* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Choose the word or term that best completes each sentence. 1. 7xy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
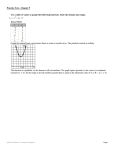
Study Guide and Review - Chapter 7 Choose the word or term that best completes each sentence. 4 1. 7xy is an example of a(n)___________ . SOLUTION: A product of a number and variables is a monomial. 5 2. The ___________ of 95,234 is 10 . SOLUTION: 5 5 95,234 is almost 100,000 or 10 , so 10 is its order of magnitude. 3. 2 is a(n) __________ of 8. SOLUTION: 3 Since 8 = 2 , 2 is the cube root of 8. 4. The rules for operations with exponents can be extended to apply to expressions with a(n) ___________ such as . SOLUTION: The exponent is a rational exponent. n 5. A number written in is of the form a × 10 , where 1 ≤ a < 10 and n is an integer. SOLUTION: n A number written as a × 10 , where 1 ≤ a < 10 and n is an integer, is written in scientific notation. x 6. f (x) = 3 is an example of a(n) ______________ . SOLUTION: x A function in the form y = ab , where a ≠ 0, b > 0, and b ≠ 1 is an exponential function. 7. is a(n) ______________ for the sequence . SOLUTION: A formula that gives the first term of a sequence and tells you how to find the next term when you know the preceding term is called a recursive formula. 3x – 1 8. 2 = 16 is an example of a(n) _______________ . SOLUTION: An equation in which the variable occurs as exponent is an exponential equation. t 9. The equation for _____________ is y = C(1 – r) . SOLUTION: Since 0 < 1 – r < 1, this is an example of exponential decay. n 10. If a = b for a positive integer n, then a is a(n) _______________ of b. SOLUTION: n eSolutions - Powered by Cognero If a Manual = b for a positive integer Simplify each expression. 3 5 n, then a is an nth root of b. Page 1 t 9. The equation for _____________ is y = C(1 – r) . SOLUTION: Study Guide and Review - Chapter 7 Since 0 < 1 – r < 1, this is an example of exponential decay. n 10. If a = b for a positive integer n, then a is a(n) _______________ of b. SOLUTION: n If a = b for a positive integer n, then a is an nth root of b. Simplify each expression. 3 11. x ⋅ x ⋅ x 5 SOLUTION: 2 5 12. (2xy)( −3x y ) SOLUTION: 4 5 2 13. (−4ab )(−5a b ) SOLUTION: 3 2 2 14. (6x y ) SOLUTION: 3 3 2 15. [(2r t) ] SOLUTION: eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero Page 2 Study Guide and Review - Chapter 7 3 3 2 15. [(2r t) ] SOLUTION: 3 16. (−2u )(5u) SOLUTION: 2 3 3 3 17. (2x ) (x ) SOLUTION: 18. 3 3 (2x ) SOLUTION: eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero 2 19. GEOMETRY Use the formula V = πr h to find the volume of the cylinder. Page 3 Study Guide and Review - Chapter 7 2 19. GEOMETRY Use the formula V = πr h to find the volume of the cylinder. SOLUTION: Simplify each expression. Assume that no denominator equals zero. 20. SOLUTION: 21. SOLUTION: 22. SOLUTION: eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero Page 4 Study Guide and Review - Chapter 7 22. SOLUTION: −3 0 6 23. a b c SOLUTION: 24. SOLUTION: 25. SOLUTION: eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero Page 5 Study Guide and Review - Chapter 7 25. SOLUTION: 26. SOLUTION: 27. SOLUTION: eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero Page 6 Study Guide and Review - Chapter 7 27. SOLUTION: 2 4 28. GEOMETRY The area of a rectangle is 25x y square feet. The width of the rectangle is 5xy feet. What is the length of the rectangle? SOLUTION: 3 The length of the rectangle is 5xy ft. Simplify. 