* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Networks
TCP congestion control wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Serial digital interface wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Peer-to-peer wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Routing in delay-tolerant networking wikipedia , lookup
UniPro protocol stack wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
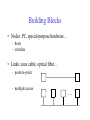
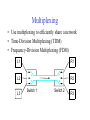
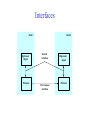
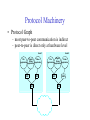
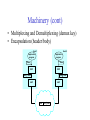
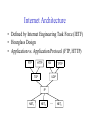
Foundation Outline Requirements Network Architecture Implementing Network Software Problem: Building a Network • How to build a network: – Requirements – Architecture – Key elements in the implementation Requirements Outline Statistical Multiplexing Inter-Process Communication Performance Metrics Building Blocks • Nodes: PC, special-purpose hardware… – hosts – switches • Links: coax cable, optical fiber… – point-to-point – multiple access … Switched Networks • A network can be defined recursively as... – two or more nodes connected by a link, or – two or more networks connected by two or more nodes Strategies • Circuit switching: carry bit streams – original telephone network • Packet switching: store-and-forward messages – Internet Addressing and Routing • Address: byte-string that identifies a node – usually unique • Routing: process of forwarding messages to the destination node based on its address • Types of addresses – unicast: node-specific – broadcast: all nodes on the network – multicast: some subset of nodes on the network Multiplexing • Use multiplexing to efficiently share a network • Time-Division Multiplexing (TDM) • Frequency-Division Multiplexing (FDM) L1 R1 L2 R2 L3 Switch 1 Switch 2 R3 Statistical Multiplexing • On-demand time-division • Schedule link on a per-packet (limited-size block of data) basis • Packets from different sources interleaved on link • Buffer packets that are contending for the link • Buffer (queue) overflow is called congestion • FIFO or round-robin to make flow in a fair maner Statistical Multiplexing • A network that allow flows not to be delayed for more than certain length of time is said to support qualify of service (QoS). … Inter-Process Communication • Turn host-to-host connectivity into process-to-process communication. • Fill gap between what applications expect and what the underlying technology provides. • Provide a logical channel. Host Host Application Host Channel Application Host Host IPC Abstractions • Request/Reply – distributed file systems – digital libraries (web) • Stream-Based – video: sequence of frames • 1/4 NTSC = 352x240 pixels • (352 x 240 x 24)/8=247.5KB • 30 fps = 7500KBps = 60Mbps – video applications • on-demand video • video conferencing What Goes Wrong in the Network? • Bit-level errors (electrical interference) • Packet-level errors (congestion) • Link and node failures • Messages are delayed • Messages are deliver out-of-order • Third parties eavesdrop Performance Metrics • Bandwidth (throughput) – data transmitted per time unit – link versus end-to-end – notation • KB = 210 bytes • Mbps = 106 bits per second • Latency (delay) – time to send message from point A to point B – one-way versus round-trip time (RTT) – components Latency = Propagation + Transmit + Queue Propagation = Distance / SpeedOfLight Transmit = Size / Bandwidth Bandwidth versus Latency • Relative importance – 1-byte: 1ms vs. 100ms dominates 1Mbps vs. 100Mbps – 25MB: 1Mbps vs. 100Mbps dominates 1ms vs. 100ms • Infinite bandwidth – RTT dominates • Throughput = TransferSize / TransferTime • TransferTime = RTT + 1/Bandwidth x TransferSize – 1-MB file to 1-Gbps link as 1-KB packet to 1-Mbps link Delay x Bandwidth Product • Amount of data “in flight” or “in the pipe” • Example: 100ms x 45Mbps = 560KB Delay Bandw idth OSI vs. Internet Architecture • Countless debates on the technical advantages of the ISO protocols versus the Internet protocols are no longer relevant. – ISO protocols are largely ignored. – An implementation of the TCP/IP protocol suite was bundled with the Unix operating system. – The ISO/ITU culture has always been to specify first and implement later. – In 1988, the NIST approved a mandate that required government agencies to procure equipment that could run the ISO protocols. – In reality, computers were shipped with ISO-compliant code, but people kept using TCP/IP. This mandate was rescinded in September 1994. Network Architecture • A computer network must provide general, costeffective, fair, robust, and high-performance connectivity among a large number of computers. • To deal with the complexity, designers developed a network architecture. • OSI and Internet architecture are two widely referenced architectures. Layering • Use abstractions to hide complexity • Abstraction naturally lead to layering • Alternative abstractions at each layer Application programs Request/reply Message stream channel channel Host-to-host connectivity Hardware Protocols • Building blocks of a network architecture • Each protocol object has two different interfaces – service interface: operations on this protocol – peer-to-peer interface: messages exchanged with peer • Term “protocol” is overloaded – specification of peer-to-peer interface – module that implements this interface Interfaces Host 1 High-level object Protocol Host 2 Service interface Peer-to-peer interface High-level object Protocol Protocol Machinery • Protocol Graph – most peer-to-peer communication is indirect – peer-to-peer is direct only at hardware level Host 2 Host 1 Digital Video File library application application application RRP MSP HHP Digital Video File library application application application RRP MSP HHP Machinery (cont) • Multiplexing and Demultiplexing (demux key) • Encapsulation (header/body) Host 1 Host 2 Application program Application program Data Data RRP RRP RRP Data RRP Data HHP HHP HHP RRP Data ISO 7-Layer Reference Model End host End host Application Application Various applications (FTP,HTTP,…) Presentation Presentation Present data in a meaningful format Session Session Provide session semantics (RPC) Transport Transport Reliable, end-to-end byte stream (TCP) Network Network Network Network Unreliable end-to-end tx of packets Data link Physical Data link Data link Data link Reliable transmission (tx) of frames Physical Physical Physical Unreliable transmission (tx) of raw bits One or more nodes within the network Internet Architecture • Defined by Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) • Hourglass Design • Application vs. Application Protocol (FTP, HTTP) FTP HTTP NV TFTP UDP TCP IP NET1 NET2 … NETn OSI vs. Internet Architecture • Countless debates on the technical advantages of the ISO protocols versus the Internet protocols are no longer relevant. – ISO protocols are largely ignored. – An implementation of the TCP/IP protocol suite was bundled with the Unix operating system. – The ISO/ITU culture has always been to specify first and implement later. – In 1988, the NIST approved a mandate that required government agencies to procure equipment that could run the ISO protocols. – In reality, computers were shipped with ISO-compliant code, but people kept using TCP/IP. This mandate was rescinded in September 1994. Open Issue – Ubiquitous Networking • Networking has become a big business. Three major players are: – Computing industry – Telephone carriers – TV industry • A ubiquitous networking is to bring the network into every household.