* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Body Systems - Fall River Public Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
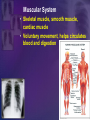
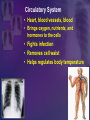
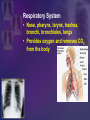
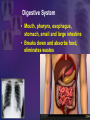
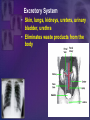
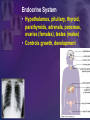
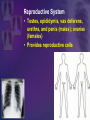
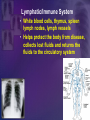
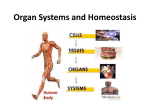
Human Body Systems Biology Facilitator: Mr. Lee Room 320 Objectives • Describe how the human body is organized • Explain homeostasis Organization of the Body – Every cell in the body is both an independent unit and an interdependent unit – The levels of organization in a multicellular organism includes: • Cells • Tissues • Organs • Organ systems Cells • The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things • Specialized cells perform a particular function Tissues – A group of cells that perform a single function – There are four basic types of tissues in a human body: • Epithelial tissues- includes glands and tissues that cover body surfaces • Connective tissues- provides support for the body and connects its parts • Nervous tissues- transmits nerve impulses • Muscle tissues- along with bones, enables the body to move Organs • A group of different types of tissues that work together to perform a single function • For example the eye has: – Epithelial tissue – Nervous tissue – Muscle tissue – Connective tissue Organ Systems • A group of organs that perform a closely related function • For example the brain is part of the nervous system • There are eleven organ systems in the human body that help maintain homeostasis Inside human body Nervous System • Brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves • Coordinates the body Integumentary System • Skin, hair, nails, sweat and oil glands • Provides protection and helps to regulate the body’s temperature Skeletal System • Bones, cartilage, ligaments, tendons • Supports and protects the body • Stores mineral, blood cell formation Muscular System • Skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, cardiac muscle • Voluntary movement, helps circulates blood and digestion Circulatory System • Heart, blood vessels, blood • Brings oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to the cells • Fights infection • Removes cell waist • Helps regulates body temperature Respiratory System • Nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, lungs • Provides oxygen and removes CO2 from the body Digestive System • Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestine • Breaks down and absorbs food, eliminates wastes Excretory System • Skin, lungs, kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra • Eliminates waste products from the body Endocrine System • Hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroids, adrenals, pancreas, ovaries (females), testes (males) • Controls growth, development Reproductive System • Testes, epididymis, vas deferens, urethra, and penis (males); ovaries (females) • Provides reproductive cells Lymphatic/Immune System • White blood cells, thymus, spleen lymph nodes, lymph vessels • Helps protect the body from disease, collects lost fluids and returns the fluids to the circulatory system Maintaining Homeostasis • Homeostasis-maintaining internal balance • Homeostasis requires the integration of all organ systems at the same time • Feedback inhibition (negative feedback) – Process where a stimulus produces a response that opposes the original stimulus – If our body temperature gets too low, part of the brain signals the body to produce more heat Review • Describe how the human body is organized – The levels of organization in the human body : • Cells • Tissues • Organs • Organ systems • Explain homeostasis – Homeostasis is the process how the body keeps internal conditions relatively consistent