29. SOLUTION: 30. SOLUTION: eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero 31. Page 7 SOLUTION: Study Guide and Review - Chapter 7 30. SOLUTION: 31. SOLUTION: 32. SOLUTION: 33. SOLUTION: 34. SOLUTION: 35. eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero SOLUTION: Page 8 Study Guide and Review - Chapter 7 35. SOLUTION: 36. SOLUTION: Solve each equation. x 37. 6 = 7776 SOLUTION: Therefore, the solution is 5. 4x – 1 38. 4 = 32 SOLUTION: Therefore, the solution is . Express each number in scientific notation. 39. 2,300,000 eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero SOLUTION: Page 9 Study Guide and Review - Chapter 7 Therefore, the solution is . Express each number in scientific notation. 39. 2,300,000 SOLUTION: 2,300,000 → 2.300000 The decimal point moved 6 places to the left, so n = 6. 6 2,300,000 = 2.3 × 10 40. 0.0000543 SOLUTION: 0.0000543 → 5.43 The decimal point moved 5 places to the right, so n = –5. −5 0.0000543 = 5.43 × 10 41. ASTRONOMY Earth has a diameter of about 8000 miles. Jupiter has a diameter of about 88,000 miles. Write in scientific notation the ratio of Earth’s diameter to Jupiter’s diameter. SOLUTION: Earth: 8000 = 8.0 × 10 3 Jupiter: 88,000 = 8.8 × 10 4 −2 In scientific notation, the ratio of Earth’s diameter to Jupiter’s diameter is about 9.1 × 10 . Graph each function. Find the y-intercept, and state the domain and range. x 42. y = 2 SOLUTION: Complete a table of values for –2 < x < 2. Connect the points on the graph with a smooth curve. x x y 2 –2 –2 2 –1 2 0 2 1 2 2 2 –1 0 1 1 2 2 4 eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero Page 10 Study Guide and Review - Chapter 7 −2 In scientific notation, the ratio of Earth’s diameter to Jupiter’s diameter is about 9.1 × 10 . Graph each function. Find the y-intercept, and state the domain and range. x 42. y = 2 SOLUTION: Complete a table of values for –2 < x < 2. Connect the points on the graph with a smooth curve. x x y 2 –2 –2 2 –1 2 0 2 1 2 2 2 –1 0 1 1 2 2 4 The graph crosses the y-axis at 1. The domain is all real numbers, and the range is all real numbers greater than 0. x 43. y = 3 + 1 SOLUTION: Complete a table of values for –2 < x < 2. Connect the points on the graph with a smooth curve. x x y 3 +1 –2 +1 –1 +1 –2 3 –1 3 0 3 +1 1 3 +1 2 3 +1 0 2 1 4 2 10 eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero Page 11 The graph crosses the y-axis at 2. The domain is all real numbers, and the range is all real numbers greater than 1. Study Guide Review - Chapter The graphand crosses the y-axis at 1. 7The domain is all real numbers, and the range is all real numbers greater than 0. x 43. y = 3 + 1 SOLUTION: Complete a table of values for –2 < x < 2. Connect the points on the graph with a smooth curve. x x y 3 +1 –2 +1 –1 +1 –2 3 –1 3 0 3 +1 1 3 +1 2 3 +1 0 2 1 4 2 10 The graph crosses the y-axis at 2. The domain is all real numbers, and the range is all real numbers greater than 1. x 44. y = 4 + 2 SOLUTION: Complete a table of values for –2 < x < 2. Connect the points on the graph with a smooth curve. x x y 4 +2 –2 –2 4 –1 4 0 4 +2 1 4 +2 2 4 +2 –1 +2 +2 0 3 1 6 2 18 eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero Page 12 The graph crosses the y-axis at 3. The domain is all real numbers, and the range is all real numbers greater than 2. x Study Guide and Review - Chapter 7 The graph crosses the y-axis at 2. The domain is all real numbers, and the range is all real numbers greater than 1. x 44. y = 4 + 2 SOLUTION: Complete a table of values for –2 < x < 2. Connect the points on the graph with a smooth curve. x x y 4 +2 –2 –2 4 –1 4 0 4 +2 1 4 +2 2 4 +2 –1 +2 +2 0 3 1 6 2 18 The graph crosses the y-axis at 3. The domain is all real numbers, and the range is all real numbers greater than 2. x 45. y = 2 − 3 SOLUTION: Complete a table of values for –2 < x < 2. Connect the points on the graph with a smooth