* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Tissue Level of Organization
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Nerve guidance conduit wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
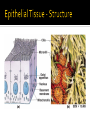
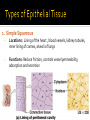
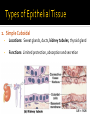
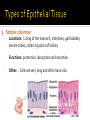
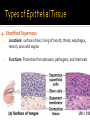
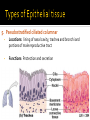
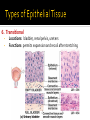
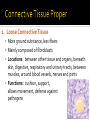
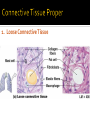
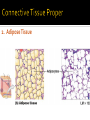
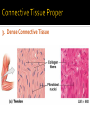
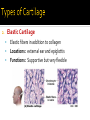
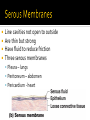
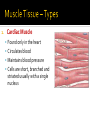
CHAPTER 4 Tissues are collections of cells and cell products that perform specific, limited functions Histology = study of tissues There are 4 types of tissues 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Neural Covers body surfaces, lines cavities and tubular structures Includes epithelia and glands Characteristics Cells are tightly packed together Free (apical) surface exposed to environment Attached to underlying connective tissue (basement membrane) Avascular (no blood supply) Continually replaced at exposed surface Physical protection (abrasion, dehydration, destruction) Control permeability Provide sensation Produce specialized secretions 1. 2. 3. 4. Exocrine= secretions are discharged onto the surface o Milk, sweat, enzymes entering the digestive tract Endocrine = secretions are discharged into tissue fluid and blood o hormones Cell layers 1. Simple epithelium: single layer of cells Stratified epithelium: several layers of cells Pseudostratified epithelium: appears to be stratified but is not Cell shapes 2. Squamous – thin and flat Cuboidal – cube shaped Columnar – tall, slender rectangles 1. Simple Squamous ▪ Locations: Lining of the heart , blood vessels, kidney tubules, inner lining of cornea, alveoli of lungs ▪ Functions: Reduce friction, controls vessel permeability, adsorption and secretion 2. Simple Cuboidal ▪ Locations: Sweat glands, ducts, kidney tubules, thyroid gland ▪ Functions: Limited protection, absorption and secretion 3. Simple columnar ▪ Locations: Lining of the stomach, intestines, gall bladder, uterine tubes, collecting ducts of kidney ▪ Functions: protection, absorption and secretion ▪ Other: : Cells are very long and often have cilia 4. Stratified Squamous ▪ Locations: surface of skin, lining of mouth, throat, esophagus, rectum, anus and vagina ▪ Functions: Protection from abrasion, pathogens, and chemicals 5. Pseudostratified ciliated columnar ▪ Locations: lining of nasal cavity, trachea and bronchi and portions of male reproductive tract ▪ Functions: Protection and secretion 6. Transitional ▪ ▪ Locations: bladder, renal pelvis, ureters Functions: permits expansion and recoil after stretching Practice Identifying epithelial tissues Most diverse tissue of the body Highly vascular Never exposed to external environment Characteristics Specialized cells Extracellular matrix (majority of tissue volume; determines function) ▪ Solid extracellular protein fibers ▪ Fluid extracellular ground substance (amorphous gel like substance composed of large carbohydrates and proteins) 1. 2. 3. 4. Support and protection Transportation of materials Storage of energy reserves Defense of the body 1. Connective Tissue Proper a) Loose (underlying skin, fat) b) Dense (tendons and ligaments) 2. Supporting Connective Tissues a) Cartilage (solid rubbery matrix) b) Bone (solid crystalline matrix) 3. Fluid Connective Tissues a) Blood b) Lymph 1. Loose Connective Tissue More ground substance, less fibers Mainly composed of fibroblasts Locations: between other tissue and organs, beneath skin, digestive, respiratory and urinary tracts, between muscles, around blood vessels, nerves and joints Functions: cushion, support, allows movement, defense against pathogens 1. Loose Connective Tissue 2. Adipose Tissue Fibroblasts enlarge and store fat Very little matrix Locations: beneath the skin and around organs especially at