* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 17 sections 1,2,4 and 5 Notes
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
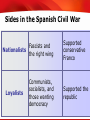
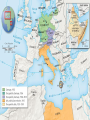
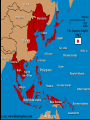
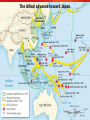
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Lead-Up to World War II Chapter 17 section 1 TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Today TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Objectives • Analyze the threat to world peace posed by dictators in the 1930s and how the Western democracies responded. • Describe how the Spanish Civil War was a “dress rehearsal” for World War II. • Summarize the ways in which continuing Nazi aggression led Europe to war. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Terms and People • appeasement – giving in to the demands of an aggressor to keep peace • pacifism – opposition to all war • Neutrality Acts – a group of laws enacted by the United States to avoid involvement in a European conflict • Axis powers – Germany, Italy, and Japan TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Terms and People (continued) • Francisco Franco – a conservative Spanish general supported by Fascists and Nationalists in the Spanish Civil War; later became dictator • Anschluss – union of Austria and Germany • Sudetenland • Nazi-Soviet – a region of Czechoslovakia Pact – a nonaggression pact uniting Germany and the Soviet Union TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. What events unfolded between Chamberlain’s declaration of “peace for our time” and the outbreak of a world war? After the horrors of World War I, Western democracies tried to preserve peace. However, Germany, Italy, and Japan were preparing to build new empires, and the world was headed to war again. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Dictators took aggressive action in the 1930s. Japan Military leaders Germany Hitler Italy Overran Manchuria and much of eastern China Rebuilt the military and invaded the Rhineland Invaded and Mussolini conquered Ethiopia TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Western democracies denounced these invasions but chose a policy of appeasement. • France could not take on Hitler without British support, and Britain did not want to confront him. Both countries viewed Hitler’s fascism as a defense against the spread of Soviet communism. • The Great Depression exhausted Western nations. • Disillusion with the previous war had led to widespread pacifism. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. What was the US stance? • In the United States, Congress passed a series of Neutrality Acts aimed at avoiding involvement in a European war. • Americans did not want involved in another European conflict TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. By the mid-1930s, the antidemocratic aggressive powers formed an alliance. • Italy, Germany, and Japan became the Axis powers. • The Rome-BerlinTokyo Axis agreed to fight Soviet communism. • They also pledged not to interfere with one another’s plans for territorial expansion. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. A civil war in Spain increased tensions. •In 1931, a rebellion ousted the king of Spain. •Reformers created a republic with a liberal constitution, and took land and privileges from the Church and old ruling classes. •Conservative general Francisco Franco launched a revolt against the republic in 1936. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Sides in the Spanish Civil War Fascists and Nationalists the right wing Loyalists Communists, socialists, and those wanting democracy Supported conservative Franco Supported the republic TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The Spanish Civil War became a “dress rehearsal” for a wider European war. • Hitler and Mussolini sent arms and forces to support Franco, while the Soviet Union sent soldiers to help the Loyalists. • Nazi leaders used the war to test new bombers. • More than 500,000 people died in the struggle. • By 1939, Franco had won. He created a fascist dictatorship similar to those of Germany and Italy. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Meanwhile, Hitler took aggressive steps to bring all German-speaking people into the Third Reich. • One of Hitler’s goals was the Anschluss, or union of Austria and Germany. • In 1938, German troops entered Austria. • Although Hitler’s annexation of Austria violated the Treaty of Versailles, the Western democracies took no action. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Hitler next threatened to annex the Sudetenland. Britain and France protested, but they were unwilling to go to war. At the Munich Conference in 1938, British and French leaders gave in to Hitler’s demands. Hitler promised that he had no further plans to expand. British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain announced that they had achieved “peace for our time.” TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Hitler and British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlin TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Europe rapidly plunged toward war. • After gaining the Sudetenland, Hitler broke his promises and took the rest of Czechoslovakia. • The democracies accepted that appeasement had failed. They pledged to protect Poland. • In August 1939, Hitler and Stalin announced the Nazi-Soviet Pact. This was a shaky alliance, since neither Hitler nor Stalin trusted the other. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. On September 1, 1939, a week after the Nazi-Soviet Pact, German forces invaded Poland. Two days later, Britain and France declared war on Germany. World War II had begun. