* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Class XII Physics 50 short questions
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Crystal radio wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
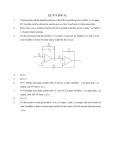
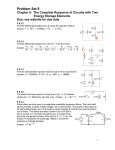
KV ONGC CHANDKHEDA Question Bank 2015-16 Physics Class XII 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Where the energy of capacitor does resides? Do electrons tend to go to region of low or high potential? What is the net charge on the charged capacitor? A Gaussian surface encloses an electric dipole within it. What is the total flux across sphere? State Gauss’s law of electrostatics. Using it derive the expression for the electric filed due to a) an uniformly charged conductor of infinite length. b)an infinitely large sheet which is uniformly charged.c) an uniformly charged spherical shell. Define electric dipole. Deduce the expression for the electric field at axial and equatorial axis of the dipole. Derive the relation between current and drift speed.D Define the equipotential surface. State its important properties D Draw the electric filed lines for a) a positive point charge.b) a negative point charge c) an electric dipole .d) two like charges kept near each other. 10. State Kirchhoff’s voltage and current law. 11. . A ray of light while traveling from a denser to a rarer medium undergoes total reflection.Derive the expression for the critical angle in terms of the speed of light in the respective media. 12. Why is the focal length of an objective in compound microscope little shorter than the focal length of the eyepiece? 13. How does the focal length of a convex lens change if monochromatic red light is used instead of violet light? 14. What are the characteristics properties of electromagnetic waves? 15. What is the work done by a magnetic field on moving a charge? Give reason. 16. Why is copper wire not suitable for a potentiometer? 17. Explain the flow of charges in a metallic conductor. 18. Distinguish between drift velocity and mobility. Establish a relation between drift velocity and current. 19. State Ohm’s law. 20. Define resistivity of a material. How are materials classified based on resistivity? 21. The colours of a carbon resistor is orange, orange, orange. What is the value of resistor? 22. Draw a labelled ray diagram of a reflecting telescope. Mention its two advantages over the refracting telescope. 23. Explain the effective resistance of a series network and parallel network. 24. A diverging lens of focal length F is cut into two identical parts, each forming a Plano concave lens. What is the focal length of each part? 25. What is meant by ‘normal adjustment’ in case of an astronomical telescope? With the help of a neat and labeled ray diagram, obtain an expression for the magnifying power of the telescope in normal adjustment. 26. Deduce an expression for the force on a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field. 27. Explain in detail the principle, construction and the theory of moving coil galvanometer 28. Explain how you will convert a galvanometer into (i) an ammeter and (ii) a voltmeter. 29. Draw a circuit diagram of n-p-n transistor amplifier in CE configuration. Under what condition does the transistor act as an amplifier? 30. In the circuit shown in the figure, identify the equivalent gate of the circuit and make its truth table. 2 31. 32. 33. How the size of depletion region changes when p-n junction diode is in (a) forward bias (b) reverse bias and the conductivity of diode changes with bias. 34. What is zener diode? Draw V-I characteristic curve of zener diode. Explain its use as a voltage regulator. 35. Discuss the variation of resistance with temperature with an expression and a graph. 36. What is ground wave communication? On what factors does the maximum range of propagation in this mode depend? 37. Write the functions of the following in communication systems: (i) Transducer (ii) Repeater 38. Write two application of GPS. 39. By what percentage will the transmission ranges of TV tower be affected when the height of the tower is increased by 21%? 40. Write briefly any two factors which demonstrate the need for modulating a signal. Draw a suitable diagram to show amplitude modulation using a sinusoidal signal as the modulating signal. 41. Mention three different modes of propagation used in communication system. Explain with the help of a diagram how long distance communication can be achieved by ionospheric reflection of radio waves. 42. A 25 mF capacitor, a 0.10 H inductor and a 25 ohm resistor are connected in series with an AC source whose emf is given by ε = 310 sin 314 t volt. (i) What is the frequency of the emf ? ( 50 Hz) (ii) What is the reactance of the circuit ? ( 95.9 Ω capacitive ) (iii) What is the impedance of the circuit ? ( 99.1 Ω ) (iv) What is the current of the circuit ? ( 2.22 A) (v) What is the phase angle of the current by which it leads or lags the applied emf ? ( tanφ = 3.84 ) (vi) What is the value of instantaneous value of current in the circuit ? ( I = 3.13 sin ( 314t + 1.31 ) (vi) What are the effective voltage across the capacitor, inductor and resistance ? ( 282.6 V, 69.7 V , 55.5 V ) (vii ) What value of inductance will make the impedance of the circuit minimum ? ( XL = XC which gives L = 0.405 H ) 43. Explain the determination of the internal resistance of a cell using voltmeter. 44. State and explain Kirchoff’s laws for electrical networks. 45. (a) Define self inductance. Write its SI unit. (b)Derive an expression for self inductance of a long solenoid of length l, cross section area A having N number of turns. 46. State the condition for resonance to occur in a series LCR circuit and derive an expression for the resonant frequency. Draw a plot showing the variation of peak current (im) with frequency ofthe ac source used. Define the Q factor of the circuit. 47. (a)What are eddy currents? Write their two applications. (b)Figure shows a rectangular conducting loop PQRS in which arm RS of length l is movable. The loop is kept in a uniform magnetic field B directed perpendicular to the plane of the loop. The arm RS is moved with a uniform speed v. Deduce an expression for (i)emf induced across the rod ‘RS’ (ii)The external force required to move the arm. (iii)The power dissipated as heat. 48. (a)State Lenz’s law. Give one example to illustrate this law. ‘The Lenz’s law is a consequence to the principle of conservation of energy’. Justify this statement. (b)Deduce an expression for the mutual inductance of two long coaxial solenoids but having different radii and different number of turns. 49. Draw a schematic diagram of a step up transformer. Explain its working principle. Deduce the expression for the secondary to primary voltage in terms of the number of turns in the two coils. In an ideal transformer , how is the ratio related to the current in the two coils? How is the transformer used in large scale transmission and distribution of electrical energy over long distances? 50. State the working of an a.c. generator with the help of a lebelled diagram. The coils of a.c. generator have N turns, each of area A, is rotated with a constant angular velocity ‘ω’. Deduce the expression for the alternating emf generated in the coil. What is the source of energy generation in this device. 51. Define resolving power of a compound microscope. How does the resolving power of a compound microscope change when (i) Refractive index of the medium between the object and objective lens increases? (ii) Wavelength of the radiation used is increased?