value” the same kinds of development? Development Models Modernization Model Walt Rostow’s model assumes all countries follow a similar path to development or modernization, advancing through five stages of development, climbing a ladder of development. - traditional - preconditions of takeoff - takeoff - drive to maturity - high mass consumption Rostow’s Ladder of Development Is the idea of economic development inherently Western? If the West (North America and Europe) were not encouraging the “developing world” to “develop,” how would people in the regions of the “developing world” think about their own economies? Key Question: How does Geography affect Development? Dependency Theory The political and economic relationships between countries and regions of the world control and limit the economic development possibilities of poorer areas. -- Economic structures make poorer countries dependent on wealthier countries. -- Little hope for economic prosperity in poorer countries. Dollarization – Abandoning the local currency of a country and adopting the dollar as the local currency. El Salvador went through dollarization in 2001 Geography and Context * Cannot simply study what is produced. * Need to examine how and where it is produced and where the production is on the commodity chain. * Examine commodity chains and look for the kinds of economic processes operating at each link in the chain. Commodity Chain Series of links connecting the many places of production and distribution and resulting in a commodity that is then exchanged on the world market. How processes operated at each step in the commodity chain that produced the dolomite stone for this fireplace? Three Tier Structure Core Periphery Processes that incorporate higher levels of education, higher salaries, and more technology * Generate more wealth in the world economy Processes that incorporate lower levels of education, lower salaries, and less technology * Generate less wealth in the world economy Semi-periphery Places where core and periphery processes are both occurring. Places that are exploited by the core but then exploit the periphery. * Serves as a buffer between core and periphery Compare and contrast Rostow’s ladder of development with Wallerstein’s three-tier structure of the world economy. Key Question: What are the Barriers to and the Costs of Economic Development? Barriers to Economic Development • Low Levels of Social Welfare – Trafficking • Foreign Debt – Structural adjustment loans • Political Instability • Widespread Disease – Malaria Foreign Debt Obligations Total interest payments compared to the export of goods and services. Foreign Debt Obligations Foreign Debt and Economic Collapse in Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2001 Widespread Disease • Malaria kills 150,000 children in the global periphery each month. Tamolo, India This baby sleeps under a mosquito net distributed to villagers by UNICEF workers. Global Distribution of Malaria Transmission Risk Costs of Economic Development • Industrialization – Export Processing Zones (EPZs), maquiladoras, and special economic zones (SEZs). • Agriculture – desertification • Tourism Export Processing Zones Areas Threatened by Desertification Think of a trip you have made to a poorer area of the country or a poorer region of the world. Describe how your experience in the place as a tourist was fundamentally different from the everyday lives of the people who live in the place. Key Question: Why do Countries experience Uneven Development within the State? How Government Policies Affect Development • Governments – get involved in world markets – price commodities – affect whether core processes produce wealth – shape laws to affect production – enter international organizations that affect trade – focus foreign investment in certain places – support large-scale projects Governments and Corporations can create Islands of Development Places within a region or country where foreign investment, jobs, and infrastructure are concentrated. Government-created Island of Development Malaysian government built a new, ultramodern capital at Putrjaya to symbolize the country’s rapid economic growth. Corporate-created Island of Development The global oil industry has created the entire city of Port Gentile, Gabon to extract Gabon’s oil resources. Nongovernmental Organizations (NGOs) entities that operate independent of state and local governments, typically, NGOs are non-profit organizations. Each NGO has its own focus/set of goals. Microcredit program: loans given to poor people, particularly women, to encourage development of small businesses. How do actors in nongovernmental organizations (NGOs) mobilize political change? An Indonesian woman (on left) who migrated to Saudi Arabia as a guest worker talks with an Indonesian activist (on right) who works to defend migrant workers’ rights. Take an item of clothing out of your closet, and using the Internet, try to trace the commodity chain of production. What steps did the item go through before reaching you? Consider whether core or peripheral processes were operating at each step and consider the roles governments and international political regimes played along each step.