* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Computed tomography
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
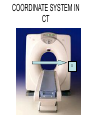
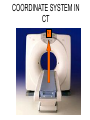
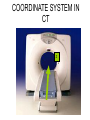
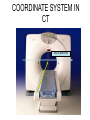
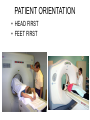
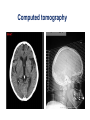
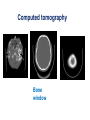
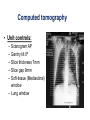
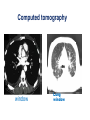
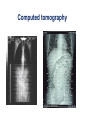
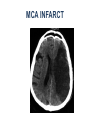
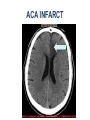
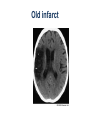
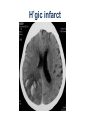
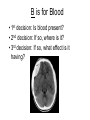
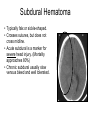
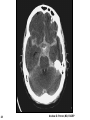
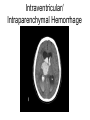
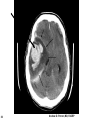
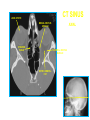
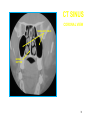
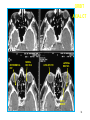
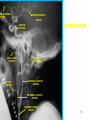
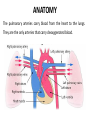
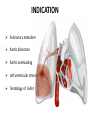
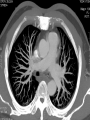
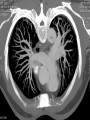
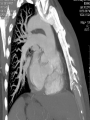
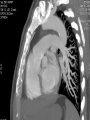
Mid Term Revision Imaging Procedure 3 Dr Mohamed El Safwany, MD. GOALS OF CT • MINIMAL SUPERIMPOSITION • IMAGE CONTRAST IMPROVEMENT • SMALL TISSUE DIFFERENCE RECORDING CT MAIN SYSTEMS • IMAGING SYSTEM • COMPUTER SYSTEM • DISPLAY, RECORDING, STORAGE SYSTEM • DATA ACQUISITION SYSTEM COORDINATE SYSTEM IN CT X COORDINATE SYSTEM IN CT Y COORDINATE SYSTEM IN CT Z COORDINATE SYSTEM IN CT ISO-CENTER PATIENT ORIENTATION • HEAD FIRST • FEET FIRST Computed tomography Softtissue Computed tomography Bone window Computed tomography • Unit controls: – – – – – Scanogram AP Gantry tilt 0º Slice thickness 7mm Slice gap 9mm Soft-tissue (Mediastinal) window – Lung window Computed tomography Mediastinal window Lung window Computed tomography Computed tomography • Positioning: – Supine and feet first – Arms above the head – The knees flexed 30º • Parameters: – Starting at xiphoid process – Ending at the level of hip joint – Respiration suspended in expiration Computed tomography Unit controls • • • • Gantry tilt: 0º. Lateral scout view. Gantry tilt: parallel to the disc space • Slice thickness: – 3mm air --- 1000 fat Pure water Csf White matter Gray matter blood Bone/cacification ---70 0 +8 +30 +45 +70 +1000 MCA INFARCT ACA INFARCT Old infarct H’gic infarct CSF Production • Produced in choroid plexus in the lateral ventricles Foramen of Monroe IIIrd Ventricle Acqueduct of Sylvius IVth Ventricle Lushka/Magendie • 0.5-1 cc/min • Adult CSF volume is approx. 150 cc’s. • Adult CSF production is approx. 500-700 cc’s per day. 25 B is for Blood • 1st decision: Is blood present? • 2nd decision: If so, where is it? • 3rd decision: If so, what effect is it having? 26 Subdural Hematoma • Typically falx or sickle-shaped. • Crosses sutures, but does not cross midline. • Acute subdural is a marker for severe head injury. (Mortality approaches 80%) • Chronic subdural usually slow venous bleed and well tolerated. 27 CT Scan 28 Andrew D. Perron, MD, FACEP Intraventricular/ Intraparenchymal Hemorrhage 29 CT Scan 30 Andrew D. Perron, MD, FACEP CT SINUS AXIAL FRONTAL SINUS 31 CT SINUS LENS OF EYE MEDIAL RECTUS MUSCLE ETHMOID SINUS AXIAL LATERAL RECTUS MUSCLE RETRO ORBITAL FAT 32 CT SINUS CORONAL VIEW MAXILLARY SINUS NASAL SEPTUM 33 ORBIT AXIAL CT RETRORBITAL FAT MEDIAL RECTUS LENS OF EYE LATERAL RECTUS OPTIC NERVE 34 OR CEREBRAL ARTERY MIDDLE CEREBRAL ARTERY CAROTID SYPHON MAXILLARY ARTERY FACIAL ARTERY ARTERIOGRAM OCCIPITAL ARTERY INTERNAL CAROTID ARTERY EXTERNAL CAROTID ARTERY COMMON CAROTID ARTERY 35 ANATOMY The pulmonary arteries carry blood from the heart to the lungs. They are the only arteries that carry deoxygenated blood. INDICATION Pulmonary embolism Aortic dissection Aortic overloading Left ventricular stress Teratology of Fallot CONTRAST DOSAGE 1.2ml /kg (body weight) of non-ionic iodinated contrast medium is injected intravenously into the patient using a pressure injector. Rate of injection being 4-5 ml /sec Pressure 325 ppm PATIENT POSITIONING Proper breath hold instructions should be given Ensure the patient connected IV lines, are long enough to allow full travel of the couch without being pulled or entangled while undergoing a CT SMART PREP TECHNIQUE It is a software, that allows real-time monitoring of IV Contrast enhancement in the area of interest. Good Luck