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Map Of Europe Directions: • • Shade the territories Hitler took over to break the Treaty of Versailles-Anschluss, Rhineland, and the Sudetenland Shade the area that Stalin took over by 1939 TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Aggression in Europe and Africa to September 1939 TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. World War II to 1941 and the Holocaust Chapter 17 Section 2 TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Objectives •Describe how the Axis powers came to control much of Europe, but failed to conquer Britain. •Summarize Germany’s invasion of the Soviet Union. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Terms and People • blitzkrieg – “lightning war” using improved tanks and airpower • Luftwaffe – German air force • Dunkirk – site of British troops stranded in France, and their rescue by sea • Vichy – location in France of Germany’s “puppet state” • General Erwin Rommel – German general known as the “Desert Fox” TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Terms and People (continued) • concentration camps – Nazi detention and killing centers for civilians considered enemies of the state • Holocaust – the systematic genocide of about six million European Jews by the Nazis during World War II • Lend-Lease Act – law allowing FDR to sell or lend war materials to those who were fighting TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Which regions were attacked and occupied by the Axis powers, and what was life like under their occupation? Diplomacy and compromise did not bring peace with Nazi Germany, Fascist Italy, or imperial Japan. The Axis powers advanced, attacking countries in Eastern and Western Europe. In the Pacific, Japan captured countries and colonies on the islands and the mainland of Asia. The Axis powers brought misery to the peoples they conquered. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Hitler used the tactic of blitzkrieg, or “lightning war,” to overrun much of Europe, starting with Poland. The German air force, the Luftwaffe, bombed airfields, factories, and cities in Poland. Then, fastmoving tanks and troops pushed their way in from the west. Meanwhile, Stalin’s forces invaded Poland from the east. Within a month, Poland ceased to exist. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Hitler waited out the winter. Then, in the spring of 1940, German forces overran Norway, Denmark, the Netherlands, and Belgium. Next, German troops poured into France, trapping the retreating British forces at Dunkirk. British vessels crossed the English Channel and ferried more than 300,000 British troops to safety. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Dunkirk http://www.rania.co.uk/dunkirk/html/images.htm http://www.bbc.co.uk/history/interactive/animations/wwtwo_map_fall_franc e/index_embed.shtml Interactive map link TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Germany continued to attack Western Europe. • German forces headed to Paris. With Italy attacking from the south, France was forced to surrender in June 1940. • Germany occupied northern France and set up a puppet government at Vichy in southern France. • Next Hitler set his sights on Britain, calling this planned invasion “Operation Sea Lion.” TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Quote from a Londoner during the Battle of Britain “After an explosion of a nearby bomb, you could actually feel your eyeballs being sucked out. I was holding my eyes to try and stop them going. And the suction was so vast, it ripped my shirt away, and ripped by trousers. Then I couldn’t get my breath, the smoke was like acid and everything around me was black and yellow” - quoted in London at War TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Churchill’s comments on the Battle of Britain “We shall defend our island, whatever the cost may be…We shall never surrender.” “Never in the field of human conflict was so much owed by so many to so few.” -Winston Churchill TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. London did not break under the Nazi blitz. •Citizens carried on with their daily lives, seeking protection in shelters and subways. •The Luftwaffe could not gain superiority over Britain. Operation Sea Lion was a failure. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Despite his failure to conquer Britain, Hitler seemed unstoppable. • German armies under the command of General Erwin Rommel pushed into North Africa. • In addition, Axis armies invaded Greece, Yugoslavia, Bulgaria, and Hungary. • By 1941, the Axis powers or their allies controlled most of Europe. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Battles in Northern Africa-Desert Warfare Erwin RommelDesert Fox TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Nazis Displaying the flag on the Acropolis TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. In June 1941, Hitler broke the NaziSoviet Pact when he attacked the Soviet Union. The attack stalled during the winter when thousands of unprepared Germans froze to death. Leningrad withstood a two-and-ahalf-year siege. Stalin made an agreement to work with Britain. Invasion of the USSR TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Operation Barbarossa –June 22, 1941 Soviets are caught by surprise even though they had the largest army in the world Germans pushed in 500 miles using scorched earth policy Leningrad German cut off the city and surrounded it Hitler was ready to starve the 2.5 million people living there Nazis took out warehouses of food Nazis separating women and Nearly one million people children after invading the died but the Russians Soviet Union maintained control http://www.ushmm.org/wlc/en/media_fi.php?ModuleId =10005164&MediaId=250 TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Invasion of USSR cont… Moscow Hitler focused on Moscow since Leningrad was not falling The Nazis failed to move as quickly as planned and winter set in Nazi troops were not equipped Hitler sent the order “No retreat!” TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Debate: What Circumstances Justify War? Should America enter WWII? What is the American position toward WWII by 1941? •Neutrality Acts 1935 •Cash and Carry •Lend-Lease Act •Atlantic Charter •German U-boats firing on US cargo ships •Shoot on sight “No man can tame a tiger into a kitten by stroking it” - FDR TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Interactive map of Hitler’s takeover of Europe http://www.ushmm.org/wlc/en/media_nm.php?ModuleId=100 05143&MediaId=7827 Japan and Germany set out to build a “new order” in the lands they occupied. