* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Grade 6 – Expressions, Equations and Inequalitie
Survey
Document related concepts
Foundations of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Ethnomathematics wikipedia , lookup
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematical notation wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical model wikipedia , lookup
Laws of Form wikipedia , lookup
List of important publications in mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
System of linear equations wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
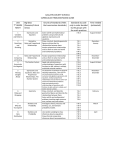
Lexington School District One Curriculum Unit Plan Mathematics Grade Level/Course Unit Summary Grade 6 Course 1 Expressions, Equations, and Inequalities Students will apply and extend previous understandings of arithmetic to algebraic expressions, reason about and solve one-variable equations and inequalities, and represent and analyze quantitative relationships between dependent and independent variables. Duration Chapter 7: 10 Days Chapter 8: 10 Days Chapter 9: 11 Days (Total: 31 Days) Enduring Understandings Essential Questions Rational numbers can be represented in multiple ways and are useful when examining situations involving numbers that are not whole. How can algebraic expressions and equations be used to model, analyze, and solve mathematical situations? Standards 6.EEI.1 Write and evaluate numerical expressions involving whole-number exponents and positive rational number bases using the Order of Operations. 6.EEI.2 Extend the concepts of numerical expressions to algebraic expressions involving positive rational numbers. a. Translate between algebraic expressions and verbal phrases that include variables. b. Investigate and identify parts of algebraic expressions using mathematical terminology, including term, coefficient, constant, and factor. c. Evaluate real-world and algebraic expressions for specific values using the Order of Operations. Grouping symbols should be limited to parentheses, braces, and brackets. Exponents should be limited to whole-numbers. 6.EEI.3 Apply mathematical properties (e.g., commutative, associative, distributive) to generate equivalent expressions. 6.EEI.4 Apply mathematical properties (e.g., commutative, associative, distributive) to justify that two expressions are equivalent. 6.EEI.5 Understand that if any solutions exist, the solution set for an equation or inequality consists of values that make the equation or inequality true. 6.EEI.6 Write expressions using variables to represent quantities in real-world and mathematical situations. Understand the meaning of the variable in the context of the situation. 6.EEI.7 Write and solve one-step linear equations in one variable involving nonnegative rational numbers for real-world and mathematical situations. 6.EEI.8 Extend knowledge of inequalities used to compare numerical expressions to include algebraic expressions in real-world and mathematical situations. x > ca. Write x < c an inequality of the form or and graph the solution set on a number line. b. Recognize that inequalities have infinitely many solutions. 6.EEI.9 Investigate multiple representations of relationships in real-world and mathematical situations. a. Write an equation that models a relationship between independent and dependent variables. b. Analyze the relationship between independent and dependent variables using graphs and tables. c. Translate among graphs, tables, and equations. Learning Plan Focus Lesson Chapter 7: Introduction to Expressions 7.1 There’s a Reason Behind the Rhyme (Order of Operations) 7.2 Getting to the Root of It (Exploring Squares, Cubes, and Roots) 7.3 Things that Vary (Understanding Variables) Standard/Learning Targets ● I can apply the order of operations when evaluating expressions. (6.EEI.1) OMIT LESSON ● I can translate a relationship given in words into an algebraic expression. (6.EEI.2) ● I can apply the order of operations when evaluating algebraic expressions. (6.EE.2) Instructional Notes Adequate Problems: -Prob. 1 -Prob. 2 -Talk the Talk Omit square roots and cube roots Adequate Problems: -Prob. 1 -Prob. 2 (as needed) Language Targets 7.4 What’s My Number? (Writing Algebraic Expressions) 7.5 Different Ways (Multiple Representation s of Algebraic Expressions) 7.6 There’s More