sides, buttocks, breasts, around eyes and kidneys Functions: padding, shocks insulates, stores energy 2. Adipose Tissue 3. Dense Connective Tissue More fibers, less ground substance Fibroblast matrix composed of parallel collagen fibers Locations: between skeletal muscles (tendons) between bones (ligaments), covering skeletal muscles Functions: firm attachment; conducts pull of muscle, reduces friction between muscles, stabilizes position of bones, helps prevent overexpansion of organs (bladder) 3. Dense Connective Tissue Gel-type ground substance For shock absorption and protection No blood vessels Types of cartilage include Hyaline cartilage Elastic cartilage Fibrous cartilage Hyaline Cartilage 1. Most common Location: between ribs and sternum, bone joints, trachea, bronchi and nasal septum Function: Stiff but flexible support; Reduces friction between bones Elastic Cartilage 2. Elastic fibers in addition to collagen Locations: external ear and epiglottis Functions: Supportive but very flexible Fibrous Cartilage (fibrocartilage) 3. Strong collagen fibers in matrix Locations: knees, pubic bones, intervertebral discs Functions: Limits movement, prevents bone-tobone contact, absorbs shock, reduces friction Most rigid connective tissue Matrix composed of hard mineral salts deposited around collagen fibers Gives bone rigidity and elasticity Bone cells (osteocytes) Periosteum (Covers bone surfaces) Physical barriers Line internal spaces of organs and tubes that open to the outside Line body cavities Different types of membranes\ Mucous Serous Cutaneous Synovial Meninges Mucous = protection Line passages that have external connections Lining of digestive, respiratory, urinary and reproductive tracts Epithelial surfaces are moist to reduce friction and help absorption and excretion Line cavities not open to outside Are thin but strong Have fluid to reduce friction Three serous membranes Pleura – lungs Peritoneum – abdomen Pericardium - heart Outer covering of body Skin Thick, waterproof and dry Stratified keratinized squamous epithelium Line freely movable joint cavities Secrete synovial fluid into joint cavity – provides lubrication Protects the end of bones Lacks a true epithelium Specialized for contraction Produces all body movement Three types Skeletal Cardiac Smooth 1. Skeletal Muscle Specialized for contraction Moves and stabilizes bone Guards entrances and exits Generates heat Protects organs Cells are long, cylindrical, striated and multinucleate 2. Cardiac Muscle Found only in the heart Circulates blood Maintains blood pressure Cells are short, branched and striated usually with a single nucleus 3. Smooth muscle Walls of hollow, contracting organs (blood vessels digestive, respiratory, urinary and reproductive tracts) Moves food, urine and other secretions Controls diameter of respiratory passageways and blood vessels Cells are short, spindle-shaped and non-striated with a single central nucleus Specialized for conducting electrical impulses Rapidly senses internal or external environment Processes information and controls responses Concentrated in the central nervous system Brain and spinal cord Two kinds of neural cells Neurons Neuroglia A.k.a nerve cells Perform electrical communication Parts of a neuron Cell body – contains the nucleus Dendrites – receive incoming signals Axon (nerve fiber) – long thin extension of the cell body which carries outgoing electrical signals to the effector Supporting cells Repair and supply nutrients to neurons Tissues respond to injury to maintain homeostasis Inflammatory response The tissue’s first response to injury Signs and symptoms of the inflammatory response Swelling, redness, heat, pain Can be triggered by Trauma (physical injury) or infection Fibroblasts produce dense network of collagen fibers (scar tissue) Most successful in… epithelia, connective tissues and smooth muscle Least successful in… Neural tissue, cardiac muscle Speed and efficiency of tissue repair decrease with age due to Slower rate of energy consumption (metabolism) Hormonal alterations Reduced physical activity Osteoporosis – age related reduction in bone strength of women Tissue ID quizlet