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. • Japanese troops seized crops, destroyed cities, and brutally treated local Chinese, Filipinos, and other conquered people. • The Nazis sent millions of Jews and political opponents to concentration camps. • The Nazis also targeted other groups they considered “inferior,” including Gypsies, Slavs, homosexuals, the disabled, and the mentally ill. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. By 1941, Hitler had devised plans for his “Final Solution”—the extermination of all Jews in Europe. At special death camps in Poland, some six million Jewish men, TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The scale and savagery of the Holocaust are unequaled in history. Young survivors of Auschwitz, the largest Nazi death camp. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The United States declared neutrality, but Roosevelt wanted to be prepared for war. • In August 1941, he met secretly with British Prime Minister Winston Churchill to create the Atlantic Charter. Its goal was to destroy the Nazi reign. • Roosevelt persuaded Congress to pass the Lend-Lease Act, allowing the United States to sell or lend supplies to Britain. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. At the same time of Lend-lease Act… • At the same time, tensions between the United States and Japan grew after the United States banned sale of war materials to Japan. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Debate: What Circumstances Justify War? Should America enter WWII? What is the American position toward WWII by 1941? •Neutrality Acts 1935 •Cash and Carry •Lend-Lease Act •Atlantic Charter •German U-boats firing on US cargo ships •Shoot on sight “No man can tame a tiger into a kitten by stroking it” - FDR TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. In a sneak attack on December 7, 1941, Japanese airplanes bombed the American fleet docked at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. The next day, President Roosevelt asked Congress to declare war on Japan. On December 11, Germany and Italy declared war on the United States. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The Attack on Pearl Harbor On the morning of December 7, 1941, planes and midget submarines of the Imperial Japanese Navy issued a surprise attack on the U.S. at Pearl Harbor, the largest U.S. naval base in the Pacific At 6:00 a.m. on December 7th the six Japanese carriers launched a first wave of 181 planes composed of torpedo bombers, dive-bombers, horizontal bombers and fighters The Japanese hit American ships and military installations at 7:53 a.m. They attacked military airfields at the same time they hit the fleet anchored in Pearl Harbor TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Results Overall, 21 ships (8 battleships) of the U.S. Pacific fleet and more than 300 aircraft damaged or destroyed 2,403 Americans killed; 1,178 wounded Battle was particularly bad because the U.S. did not anticipate an aerial attack •Pearl Harbor was too shallow for conventional torpedoes to be dropped (they would bottom out); however, Japanese modified the tail to allow them to be dropped into shallower water •Japan seen as too far away to launch full-scale attack •Racism played a role – Japanese seen as not strong enough / question of vision from aircrafts Focused instead on potential sabotage •To guard planes and ships against sabotage, the U.S. put all of their planes and ships together so it would be easier to guard them TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Pearl Harbor Invasion U.S. Ships at Pearl Harbor TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor brought the United States into World War II. As the United States mobilized for war, Japan expanded deeper into Asia. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Japan’s PACIFIC Campaign Japan had conquered much of southeast Asia including Hong Kong (British colony), Burma, Thailand, the Dutch East Indies, Guam, Solomon Islands, Wake Island, and most of China Isoroku Yamamoto declared Hawaii “a dagger pointed at Japan’s throat” Pearl Harbor attacked December 7, 1941 “A date which will live in infamy.” -FDR TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Anagrams Drink UK Flat brain to bite TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Anagrams Biker Glitz Baboon or a Star Praise Addy TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The Allies turn the tide in World War II Chapter 17 Section 3 If you were the Allies where would you begin the attack on Hitler? TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Objectives • Understand how nations devoted all of their resources to fighting WWII • Explain how Allied victories began to push back the Axis powers • Describe D-day and the Allied advance toward Germany. