* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5.5 Inequalities in Triangles
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Steinitz's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
Riemann–Roch theorem wikipedia , lookup
Brouwer fixed-point theorem wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Incircle and excircles of a triangle wikipedia , lookup
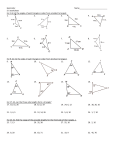
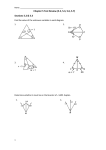
5.5 INEQUALITIES IN TRIANGLES Chapter 5 Relationships Within Triangles WARM UP Look up and write out the Triangle Exterior Angle Theorem: 5.5 INEQUALITIES IN TRIANGLES Corollary to the Triangle Exterior Angle Theorem: The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is greater than the measure of each of its remote interior angles. 3 2 m<1 > m<2 1 and m<1 > m<3 APPLYING THE COROLLARY m<2 = m<1 by the Isosceles Triangle Theorem. Explain why m<2 > m>3. 3 1 m<1 > m<3 + m<4 because <1 is the exterior angle, so m<1 > m<3. 4 By substitution property, m< 2 > m<3, since m<2 = m<1. 2 THEOREM 5-10 If two sides of a triangle are not congruent, then the larger angle lies opposite the longer side. Y 11 12 X 14 <Y is the largest angle. Z COMPARING ANGLES A landscape architect is designing a triangular deck. She wants to place benches in the two larger corners. Which corners have the larger angles? A 27ft C 18ft 21ft B <B and <A are the larger angles, <C is the smallest. THEOREM 5-11 If two sides of a triangle are not congruent, then the longer side lies opposite the larger angle. Y 98 48 34 X Z XZ is the longest side. USING THEOREM 5-11 Which side is the shortest? T 66 U 52 TV is the shortest side. 62 V Y 80 YZ is the shortest side 60 X 40 Z THEOREM 5-12 Triangle Inequality Theorem: The sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the length of the third side. c a a+b>c b+c>a c+a>b b TRIANGLE INEQUALITY THEOREM Can a triangle have sides with the given lengths? 3ft, 7ft, 8ft Yes, 3 + 7 = 10 and 10 > 8 3cm, 6cm, 10cm No, 3 + 6 = 9 and 9 is not greater than 10 TRIANGLE INEQUALITY THEOREM Can a triangle have sides with the given lengths? 2m, 7m, 9m No, 2 + 7 = 9, and 9 is not greater than 9 4yd, 6yd, 9yd Yes, 4 + 6 = 10 and 10 is greater than 9 FINDING POSSIBLE SIDE LENGTHS A triangle has side lengths of 8cm and 10cm. Describe the possible lengths of the third side. To answer this kind of question, add the numbers together and Subtract the small number from the larger number. 8 + 10 = 18 10 – 8 = 2 The value of the third side must be greater Than 2 and less than 18. (x > 2 and x < 18) 2cm < x < 18cm FINDING POSSIBLE SIDE LENGTHS A triangle has side lengths of 3in and 12in. Describe the possible lengths of the third side. To answer this kind of question, add the numbers together and Subtract the small number from the larger number. 3 + 12 = 15 12 – 3 = 9 The value of the third side must be greater Than 9 and less than 15. (x > 9 and x < 15) 9in < x < 15in PRACTICE Pg 294 1,2, 3, 4, 6, 16-27 even, 35-37