* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Concept Analysis Diagram
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
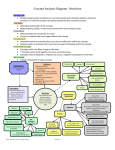
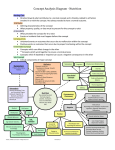
Concept Analysis Diagram - Nutrition Nursing Care Directed toward what contributes to a normal concept and is thereby related to all factors involved in or with the concept. Not always needed to have a normal outcome. Attributes Defining characteristics of the concept What property, quality, or data must be present for the concept to exist Antecedents What precedes the concept for it to exist Events or incidents that must happen before the concept Consequences Untoward events or outcomes that occur due to malfunction within the concept Positive events or outcomes that occur due to proper functioning within the concept Interrelated Concept Concepts which can affect change in the other ””Concepts which work together to ensure a normal process Concepts which if depleted or impaired can cause a negative consequence in the other Sub-Concept Critical components of major concept Metabolism Attributes Nursing Care Adequate Intake for: Development-Energy- GrowthTissue Repair Ideal Ht-Wt-BMI—(MAC) (MAMM) Muscle Tone-Strength-Agility-Reflex Response Cognitive & Mood Response Albumin WNL Hemoglobin & Hematocrit WNL Electrolytes WNL Primary, Secondary, Tertiary Interpersonal Relationships Cognition Diversity Patient Education Interrelated Concepts Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Thermoregulation Clotting Antecedents Human Development Normal Alimentary Tract and Associated Organs Adequate Ingestion of Nutrients and Water Normal Temperature Normal ph Medical Conditions Nutrition Consequences (Outcomes) The process by which the body ingests, absorbs, transports uses and eliminates nutrients and foods. (NC) Negative Risk factors Medications Diets Malnutrition Physiological-Psychological- Dysfunction Ingestion- Digestion-AbsorptionMetabolism Positive Altered Hydration Status Lifestyle Behaviors Age-Gender-Genetics Malnutrition Insufficient/Excess Intake Failure to thrive--Obesity Sub Concepts Growth & Tissue Repair Ethnicity Socioeconomics Knowledge Nutrients Physiological & Psychological Development Food Allergies Engage in Physical Activity Physiological and Psychological Wellness Homeostasis/Adequate Nutrition Hydration 106 © 2015, Texas CBC Consortium. All Rights Reserved. Revised 6.15 Low energy-Fatigue Depression-Isolation Growth/ Developmental Delay Decreased Bone Density Delayed-Inadequate Healing Illness-Muscle wasting-Death Concept Analysis Diagram - Nutrition Explanation of Nutrition Diagram: Nursing - Directed toward what contribution nursing would make to the concept and a positive consequence. Related to all factors involved in or with the concept. Not always needed to have a normal outcome. For example an individual may work with an outpatient dietician to learn what diet would have the most positive influence on their cardiovascular disease. This may result in a positive outcome without the involvement of nursing. The same individual in an acute care setting may have the same education from the dietician but they would also have nursing to reinforce and expand the education that takes place. Before interventional measures can be organized and put into action, the negative consequences must be traced back to the contributing inefficient antecedent. Nursing interventions focus on enhancing antecedents to allow for optimal measurement of attributes resulting in positive consequences. Definition of Nutrition – the process by which the body ingests, absorbs, transports, uses and eliminates nutrients and foods. Attributes are characteristics of the concept. An individual who has adequate nutrition will have attributes that characterize adequate nutrition and therefore consequences that are positive. If attributes are not present the individual has an increased risk of experiencing negative consequences and further assessment may be needed. Antecedents are those circumstances that lead to the concept as defined. These circumstances must be present for nutrition to occur. If the antecedents are not present the individual’s nutrition could be suboptimal or inadequate. For example individuals who have limited access to nutritious foods may have inadequate ingestion of nutrients leading to malnutrition. Or the individual could have a disease of the colon such as Crohn’s Disease which could also lead to malnutrition. Nutrition is a concept that is related to most health and illness concepts. Interrelated concepts are those affected by adequate or inadequate nutrition and those that influence nutrition. For example if an individual cannot ingest the nutrients needed for specific processes such as clotting, development, and/or maintaining their fluid and electrolyte balance than negative consequences can occur and illness can ensue. Cognition can be affected by nutrition and also can affect nutritional intake as in the case of Alzheimer’s disease. An individual’s religion and lifestyle can affect their nutrition and influence the consequences. Consequences are outcomes. They can be positive or negative based on an individual’s nutritional status. Suboptimal or inadequate nutrition can result in developmental delays, depression, loss of energy, fatigue, obesity, failure to thrive, delayed wound healing, muscle atrophy and even death. Malnutrition is on both sides of a nutritional continuum, less than body requirements on one end and more than body requirements on the other end. Health is somewhere in the middle and requires the antecedents to be present. Positive consequences or outcomes are those which indicate an individual is adequately nourished. These include; growth, tissue repair, homeostasis, ability to engage in physical activity, physiological and psychological wellness. Sub-concepts are more specific than the general concept of nutrition. Sub-concepts are components/factors of nutrition such as age, genetics, ethnicity, allergies, and medications. Nutrition affects an individual’s health, and health/illness can affect an individual’s nutritional status. 107 © 2015, Texas CBC Consortium. All Rights Reserved. Revised 6.15