curve. x x 2 –3 –2 2 –1 2 0 2 –3 1 2 –3 2 2 –3 –2 –3 –1 –3 y 0 –2 1 –1 2 1 eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero Page 13 The graph crosses the y-axis at –2. The domain is all real numbers, and the range is all real numbers greater than –3. Study Guide and Review - Chapter 7 The graph crosses the y-axis at 3. The domain is all real numbers, and the range is all real numbers greater than 2. x 45. y = 2 − 3 SOLUTION: Complete a table of values for –2 < x < 2. Connect the points on the graph with a smooth curve. x x 2 –3 –2 2 –1 2 0 2 –3 1 2 –3 2 2 –3 –2 –3 –1 –3 y 0 –2 1 –1 2 1 The graph crosses the y-axis at –2. The domain is all real numbers, and the range is all real numbers greater than –3. 0.008t , where t is 46. BIOLOGY The population of bacteria in a petri dish increases according to the model p = 550(2.7) the number of hours and t = 0 corresponds to 1:00 P.M. Use this model to estimate the number of bacteria in the dish at 5:00 P.M. SOLUTION: If t = 0 corresponds to 1:00 P.M, then t = 4 represents 5:00 P.M. There will be about 568 bacteria in the dish at 5:00 P.M. 47. Find the final value of $2500 invested at an interest rate of 2% compounded monthly for 10 years. SOLUTION: Use the equation for compound interest, with P = 2500, r = 0.02, n = 12, and t = 10. eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero Page 14 Study Guide and Review - Chapter 7 There will be about 568 bacteria in the dish at 5:00 P.M. 47. Find the final value of $2500 invested at an interest rate of 2% compounded monthly for 10 years. SOLUTION: Use the equation for compound interest, with P = 2500, r = 0.02, n = 12, and t = 10. The final value of the investment is about $3053.00. 48. COMPUTERS Zita’s computer is depreciating at a rate of 3% per year. She bought the computer for $1200. a. Write an equation to represent this situation. b. What will the computer’s value be after 5 years? SOLUTION: a. Use the equation for exponential decay, with a = 1200 and r = 0.03. t The equation that represents the depreciation of Zita’s computer is y = 1200(1 − 0.03) . b. Substitute 5 for t and solve. After 5 years, Zita’s computer value is about $1030.48. Find the next three terms in each geometric sequence. 49. −1, 1, −1, 1, ... SOLUTION: Calculate the common ratio. The common ratio is –1. Multiply each term by the common ratio to find the next three terms. 1 × –1 = –1 –1 × –1 = 1 1 × –1 = –1 The next three terms of the sequence are –1, 1, and –1. 50. 3, 9, 27 ... SOLUTION: eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero Calculate the common ratio. Page 15 The common ratio is –1. Multiply each term by the common ratio to find the next three terms. 1 × –1 = –1 –1 × –1 = 1 1 × –1 = –1 Study Guide 7 are –1, 1, and –1. The next and threeReview terms of- Chapter the sequence 50. 3, 9, 27 ... SOLUTION: Calculate the common ratio. The common ratio is 3. Multiply each term by the common ratio to find the next three terms. 27 × 3 = 81 81 × 3 = 243 243 × 3 = 729 The next three terms of the sequence are 81, 243, and 729. 51. 256, 128, 64, ... SOLUTION: Calculate the common ratio. The common ratio is . Multiply each term by the common ratio to find the next three terms. 64 × = 32 32 × = 16 16 × = 8 The next three terms of the sequence are 32, 16, and 8. Write the equation for the nth term of each geometric sequence. 52. −1, 1, −1, 1, ... SOLUTION: The first term of the sequence is –1. So, a 1 = –1. Calculate the common ratio. The common ratio is –1. So, r = –1. 53. 3, 9, 27, ... SOLUTION: The first term of the sequence is 3. So, a 1 = 3. Calculate the common ratio. eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero Page 16 The common ratio is –1. So, r = –1. Study Guide and Review - Chapter 7 53. 