* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
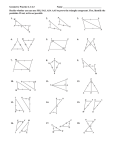
Chapter 4 Notes Congruent Polygons: Symbol: ≅ Definition: -Simplified: shapes that have the same angles or sides -Text Book: two polygons are congruent if they are the same size and shape - that is, if their corresponding angles and sides are equal Steps to Naming: 1. Congruent Polygons: B C F G A D E H Name ALL of the CONGRUENT angles and sides: Congruent Polygons: B C F G A D E H Give the congruence Statement for the two figures: Congruent Polygons: If LAMPS ≅ BRITE, What are the congruent corresponding parts? L A M S E T P I R B Congruent Polygons: If FEAR ≅ RUNS, 1. Draw the figure. 2. List the congruent corresponding parts. Congruent Triangles The congruent statement ∆𝐴𝐵𝐶 ≅ ∆𝑅𝑆𝑇 --tell us that triangles ABC and RST are congruent. Order matters! A corresponds to R. (A≅R) B corresponds to S. (B≅S) C corresponds to T. (C≅T) Congruent Triangles If DNA ≅ YOU, then list the congruent corresponding parts. Congruent Right Triangles • Same as before except: the RIGHT ANGLE has to be in the MIDDLE of the triangle’s name • SAM ≅ ROB Congruent Triangles Congruent Triangles Words you need to know to do PROOFS: •Congruent •Vertical angles •Addition Property •Subtraction Property •Multiplication Property Words you need to know to do PROOFS: •Division Property •Substitution Property •Symmetric Property •Reflexive Property •Third Angle Theorem •Midpoint Words you need to know to do PROOFS: •Parallel •Alternate Interior •Alternate Exterior •Interior •Exterior •Perpendicular Bisector Introduction to PROOFS: • 2 Column Proofs: STATEMENT REASONS 1. 2. 3. 1. 2. 3. Introduction to PROOFS: Write a proof for the following: STATEMENT 5x + 3 = 18 REASONS 1. 1. 2. 2. 3. 3. Introduction to PROOFS: Write a proof for the following: 2x − 6 = 10 STATEMENT 3 REASONS 1. 1. 2. 2. 3. 3. Introduction to PROOFS: Write a proof for the following: 3x − 8 = 11 STATEMENT 2 REASONS 1. 1. 2. 2. 3. 3. Proving Triangles are Congruent • Steps: 1. If not given a picture, draw one. 2. Mark what you know on the picture (not what you are trying to prove). 3. Decide how you know the triangles are congruent (SSS, SAS, ASA, AAS). 4. State the given and the prove. 5. Complete the proof with the information. Triangle Congruence Principles Side-Side-Side (SSS) If the three sides of one triangle have the same measures as the three sides of a second triangle, then those triangles are congruent. If: 𝐴𝐵 ≅ 𝑅𝑆 𝐴𝐶 ≅ 𝑅𝑇 𝐶𝐵 ≅ 𝑇𝑆 Then: ∆𝐴𝐶𝐵 ≅ ∆𝑅𝑇𝑆 Side-Side-Side (SSS) Given: 𝑃𝑁 ≅ 𝑀𝐿 𝐿𝑃 ≅ 𝑁𝑀 Prove: ∆𝑃𝑁𝐿 ≅ ∆𝑀𝐿𝑁 STATEMENT REASONS 1. 