* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2/13 Human Organ System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
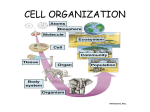
2/14 Write both in your SHOES & Prefix, Suffix & Root Word Section in your CJ. ( 2 Separate Words) 2/16 Tissue A group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function. Example: The heart is an organ made of cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and blood tissue. 2/14 Organ A structure made of two or more tissues working together to perform a specific function in an organism Example: The heart is an organ that pumps blood throughout the body. 2/13 Human Organ System A group of organs that are interdependent and work together to perform body functions. Human organ systems include: circulatory, digestive, endocrine, excretory, immune, integumentary, lymphatic, muscular, nervous, reproductive, respiratory, and skeletal. 2/15 Voluntary Movement that you can control. Ex. Any skeletal muscle 2/22 Involuntary Movement that can not be controlled. 2/23 Write both in your SHOES & Prefix, Suffix & Root Word Section in your CJ. ( 2 Separate Words) 2/17 NO word• Pick up hand out and Add skeletal /muscular/ integumentary quiz for next Friday 2/24 • Add end of 3 weeks –March 2nd • Add end of 6 weekd April 6th • FROG Dissection: March 29th & 30th!! 2/20 Tendon Bands of tissue that attach bones to muscle 2/21 Ligament Bands of tissue that attach bones together at joints 2/22 Epidermis The protective most outer layer of the skin in animals, the outer layer of cells of the stems, roots, and leaves in plants. Ex. The outermost layer of the skin is called the epidermis. 2/28 Adaptation A change in structure or habits, often hereditary, by which an organism improves its condition in relationship to its environment. 3/25 Hemoglobin A protein in red blood cells that transports oxygen and carbon dioxide and gives blood its red color. 2/28 Cartilage Cartilage is a stiff yet flexible connective tissue found in many areas in the bodies of humans and other animals. Example: Found in the joints between bones, the rib cage, the ear, the nose, the elbow, the knee, the ankle, the bronchial tubes and the intervertebral discs. 2/23 Write both in your SHOES! ( 2 Separate Words) 2/24 Practice Test Questions *Add to CJ section Practice test questions then Start on Practice test questions you picked up at the door using the following strategy: 1. Read the QUESTION first. 2. Read the whole passage highlighting anything relevant/ important. (NOT everything!) 3. Answer question. 4. Prove it! Go back to question and circle where you got that. 3/2 Neuron A nerve cell that is specialized to conduct nerve impulses. Impulse Nerve Impulse: the electrical discharge that travels along a nerve fiber 3/5 Peripheral Nervous System The nervous system which links the spinal cord and brain to the skin, muscles, blood vessels and other sensory organs. Example: The PNS is composed of two types of neurons. The sensory neurons and the motor neurons. 3/6 Central Nervous System This system consists of the brain and spinal cord, where many bodily functions are controlled, many sensations are processed and signals are sent to different parts of the body. Example: Functions affected by the CNS include muscle control, eyesight, breathing and memory. 3/7 Write both in your SHOES! ( 2 Separate Words) 2/29 Enzyme A type of protein that speeds up the rate of chemical reactions in the body but is not used up or changed itself in any way during the reaction. Example: Chemical digestion is caused by digestive juices such as stomach acid, and enzymes produced by glands. 3/1 Peristalsis • Process of a wave-like contraction of the digestive tract that forces food through it. 3/10 Nephrons Tiny filtering units in the kidney. (Part of the Excretory System) Example: They remove waste products from the blood, recover some substances to be used again by the body, and eliminate what is left as urine. 3/10 Villi Fingerlike projections in the wall of the small intestine that increase the surface area for absorption of nutrient molecules. 3/2 Excretion Excretion is the process of eliminating waste products of metabolism and other non-useful materials from the body. Example: The urinary system rids the blood of wastes produced by the cells. 2/28 Alveoli Tiny, thin walled air sacs in the lungs where oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange places. 2/27 Capillaries Tiny blood vessels that branch through body tissues to deliver oxygen and nutrients and carry away waste products. They connect arteries to veins. 2/29 Practice Test Questions *Add to CJ section Practice test questions then Start on Practice test questions you picked up at the door using the following strategy: 1. Read the QUESTION first. 2. Read the whole passage highlighting anything relevant/ important. (NOT everything!) 3. Answer question. 4. Prove it! Go back to question and circle where you got that. 3/21 Write both in your SHOES & Prefix, Suffix & Root Word Section in your CJ. ( 2 Separate Words) 3/23 Arterioles The smallest arteries of the circulatory system that carry arterial (oxygenated) blood. 3/28 Platelets Special blood cells that plug up damaged blood vessels and help blood clot to stop bleeding. Platelets also contribute to the immune response. 3/29 Antibodies Proteins produced by white blood cells to fight bacteria, viruses, and other foreign substances. 3/30 Hormones Chemical substances produced by the endocrine glands in the body, which circulate in the blood and help to control growth, reproduction and other functions. 3/31 Pathogen Any organism or substance, especially a microorganism, capable of causing disease, such as bacteria, viruses, protozoa or fungi. 4/1 Lymph The clear, watery protein-rich fluid found in the lymphatic vessels. It carries cells that help fight infection and disease. 4/6 Write both in your SHOES & Prefix, Suffix & Root Word Section in your CJ. ( 2 Separate Words) Structure The shape and composition of part of an organism or system Example: An organism’s structure determines its function. Function The specific job performed by a part of an organism or system Example: The function of muscle cells is to assist in movement. 4/7 No Word Today! Read over the Frog Dissection Hand-out in your CJ