* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Data Modeling
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
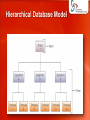
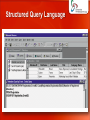
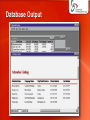
http://singadji.web.id/files/materikuliah/PSI/ Pengantar Sistem Informasi Marcello Singadji, S.Kom, M.T [email protected] [email protected] [email protected] Learning Objectives • Define general data management concepts and terms, highlighting the advantages and disadvantages of the database approach to data management. • Name three database models and outline their basic features, advantages, and disadvantages. • Identify the common functions performed by all database management systems and identify three popular end-user database management systems. • Identify and briefly discuss recent database applications. The Hierarchy of Data Date entries, attributes & keys • Entity: Generalized class of people, places, systems for which data is collected. (Ex. Employees, customers) • Attribute: Characteristic of an entity (Ex. First name, last name) • Key: A set of fields used to identify an entity • Primary Key: A key that uniquely identified the entity Keys and Attributes The Traditional Approach To Data Management • Create new files for each application • Data redundancy • Data integrity The Database Approach to Data Management Advantages of the Database Approach (1) • Improved strategic use of corporate date • Accurate information always available • Reduced data redundancy • Data is stored in one place • Improved data integrity • Changes are reflected throughout • Easier modification and update • No need to know where the data is • Data and program independence • Accurate information always available Advantages of the Database Approach (2) • Better access to data and information • Simple instructions to access data • Standardization of data access • Each DBMS uses the same set of instructions • Standardization for programmers • Should only know how to access the DBMS • Better protection of data • Require authorization on the data • Shared data resources • Setup the database once • Several applications can use it Disadvantages of the Database Approach • Costly • Specialized DBMS software • Specialized DBMS administrators and operators • Increased vulnerability • Single point of failure • Targets for attacks Data Modeling • Planned data redundancy • To have it available in more than one place • To improve system performance • Data model • A diagram of entities and their relationships • Enterprise data modeling • Done at the level of enterprise • Entity-relationship diagrams • Use graphs to show how data is organized and how it is related Entity-Relationship Diagram for a Customer Ordering Database Entity Relationship (one-to-many) Relationship (many-to-one) Relationship (one-to-one) Database Models • Hierarchical (tree) • Data is organized top-down • Network • Owner-membership relationship • A member can have many owners • Relational • Uses tabular format with 2-dimensional tables (relations) • Relations resemble files Hierarchical Database Model Network Database Model Relational Database Model Project table Manager table Department table Relational Models • Describe data using a standard tabular format with all data elements placed in two-dimensional tables, called relations, that are the logical equivalent of files. • Rows represent data entity • Columns represent attributes Providing a User View • Schema - a description of the entire database • First create a schema, then create the tables • Subschema - a file that contains a description of a subset of the database and identifies which users can modify the data items in that subset • A sales representative has to see the data for her office, not the company stock data The Use of Schemas and Subschemas Data Access • Concurrency control: Lock the record so that only one application can access it at a time • Data manipulation language (DML) • Structured Query Language (SQL) • SELECT * FROM Project WHERE Project_number=“155” • UPDATE Project SET Project_number=“156” WHERE Project_number=“155” Structured Query Language Database Output Popular Database Management Systems • • • • • • Oracle MySQL Paradox database FileMaker Pro Microsoft Access Lotus 1-2-3 Spreadsheet Selecting a Database Management System (1) • Database size: Number of records in the database • Number of concurrent users: People or applications that will access it at the same time • Performance: How fast can the DBMS access or update records? • Integration: Which operating system can it run under? • Features: Which security procedures or privacy policies are in place? • Vendor: Size and reputation of the vendor • Cost: Initial cost, maintenance costs, hardware costs, personnel costs Data Warehouses, Data Marts, and Data Mining • Data Warehouse - a database that collects business information from many sources in the enterprise, covering all aspects of the company’s processes, products, and customers. • Data Mart – a subset of a data warehouse. • For small and medium size businesses • Used mostly for decision support system • Data Mining - an information analysis tool that involves the automated discovery of patterns and relationships in a data warehouse. Elements of a Data Warehouse Common Data Mining Applications Common Data Mining Applications • Branding and positioning of products • Customer churn • Which customers can switch to competitors? • Direct marketing • Who would respond to telemarketing? • Fraud detection • Predict transactions which are likely to be illegal Common Data Mining Applications • Market-based analysis • Which products are bought at the same time (diaper, beer, chips) • Market segmentation • Group users based on similarity of products that they buy • Trend analysis • Analyze how variables change over time (e.g., sales) Business Intelligence • Gathering enough of the right information in a timely manner and usable form. • Competitive intelligence • What others are doing • Counterintelligence • Define trade secret information • Knowledge management • Capture company’s collective expertise wherever it resides • Record knowledge and share it Object-Relational Database Management System • Stores the following types of data as objects: • • • • • audio images unstructured text spatial data Spatial Technology Summary • Data - one of the most valuable resources a firm possesses. • Entity - a generalized class of objects for which data is collected, stored, and maintained. • Attribute - a characteristic of an entity. • DBMS - a group of programs used as an interface between a database and application programs. • Data mining - the automated discovery of patterns and relationships in a data warehouse. Terima kasih