1. Given 2. 2. 3. 3. Side-Side-Side (SSS) E B F Given: 𝐸𝐵 ≅ 𝐹𝐶 𝐸𝐶 ≅ 𝐹𝐵 Prove:∆𝐹𝐵𝐸 ≅ ∆𝐸𝐶𝐹 C STATEMENT REASONS 1. 𝐸𝐵 ≅ 𝐹𝐶 𝐸𝐶 ≅ 𝐹𝐵 2. 1. Given 2. 3. 3. Side-Side-Side (SSS) Triangle Congruence Principles Side-Angle-Side (SAS) If two sides and the included angle of one triangle have the same measure as two sides and the included angle of a second triangle, then those triangles are congruent. 𝑆𝑅 ≅ 𝐵𝐴 𝑅𝑇 ≅ 𝐴𝐶 ∠𝑆𝑅𝑇 ≅ ∠𝐵𝐴𝐶 Then: ∆𝑆𝑅𝑇 ≅ ∆𝐵𝐴𝐶 If: Side-Angle-Side (SAS) STATEMENT REASONS 1. 𝐵𝐴 ≅ 𝐵𝐶 1. Given ∠𝐴𝐵𝑀 ≅ ∠𝐶𝐵𝑀 2. 2. Prove that ΔABM ≅ ΔCBM. 3. 3. Side-Angle-Side (SAS) Given: 𝐻𝐼 ≅ 𝐺𝐼 I is the midpoint of 𝐽𝐸 Prove: 𝐻𝐽 ≅ 𝐺𝐸 STATEMENT 1. 𝐻𝐼 ≅ 𝐺𝐼 I is the midpoint of 𝐽𝐸 2. REASONS 1. Given 3. ∠𝐽𝐼𝐻 ≅ ∠𝐸𝐼𝐺 2. Definition of Midpoint 3. 4. ∆𝐼𝐽𝐻 ≅ ∆𝐼𝐸𝐺 4. 5. 5. Side-Angle-Side (SAS) T C STATEMENT REASONS 1. 1. Given G A 2. ∠𝐶𝐴𝑇 ≅ ∠𝐺𝐴𝐵 2. B Prove: 𝐶𝑇 ≅ 𝐵𝐺 3. 3. 4. 𝐶𝑇 ≅ 𝐺𝐵 4. Triangle Congruence Principles Angle-Side-Angle (ASA) If two angles and an included side of one triangle have the same measures as two angles and an included side of a second triangle, then those triangles are congruent. 𝐴𝐵 ≅ 𝑅𝑆 ∠𝐵𝐴𝐶 ≅ ∠𝑆𝑅𝑇 ∠𝐶𝐵𝐴 ≅ ∠𝑇𝑆𝑅 Then: ∆𝐴𝐶𝐵 ≅ ∆𝑅𝑇𝑆 If: Angle-Side-Angle (ASA) R o y STATEMENT 1.∠𝑌𝑂𝑅 ≅ ∠𝑌𝑂𝐽 ∠𝑅𝑌𝑂 ≅ ∠𝐽𝑌𝑂 2. 2. 3. J Prove: ∆𝑅𝑂𝑌 ≅ ∆𝐽𝑂𝑌 REASONS 3. 1. Given Angle-Side-Angle (ASA) A C N T O Prove: ∆𝐶𝐴𝑁 ≅ ∆ 𝑇𝑂𝑁 STATEMENT REASONS 1. 1. Given 2. 2. 3. 3. Angle-Side-Angle (ASA) U B S Prove: 𝐵𝑈 ≅ 𝑅𝑈 STATEMENT REASONS 1. 1. Given 2. 2. 3. 3. R Triangle Congruence Principles Angle-Angle-Side (AAS) If two angles and a non-included side of one triangle have the same measures as two angles and a nonincluded side of a second triangle, then those triangles are congruent. 𝐴𝐵 ≅ 𝐷𝐸 ∠𝐵𝐴𝐶 ≅ ∠𝐸𝐷𝐹 ∠𝐴𝐶𝐵 ≅ ∠𝐷𝐹𝐸 Then: ∆𝐴𝐵𝐶 ≅ ∆𝐷𝐸𝐹 If: Angle-Angle-Side (AAS) STATEMENT J R A 1. 𝐽𝑅 ≅ 𝐷𝑅 1. Given ∠𝐽𝐴𝑅 ≅ ∠𝐷𝑂𝑅 2. 2. 3. O D Prove: ∆𝑅𝑂𝐷 ≅ ∆𝐽𝐴𝑅 REASONS 3. Angle-Angle-Side (AAS) X Z Y W T Prove: ∆𝑋𝑌𝑍 ≅ ∆𝑇𝑌𝑊 STATEMENT REASONS 1. 1. Given 2. 2. 3. 3. THERE IS NO ASS CONGRUENCIES IN Triangle Congruence Principles Hypotenuse-Leg (HL) If the hypotenuse and a leg of one RIGHT triangle have the same measures as the hypotenuse and a leg of a second RIGHT triangle, then those triangles are congruent. 𝐴𝐵 ≅ 𝐷𝐸 𝐵𝐶 ≅ 𝐸𝐹 ∠𝐵𝐶𝐴 ≅ ∠𝐸𝐹𝐷 Then: ∆𝐴𝐵𝐶 ≅ ∆𝐷𝐸𝐹 If: Hypotenuse-Leg (HL) O B Prove: ∆𝐵𝑂𝑋 ≅ ∆𝑆𝑋𝑂 S X STATEMENT REASONS 1. 1. Given 2. 2. 3. 3. Hypotenuse-Leg (HL) STATEMENT REASONS 1. 1. Given 2. 2. A 3. E H Given: 𝑇𝐻 is a perpendicular bisector to 𝐸𝐴 𝑇𝐸 ≅ 𝑇𝐴 Prove: ∆𝑇𝐻𝐸 ≅ ∆𝑇𝐴𝐻 3. T Hypotenuse-Leg (HL) L G J K Prove: 𝐿𝐾 ≅ 𝐺𝐼 I H STATEMENT REASONS 1. 1. Given 2. 2. 3. 3.