3, 9, 27, ... SOLUTION: The first term of the sequence is 3. So, a 1 = 3. Calculate the common ratio. The common ratio is 3. So, r = 3. 54. 256, 128, 64, ... SOLUTION: The first term of the sequence is 256. So, a 1 = 256. Calculate the common ratio. The common ratio is . So, r = . 55. SPORTS A basketball is dropped from a height of 20 feet. It bounces to its height each bounce. Draw a graph to represent the situation. SOLUTION: Compared to the previous bounce, the ball returns to its height. So, the common ratio is . Use common ratio to find next y term eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero Page 17 Study Guide and Review - Chapter 7 Therefore, the geometric sequence that models this situation is 20, 10, 5, , , , , , and so forth. Find the first five terms of each sequence. 56. SOLUTION: Use a 1 = 11 and the recursive formula to find the next four terms. eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero Page 18 Study Guide and Review - Chapter 7 Find the first five terms of each sequence. 56. SOLUTION: Use a 1 = 11 and the recursive formula to find the next four terms. The first five terms are 11, 7, 3, –1, and –5. 57. SOLUTION: Use a 1 = 3 and the recursive formula to find the next four terms. eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero The first five terms are 3, 12, 30, 66, and 138. Page 19 Study Guide andterms Review Chapter The first five are -11, 7, 3, –1,7 and –5. 57. SOLUTION: Use a 1 = 3 and the recursive formula to find the next four terms. The first five terms are 3, 12, 30, 66, and 138. Write a recursive formula for each sequence. 58. 2, 7, 12, 17, ... SOLUTION: Subtract each term from the term that follows it. 7 – 2 = 5; 12 – 7 = 5, 17 – 12 = 5 There is a common difference of 5. The sequence is arithmetic. Use the formula for an arithmetic sequence. The first term a 1 is 2, and n ≥ 2. A recursive formula for the sequence 2, 7, 12, 17, … is a 1 = 2, a n = a n – 1 + 5, n ≥ 2. 59. 32, 16, 8, 4, ... SOLUTION: Subtract each term from the term that follows it. 16 – 32 = –16; 8 – 16 = –8, 4 – 8 = –4 There is no common difference. Check for a common ratio by dividing each term by the term that precedes it. There is a common ratio of 0.5. The sequence is geometric. Use the formula for a geometric sequence. eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero Page 20 The first term a 1 is 2, and n ≥ 2. A recursive formula for the sequence 2, 7, 12, 17, … is a 1 = 2, a n = a n – 1 + 5, n ≥ Study 2. Guide and Review - Chapter 7 59. 32, 16, 8, 4, ... SOLUTION: Subtract each term from the term that follows it. 16 – 32 = –16; 8 – 16 = –8, 4 – 8 = –4 There is no common difference. Check for a common ratio by dividing each term by the term that precedes it. There is a common ratio of 0.5. The sequence is geometric. Use the formula for a geometric sequence. The first term a 1 is 32, and n ≥ 2. A recursive formula for the sequence 32, 16, 8, 4, … is a 1 = 32, a n = 0.5a n – 1, n ≥ 2. 60. 2, 5, 11, 23, ... SOLUTION: Subtract each term from the term that follows it. 5 – 2 = 3; 11 – 5 = 6, 23 – 11 = 12 There is no common difference. Check for a common ratio by dividing each term by the term that precedes it. There is no common ratio. Therefore the sequence must be a combination of both. From the difference above, you can see each is twice as big as the previous. So r is 2. From the ratios, if each denominator was one less, the ratios would be 0.5. Thus, the common difference is 1. Then, if the first term a 1 is 2, and n ≥ 2, a recursive formula for the sequence 2, 5, 11, 23, … is a 1 = 2, a n = 2a n– 1 + 1, n ≥ 2. eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero Page 21