* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Insect Life Cycle
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
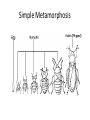
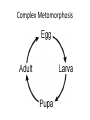
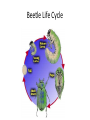
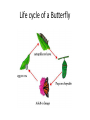
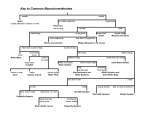
Metamorphosis Insect Life Cycle A rigid exoskeleton requires molting to grow • The number of times an insect molts is specific to the type of insect. Each growth satge is called an instar. • After hatching from an egg, the insect is called the first instar. • After the first molt, the insect is called the second instar (and so on). • Most insects begin their lives as eggs • The female deposits her eggs in a place where the emerging young can develop (host plant) • Insects complete their life cycle in in one of two ways : simple or complex metamorphosis. Simple Metamorphosis • Young insects are called nymphs • Nymphs molt several times and grow bigger each time • Nymphs do not have fully developed wings • Adults and nymphs usually appear togethre on the same food plants or in the same habitat Leaf Footed Bug Metamorphosis Cricket Life Cycle Complex Metomorphosis • The young in a complex metamorphosis are called larva (plural larvae) • Larvae look nothing like the adult • The larvae stage usually does the most feeding • Larvae often form cocoons • The main role of the adult is reproduction • The larvae often appear in different habitats than adults Beetle Life Cycle Lady Beetle Life Cycle Wasp Life Cycle Life cycle of a Butterfly