* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Warm-up - mathew1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
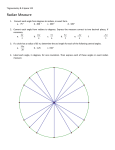
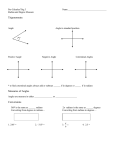
Warm-up: 1. How many degrees are in a circle? 2. What is the measure of the following angle? 3. Estimate the measure of the following angle. 1 Unlike in Geometry, in Precalculus we can have negative angles as an indicator of direction. Also, unlike in Geometry, in Precalculus we will be measuring angles in degrees and... __________ Like Celsius and Fahrenheit measure temperature, degrees and ________ measure angles. 2 Conversions between Degrees and Radians o Use the basic relationship π rad = ____ . 1. To convert degrees to radians, multiply the degree by _______ . 2. To convert radians to degrees, multiply the radian by ________ . 3 Convert from radians to degrees. 1. 9π/2 2. -π/2 3. 2 Convert from degrees to radians. 4. 1350 5. 5400 6. -3120 4 _____ 5 Complete the following using degree measures. 1. An angle is acute if its measure is between ________ and ________. 2. An angle is obtuse if its measure is between ________ and ________. 3. Two angles are complementary if the sum of their measures is ________. 4. Two angles are supplementary if the sum of their measures is ________. 6 Remembering what you know about angles in degree measure, complete the following using the equivalent radian measures. An angle is acute if its measure is between ________ and ________. An angle is obtuse if its measure is between ________ and ________. Two angles are complementary if the sum of their measures is ________. Two angles are supplementary if the sum of their measures is ________. 7 Complements and Supplements 0 Complementary angles- their sum is __ ( ___ ) 0 Supplementary angles- their sum is ___ ( __ ) To find the complement of an angle, subtract from __ if in degrees or subtract from ____ if in radians. 0 0 * angles bigger than 90 (π/2) cannot have complements. To find the supplement of an angle, subtract from ___ if in degrees or subtract from __ if in radians. 0 0 * angles bigger than 180 (π) cannot have supplements. ***Complements and supplements can never be negative. 8 Classify as acute, right, obtuse, or neither. Then determine the complement and the supplement. Type of Angle Complement Supplement 1. 2π/5 2. 4π/5 3. 49 0 4. 7π 6 9 Quadrants 0 θ = __ , ___ Quadrant I Quadrant II 0 0 0 0 __ < θ < ___ __ < θ < __ ___ < θ < __ __ < θ < ___ 0 0 θ = __ , __ θ = ___ , __ __ < θ < ____ 0 ____ < θ < __ 0 0 0 ___ < θ < ___ ___ < θ < ___ Quadrant III Quadrant IV 0 θ = ___ , ___ 10 Tell which quadrant each angle is in and Sketch each angle in standard position. 1. 68 0 3. 126 2. π/4 0 5. 5π/6 4. 5π/3 6. 4 11 Two angles are ________ if they have the same initial and terminal side. 300 In radians, you can find coterminal angles by adding or subtracting multiples of ____. In degrees, you can find coterminal angles by adding or subtracting _____. 0 12 Determine two (one pos. and one neg.) coterminal angles for each angle. Positive Negative 0 1. 62 2. 6π/5 3. 214 0 4. 23π/12 13 Homework: pg. 291 #s 5,6,8,16,17,19, 35,40,43,46,56,57 14