* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Blood and Tissue Protozoa of Dogs and Cats
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Plasmodium falciparum wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
Schistosoma mansoni wikipedia , lookup
Dracunculiasis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Toxocariasis wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Visceral leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
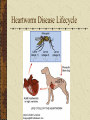
Blood Parasites of Dogs and Cats Babesia canis •B. canis is endemic in southern Florida, sporadic elsewhere, especially in the southern states; Large, pleomorphic organisms in RBC are typical; classic paired pyriform bodies (below) are rare in this species. • B. gibsoni is rarely seen in the USA and is found in dogs from Asian enzootic areas; small, singular annular bodies in RBC are typical Babesia canis • Pups, young dogs are more susceptible than adults, especially kennels • Major strain differences in pathogenicity • Rhipicephalus sanguineus transmits transovarially, transstadially • Incubation period 10 days-3 weeks; transmission possible by ticks, transplacentally or by transfusion A three week old puppy presented with anemia, icterus after several littermates died • Often concurrent with Ehrlichia canis in a greyhound kennel • Signs and pathogenesis are referable to regenerative hemolytic anemia. In clinical cases, aggregates of parasitized RBC-fibrin sludging of capillary beds tissue anoxia, vascular damage, especially brain, heart, kidneys, intestines acidosis, DIC shock and death Diagnosis of Babesia • Spleen, liver impression smears of a littermate that had died. RBC with organisms become ‘sticky’ and are taken out of circulation. Note multiple parasites in some RBC’s. • Organisms were found in <1% RBC at ‘feathered tip’ of thin smears of capillary blood. Giemsa stain is best • Coomb’s test is + • Serology: IFA of > 1:40 is diagnostic of current or previous clinical disease Ehrlichia canis Ehrlichia canis is the cause of classical ehrlichiosis in dogs. This Ehrlichia targets MONOCYTES Ehrlichia canis infection in dogs is divided into 3 clinicopathologic stages: acute phase of disease: fever, anorexia, lethargy lymphadenopathy thrombocytopenia This phase begins 1-3 weeks after exposure. Most dogs recover at this point, but others progress to the subacute and chronic phases Ehrlichia canis cont: subacute phase of disease: hypergammaglobulinemia (polyclonal or sometimes monoclonal gammopathy), thrombocytopenia and anemia usually subclinical, but can last months to years chronic phase: lethargy, weight loss PANCYTOPENIA, BONE MARROW SUPPRESSION AND HEMORRHAGE Heartworm Disease Heartworm disease or dirofilariasis is a serious and potentially fatal disease. It is caused by a blood-borne parasite known as Dirofilaria immitis. Adult heartworms are found in the heart and adjacent large blood vessels of infected dogs. Rarely, worms may be found in other parts of the circulatory system. The female worm is 6 - 14" long (15 - 36cm) and 1/8" wide (5mm). The male is about half the size of the female. One dog may have as many as 300 worms present when diagnosed. Heartworm Disease Lifecycle Transmission Since transmission requires the mosquito as an intermediate host, the disease is not spread directly from dog to dog. Spread of the disease therefore coincides with mosquito season, which can last year-round in many parts of the United States. The number of dogs infected and the length of the mosquito season are directly correlated with the incidence of heartworm disease in any given area. The mosquito usually bites the dog where the hair coat is thinnest. However, having long hair certainly does not prevent a dog from getting heartworms. Heartworm Disease in Cats Heartworm disease in the cat may involve some or all of the following: Pulmonary arterial, bronchial, and alveolar disease—Heartworm Associated Respiratory Disease (HARD)—is associated with the death of developing juvenile worms. Cats may present with cough, dyspnea, and/or wheezing. Death of adult heartworms (if present) can potentiate HARD signs. Sudden death occurs in approximately 10 to 20% of diagnosed cases. Pathogenesis is unclear, but a condition (similar to acute respiratory distress syndrome [ARDS]) caused by the release of antigenic moieties from injured or dying adult worms is suspected. Vomiting unrelated to eating may be present. Pulmonary thromboemboli (fragments from dead adult worms) may cause acute vascular and interstitial inflammatory events that lead to dyspnea and death. Hematological abnormalities may include anemia, hyperglobulinemia, basophilia, and eosinophilia. Neurological signs may indicate aberrant migration of the worm to the brain, eye, or spinal cord. Lifecycle in Cats Mycoplasma hemofelis (formerly Haemobartonella felis) is an epicellular bacterial parasite of feline red cells that can cause hemolytic anemia. In blood smears stained with polychrome stains, the organisms are recognized as small blue cocci, rings, or rods on the edges or across the faces of red cells. Stain precipitate is often mistaken for organisms, resulting in unnecessary tetracycline administration. Mycoplasma hemofelis cont: The hemolytic anemia caused by M. haemofelis is called feline infectious anemia (FIA) and is usually regenerative in nature (unless underlying disease suppresses the regenerative response, e.g. Feline Leukemia Virus infection). Therefore, a non-regenerative anemia in a cat with H. felis should not be attributed only to M. haemofelis infection and the cat should be further evaluated for another disease process Cytauxzoon felis • Causes a rapidly fatal disease in cats after <7 day illness. Signs referable to occlusion of vasculature by schizonts in MN phagocyte lining of all organs, especially lungs • Sporadic in rural cats in South, Southcentral USA; Tick vector (Dermacentor, Ixodes?) with a bobcat reservoir suspected. • There is both a tissue and RBC phase of the life cycle. Merozoites parasitize 1-4% of circulatiing RBC 1-3 days prior to death. Signs are depression, anorhexia, dyspnea, icterus, anemia, terminal 103-107 F febrile period. Dx: via organism in Giemsa or Wright’s stained RBC, bone marrow or impression smears. • Rx: Saved 6 of 500 cats by supportive care, parvaquone, 10-30mg/kg SID, 3d QUESTIONS? 15