* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
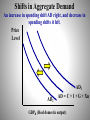
February 13, 2015 1. 2. 3. 4. Collect Unit 1 Vocabulary Unit 1 Exam Will Be Returned/Reviewed After Break! Begin Unit 2- Notes on Aggregate Demand Unit 1 Exam Results 1 Unit 2: National Income and Price Determination 2 Demand Aggregate Demand 4 Aggregate Demand Aggregate means “added all together.” Aggregate combines all prices and all quantities. Aggregate Demand is all the goods and services (real GDP) that buyers are willing and able to purchase at different price levels. The Demand for everything by everyone in the US. There is an inverse (negative) relationship between price level and Real GDP. If the price level: •Increases (Inflation), then real GDP demanded falls. •Decreases (deflation), then real GDP demanded increases. Aggregate Demand Curve Price Level ***WHEN YOU LABEL AN AD/AS GRAPH USE PRICE LEVEL AND REAL GDP! NOT P AND Q!*** AD is the demand by consumers, businesses, government, and foreign countries for domestic commodities.. What definitely doesn’t shift the curve? Changes in price level cause a move along the curve! AD = C + I + G + Xn Real GDP (Real domestic output: GDPR) 6 Why is AD downward sloping? 1. Wealth Effect • Higher price levels reduce the purchasing power of money. • This decreases the quantity of expenditures • Vice Versa Example: • If the balance in your bank was $50,000, but inflation erodes your purchasing power, you will likely reduce your spending. The quantity purchased is reduced. • So…Price Level goes up, Real GDP demanded goes down. 7 Why is AD downward sloping? 2. Interest-Rate Effect • When the price level increases, lenders need to charge higher interest rates to get a REAL return on their loans. • Higher interest rates discourage consumer spending and business investment. • Vice Versa • • Example: An increase in price level leads to an increase in the interest rate from 5% to 25%. You are less likely to take out loans to improve your business. Result…Price Level goes up, GDP demanded goes down 8 (and Vice Versa) Why is AD downward sloping? 3. Net export effect • When U.S. price level rises, foreign buyers purchase fewer U.S. goods and Americans buy more foreign goods. • Exports fall and imports rise causing Real GDP demanded to fall. (XN Decreases) • Example: If prices triple in the US, Canada will no longer buy US goods causing quantity demanded of US products to fall. • Again, Price Level goes up, GDP demanded goes down (and Vice Versa) 9 AP Economics February 23, 2015 1.Quick Review… 2.Finish Lesson 2-1: Aggregate Demand Shifters 3.Activity 3-1: Aggregate Demand Quick Lesson 3-1 Review… 1. What is AD? 2. Inverse Relationship between… 3. Movement from point to point along AD curve caused by… 4. Why is AD curve downward sloping? (3) Shifters of Aggregate Demand Shifts caused by Change in factor other than Price Level! GDP = C + I + G + Xn Shifts in Aggregate Demand An increase in spending shift AD right, and decrease in spending shifts it left. Price Level AD1 AD2 AD = C + I + G + Xn GDPR (Real domestic output) Shifters of Aggregate Demand 1. Change in Consumer Spending Consumer Wealth (Boom in the stock market…) Consumer Expectations (People fear a recession…) Taxes (Decrease in income taxes…) 2. Change in Investment Spending Business Investment is spending money on things that are used to produce other things (plant, equipment, machinery, etc.) Demand for product being produced? Real Interest Rates (Price of borrowing $) Future Business Expectations (High expectations…) Productivity and Technology (New robots…) Business Taxes (Higher corporate taxes means…) Shifters of Aggregate Demand 3. Change in Government Spending (War…) 4. Change in Net Exports (X-M) Exchange Rates (If the US dollar depreciates relative to the Euro, then to Europeans American goods are cheaper, so US exports rise and imports fall) Changes in Foreign Income Investment Specifics • 2 Determinants of Investment: 1.Output (Demand for businesses’ product) 2.Interest Rate (Borrowing or investing own $)