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Terms and People • V-E Day – the day the Allies achieved victory in Europe, May 8, 1945 • Bataan Death March – 65-mile march suffered by American and Filipino prisoners of the Japanese • Douglas MacArthur – American general who led U.S. forces in the battles to defeat Japan • island-hopping – the act of recapturing some Japanese-held islands while bypassing others TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Terms and People (continued) • kamikaze – Japanese pilot who undertook a suicide mission • Manhattan Project – code name for a collaboration of Allied scientists who raced to test the first atomic bomb • Hiroshima – city in Japan where the first atomic bomb was dropped in August 1945 • Nagasaki – city in Japan where the second atomic bomb was dropped in August 1945 TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. How did the Allies finally defeat the Axis powers? By 1945, the war in Europe was nearing its end. Germany was being attacked from east and west, and Axis armies were surrendering. In the Pacific, a series of bloody battles continued on the islands as Allied military leaders planned a land invasion of Japan. World War II finally ended when the United States dropped atomic bombs on two Japanese cities. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. In the spring of 1945, the Nazis were surrounded and defeated. • From the west the Allies surged into Germany, and from the east Soviet troops closed in on Berlin. • In Italy, guerrillas captured and executed Mussolini. Hitler committed suicide. The Allies proclaimed May 8, 1945, V-E Day. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. There were several reasons why the mighty Axis powers fell to the Allies. • Germany’s geographic location left it open to invasion from all sides. • Hitler made some poor military decisions. • The Soviet army proved far stronger than expected. • The United States had an enormous capacity for industrial production. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The Allied advance toward Japan TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The Allies could now focus on defeating Japan. Until mid-1942, Japan had been undefeated in the Pacific. They gained control of the Philippines in May 1942 and forced U.S. and Filipino soldiers on the Bataan Death March. However, after the battles of Midway and the Coral Sea, the United States took the offensive in the Pacific. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Douglas Mac Arthur TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. In the summer of 1942, U.S. Marines defeated the Japanese at Guadalcanal. Led by General Douglas MacArthur, they began an island-hopping strategy to move north toward Japan. As the Allies poured all of their resources into defeating Japan, bloody battles ensued. Kamikaze pilots undertook suicide missions, crashing their planes into American warships. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Interactive map of battle in the pacific http://www.eduplace.com/kids/socsci/books/applications/ima ps/maps/g5s_u8/ TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Doolittle’s Raid April 18, 1942—Lt. Col. James Doolittle leads raid on Tokyo / Japanese cities The Doolittle Raid was the first air raid by the United States to strike the Japanese islands during World War II Hitting Japan lifted America’s spirits The Japanese realized that they were not invincible TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The Battle of Midway TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Meanwhile, Allied scientists offered another way to end the war. • They worked on splitting the atom to create a new kind of bomb. • In July 1945, the Manhattan Project successfully tested the first atomic bomb in New Mexico. • Harry Truman, who had become president after the death of Roosevelt, realized that it was a terrible new force for destruction. Nevertheless, he decided to use the new weapon against Japan. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Iwo Jima Mt. Suribachi was one of the focal points of Japanese defense of the island of Iwo Jima Raising the Flag at Iwo Jima TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The Battle for Okinawa April 1945 U.S. Marines invade Okinawa Largest landing force in Pacific history The Japanese unleashed 1,900 Kamikaze attacks sinking 30 ships and killing 5,000 seamen April–June: 7,600 U.S. troops, 110,000 Japanese die •Bloodiest of the Pacific War •U.S. secures island TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Allied leaders warned Japan to surrender or face destruction. Japan ignored the warning. On August 6, 1945, U.S. planes dropped the first atomic bomb on Hiroshima, instantly killing more than 70,000 people. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. August 8: The Soviet Union invaded Manchuria. The Japanese did not respond. August 9: The United States dropped a second atomic bomb on Nagasaki. This time, more than 40,000 people were killed. August 10: Emperor Hirohito intervened and forced the government to surrender. September 2, 1945: A formal peace treaty was signed. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. V-J Day Hirohito surrendered August 14. Formal surrender was signed on the deck of the U.S.S. Missouri in Tokyo Bay Sept,2, 1945. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The Occupation of Japan • MacArthur commands U.S. occupation forces in Japan for seven years • International Military Tribunal for the Far East –over 1,100 Japanese tried and sentenced •Seven, including Prime Minister Hideki Tojo, sentenced to death • MacArthur reshapes Japan’s economy (free-market) • Additionally, he introduced a liberal constitution that to this day is called the MacArthur Constitution •Free elections •Women’s suffrage •Basic freedoms TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Aftermath of World War II TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Objectives • Describe the issues faced by the Allies after World War II ended. • Summarize the organization of the United Nations. • Analyze how new conflicts developed among the former Allies after World War II. