* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to IC Testing
Nanogenerator wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Digital electronics wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Charlieplexing wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Automatic test equipment wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Valve audio amplifier technical specification wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
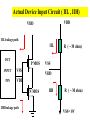
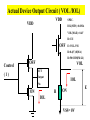
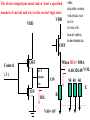
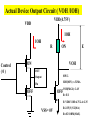
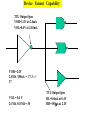
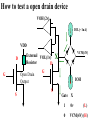
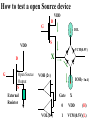
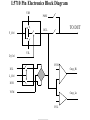
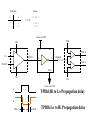
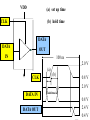
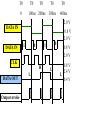
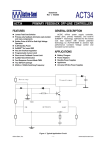
Introduction to IC Testing Testing Goals : .Improve the reliability .Save money in manufacturing Types of Tests (1) By testing purpose . Characterization . Production . Burn –in . Incoming inspection (2) By manufacturing level .wafer-in-process : on-line monitor .wafer : circuit probe (C.P.) . Package : final test (F.T.) (3) By testing item . Functional . DC parameter . AC parameter (4) By process technology . TTL . NMOS . CMOS . BiCOMS . GaAs . Others (5) By device type . Digital : uP ,Gate array,ASIC . Memory : Sram, Dram, Rom . Analog : Power IC . Mixed-Mode : ADC,DAC,Telcom . Others : CCD ,LCD, Test Items (1) Functional test . Truth table . Algorithmic pattern generation (2) DC parametric test .Open and shorts .Output drive/sink current (IOH,IOL) . Leakage . Power current . Standby current . Threshold levels( VIH,VIL) (3) AC parametric test . Propagation delays . Setup and hold times . functional speed . Rise and fall times . Jitter Terms that Apply to the DUT Input pin : A device pin that acts as a buffer between external signals and the internal logic of device Output pin : A device pin that acts as a buffer between the internal logic of a device and the external signals Tri-State : A device pin that acts as an output pin but has the added capability of turning off going to a high impedance state Power pin : A device pin that is connected to a power supply or ground Terms that Apply to the Test System PE card : Circuit used to supply input signals to the DUT and receive output signals from the DUT Drivers : Circuit on the PE card which supply logic 0 and logic 1 levels to the DUT Comparators : The circuitry located on the PE card which sense the logic 0 and logic 1 levels from the DUT Signal Format PMU DPS : The wave shape of an input signal supplied by the PE card driver circuitry : The Precision Measurement Unit Which can , Force current measure voltage Force voltage measure current : The Device Power Supply Which can , Force current measure voltage Force voltage measure current Supply voltage and current to the Negative current Source current : Current flow from the DUT into the tester : When an output pin is in the logic 1 state,it can supply current from the DUT to the tester Positive current : Current flow from the tester Sink current : When an output pin is in the logic o state,it can accept current from the tester through the device to the ground Test Cycle : The time duration of one test vector execution . The test cycle is based on the operating freqency of the DUT . 