* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 3.1 – Radian Measure
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
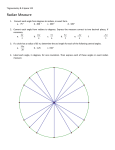
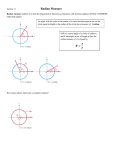
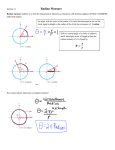
Section 3.1 – Radian Measure Goals/Objectives – Tuesday March 2, 2010 1. To be able to describe the difference between a radian and a degree 2. To be able to convert degrees to radians and vice versa 3. To find the exact values of trigonometric functions involving radian measure. What are radians? • Radian: an angle that is equal in measure to the length of an arc of a circle. – Remember arc length? • Deals with circumference…what is circumference? Circumference 2 radius Why is this different than degree? • The origin of a degree is not really known – it is said that one full rotation of an angle in standard position is 360 degrees because there are almost 360 days in a year and it is easier to divide up 360 degrees in equal increments then it is 365 days. Uses • We use degrees in lower level mathematics courses such as Geometry because of the ease in which they can be manipulated. • We use RADIAN measure in higher order mathematics courses because it allows us to treat the DOMAIN of a function as REAL NUMBERS… 1 unit If NO UNIT of an angle measure is specified, then the angle is understood to be measured in RADIANS! Conversions 0 180 1 radian = 1 = 0 180 0 Convert the following to Degrees… 9 4 5 6 Convert the following to radians… 0 45 249 0 The Special Angles Degree 0 0 0 30 0 45 0 60 0 90 0 180 0 270 3600 Radian Sine Value Cosine Value Tangent Value Find the exact value for the following… 2 tan 3 4 cos( ) 3