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Terms and People • Nuremberg – city in Germany where Nazi war crimes trials were held • United Nations (UN) – the body of nations formed to promote world peace • Cold War – state of tension and hostility between the United States and its allies and the Soviet Union and its allies; rarely resulted in direct armed conflict • Truman Doctrine – the policy of limiting communism to the areas already under Soviet control TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Terms and People (continued) • Marshall Plan – massive aid package that funneled food and economic assistance to Europe to help with rebuilding after World War II • North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) – a military alliance among several North Atlantic states to safeguard them from the presumed threat of the Soviet Union’s communist bloc • Warsaw Pact – the Soviet Union’s military alliance with seven satellite nations in Eastern Europe TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. What issues arose in the aftermath of World War II and how did new tensions develop? As many as 50 million people had been killed in World War II. After it ended, the Allies faced difficult decisions about the future. The United Nations was formed as a peacekeeping and humanitarian group. The U.S. Marshall Plan offered aid in rebuilding Europe. But the Soviet Union and the West quickly developed into worldwide rivals—the beginning of the Cold War. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Estimated Casualties of World War II Military Dead Military Wounded Civilian Dead 264,000 213,000 1,310,000 7,500,000 277,000 400,000 1,753,000 14,012,000 93,000 350,000 1,000,000 15,000,000 292,000 672,000 6,000 3,500,000 242,000 1,300,000 5,000,000 66,000 4,000,000 780,000 153,000 672,000 Allies Britain France China Soviet Union United States Axis Powers Germany Italy Japan TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. In 1945, Germany, Japan, China, the Soviet Union, and other countries were in ruins. • Cities, factories, harbors, bridges, and railroads were destroyed. • More than twenty million refugees wandered through Europe. • Hunger, disease, and mental illness were rampant. The Allies needed to help these devastated countries. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. After the war, the horrors committed by the Axis powers became apparent to the world. • The full extent of the inhumanity of the Holocaust was revealed. • At the Nuremberg trials, a number of Nazi leaders were tried for war crimes and sentenced to death. Similar trials were held in Japan. • The Allies built new democratic governments in Germany and Japan to promote tolerance and peace. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The United Nations was another attempt to promote peace. • In April 1945, delegates from 50 nations met to form a United Nations charter. • Each nation had one vote. However, the five permanent members of the Security Council—the United States, the Soviet Union, Great Britain, France, and China—could veto any decision. • The UN was given the authority to back up its resolutions with economic sanctions or send a peacekeeping military force. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Plans for world peace did not go smoothly as conflicts developed between the former Allies. The United States and Britain wanted Stalin to honor his promise to hold free elections in Soviet-occupied Eastern Europe. Stalin ignored his promise. He wanted to spread communism and make Eastern Europe a buffer against Germany. Conflicting ideologies and mutual distrust soon led to the Cold War. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. By 1948, pro-Soviet communist governments were ruling in Eastern Europe, backed by the Red Army. New conflicts developed outside of Eastern Europe. Stalin was menacing Greece, and also Turkey in the Dardanelles. President Harry Truman set forth the Truman Doctrine. This policy said that communism should be limited to the areas already under Soviet control. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The United States helped relieve postwar hunger and poverty in Western Europe. • The Marshall Plan provided food and economic assistance to decimated countries. • Truman hoped the Marshall Plan would strengthen democratic governments. • Stalin refused the aid and forbade Eastern European countries to accept aid. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Germany became a focus of the Cold War. • Western Allies united their zones of control and extended the Marshall Plan. • The Soviets were furious at Western efforts to rebuild the German economy. • Stalin held on to East Germany. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Hungry Berlin residents greet planes delivering supplies during the Berlin Airlift. • In an effort to drive Western powers out of Berlin, Stalin blocked delivery of supplies to the parts of the city they controlled in June 1948. • The United States and Britain organized the Berlin Airlift to drop food and supplies into West Berlin. • After more than a year, Stalin was forced to end the blockade. TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. As tensions grew, two competing military alliances took shape. Twelve countries, including the United States and nations in Western Europe, formed NATO. Members pledged to defend one another against Soviet attack. The Soviet Union and its satellites in Eastern Europe formed the Warsaw Pact. The Soviets often used Warsaw Pact troops to keep its satellites in order.