100ns=1/10MHZ ( SSE. L5710) Tester Channel : Circuitry on the PE card which applies and/or process voltage,current and timing for one DUT pin Terms that Apply to Test parameters VCC : The supply voltage of a TTL device ICC : The current consumed by the circuitry of a TTL device VDD : The supply voltage of a MOS device IDD : The current consumed by the circuitry of a MOS device IIH : Input Leakage High is the maximum amount of current that is allowed to flow into an input pin when a high voltage value is forced onto the pin IIL : Input Leakage Low is the maximum amount of current that is allowed to flow out of an input pin when a low voltage value is forced onto the pin VOH : Voltage Out High is the voltage value produced by an output when given an logic 1 VOL : Voltage Out Low is the voltage value produced by an output when given an logic 0 IOH : Current Out High is the amount of current that an output must source when driving a logic 1 IOL : Current Out Low is the amount of current that an output must sink when driving a logic 0 Actual Device Input Circuit ( IIL , IIH) VDD VDD IIL leakage path IIL DUT P MOS INPUT VSS PIN VDD R ( ~ M ohm) VSS VDD N MOS IIH R ( ~ M ohm) IIH leakage path VSS= 0V Actual Device Output Circuit ( VOL /IOL) VDD VDD SPEC. IOL(MIN) =8.0MA VOL(MAX)= 0.4V R= E/I OFF E=VOL-VSS R=0.4(V)/8(MA) R=50 OHM(MAX) Control OFF VOL DUT (1) Output IOL Pin ON R ON IOL VSS= 0V E The device output pins must sink at least a specified IOL(MIN) =8.0MA amount of current and stay in the correct logic state VOL(MAX)= 0.4V VDD VDD SPEC. R= E/I E=VOL-VSS R=0.4(V)/8(MA) R=50 OHM(MAX) OFF Control OFF When IOL= 8MA 0.40.320.48 VOL DUT (1) Output ON Pin 50 40 60 E ON IOL R VSS= 0V Actual Device Output Circuit ( VOH /IOH) VDD(4.75V) VDD IOH IOH R Control (0) ON ON E VOH DUT Output SPEC. Pin IOH(MIN) =-5.2MA VOH(MAX)= 2.4V OFF OFF R= E/I E=VDD-VOH=4.75-2.4=2.35 VSS= 0V R=2.35(V)/5.2(MA) R=452 OHM(MAX) Device Fanout Capability TTL Output Spec VOH=2.4V at-2.6mA VOL=0.4V at 24.0mA VOH =2.4V 2.6MA /150uA = 17.3 --> 17 VOL = 0.4 V 24 MA /0.8 MA= 30 TTL Output Spec IIL=0.8mA at 0.4V IIH=150A at 2.4V Open Drain/Source Outputs OPEN DRAIN : output can only drive low - they only sink current OPEN SOURCE : output can only drive high - they only source current VDD D G VDD External Resistor VDD D P MOS Open Drain Output S G S N MOS Open Drain Open Source Output Standard CMOS Cell External Resistor Open Source How to test a open drain device VOH (2v) IOL(~ 1uA) VDD D G External VOL(1v) Resistor D Open Drain Output S VCM(4V) X G IOH S Gate X 1 0v (L) 0 VCM(4V) (H) How to test a open Source device VDD D G VDD IOL S VCM(0.5V) X D G Open Source Output S VOH (2v) External Resistor VOL(1v) IOH(~ 1uA) Gate X 0 VDD 1 VCM(0.5V)(L) (H) L5710 Pin Electronics Block Diagram VIH TO DUT DCL F_Ctrl D_Ctrl PMU VIL VOH IOL Cmp_Hi L_Ctrl IOH VCM Cmp_Lo VOL Truth table pattern A B /* AB */ 0 1 1 0 * 0H *; * 1L *; Connect to DPS VOH VIH VCC 7404 CMP_H 0/1 010101 A B HLHLHL CMP_L ON/OFF GND VIL VOL Connect to GND A TPDhl:Hi to Lo Propagation delay B TPDhl TPDlh TPDlh:Lo to Hi Propagation delay VDD (a) set up time CLK (b) hold time DATA DATA OUT IN 100 ns 2.0 V (a) CLK (b) 0.8 V 2.0 V DATA IN DATA OUT Valid Data in 0.8 V 2.4 V 0.4 V T0 T0 0 T0 100ns 200ns T0 T0 300ns 400ns 2.0 V DATA IN DATA IN 0.8 V 2.0 V 1 0 0 1 CLK H DATA OUT Output strobe L L 0.8 V 2.0 V 0.8 V L 2.4 V 0.4 V