than One Way (Using Multiple Representation s of Problems) Chapter 8: Algebraic Expressions 8.1 The Parts of Cars You Don’t See! (Relationships between Quantities) ● I can use a variable to write an algebraic expression that represents a real-world situation when a specific number is unknown. (6.EEI.6) ● I can translate a relationship given in words into an algebraic expression. (6.EEI.2) ● I can evaluate an algebraic expression for a given value. (6.EEI.2) ● I can identify parts of an algebraic expression. (6.EEI.2) ● I can translate between graphs, tables, and equations. (6.EEI.9) ● I analyze the relationship between independent and dependent variables using tables and graphs. (6.EEI.9) OMIT LESSON OMIT LESSON (Supplement terminology from 8.4 in 7.4) Adequate Problems: -Prob. 1 #10-13 -Prob. 2 Supplement Lesson 8.1 , problem 2 to address terminology. Additional practice on terminology found in the skill practice book Adequate Problems: -Prob. 2 -Prob. 3 -Prob. 4 (as needed) OMIT Lesson OMIT LESSON 8.2 Tile Work (Simplifying Algebraic Expressions) Introduction to Distributive Property 8.3 Blueprints to Floor Plans to Computers (Using the Distributive Property to Simplify Algebraic Expressions) 8.4 Are They Saying the Same Thing? (Multiple Representation of Equivalent Expressions) 8.5 Like and Unlike (Combining Like Terms) 8.6 DVDs and Songs: Fun with Expressions (Using Algebraic Expressions to Analyze and Solve Problems) ● ● ● I can apply the associative and commutative properties to justify that two expressions are equivalent (6.EEI.4) ● I can apply the associative and commutative properties to generate equivalent expressions. (6.EEI.3) I can use the distributive property to factor out a common factor of two whole number addends. (6.NS.4) ● I can apply the distributive property to justify that two expressions are equivalent (6.EEI.4) ● I can apply the distributive property to generate equivalent expressions. (6.EEI.3) Adequate Problems: -Prob. 1 (use as review) *Vocab. to introduce on 541 -Prob. 2 I can evaluate an algebraic expression for a given value. (6.EEI.2) ● I can use mathematical properties to justify that two expressions are equivalent. (6.EEI.4) Adequate Problems: -Prob. 1 -Prob. 2 OMIT LESSON ● I can translate a relationship given in words into an algebraic expression. (6.EEI.2) ● I can evaluate an algebraic expression for a given value. (6.EEI.2) ● I can use a variable to write an algebraic expression that represents a real-world situation when a specific number is unknown. (6.EEI.6) Lesson is found on the Google Drive Adequate Problems: -Prob. 1 -Prob. 2 -Prob. 3 # 4- # 6 OMIT LESSON Adequate Problems: -Prob. 1 # 1-3 (others as needed) -Prob. 2 (as needed) Chapter 9: Inequalities and Equations 9.1 Call to Order (Inequalities) 9.2 Opposites Attract to Maintain a Balance (Solving One-Step Equations Using Addition and Subtraction) 9.3 Statements of Equality Redux (Solving One-Step Equations Using Multiplication and Division) 9.4 There Are Many Ways (Representing Situations in Multiple Ways) ● I can write a simple inequality to represent a real-world or mathematical problem. (6.EEI.8) ● I can explain what the solution set of an inequality represents. (6.EEI.8) ● I can show the solution set of an inequality by graphing it on a number line. (6.EEI.8) ● I can explain that solving an equation leads to finding the value(s) that make a true mathematical statement. (6.EEI.5) ● I can substitute a given value into an algebraic equation or inequality to determine whether it is a solution. (6.EEI.5) ● I can solve one-step equations. (6.EEI.7) ● I can explain that solving an equation leads to finding the value(s) that make a true mathematical statement. (6.EEI.5) ● I can substitute a given value into an algebraic equation or inequality to determine whether it is a solution. (6.EEI.5) ● I can solve one-step equations. (6.EEI.7) ● I can explain that solving an equation leads to finding the value(s) that make a true mathematical statement. (6.EEI.5) ● I can substitute a given value into an algebraic equation or Adequate Problems: -Prob. 1 -Prob. 3 -Talk the Talk Adequate Problems: -Prob. 1 -Prob. 2 -Prob. 3 -Talk the Talk (incorporate throughout the lesson) Adequate Problems: -Prob. 1 & 2 (teacher discretion) -Prob. 3 -Talk the Talk (incorporate throughout the lesson) ● ● ● Adequate Problems: -Prob. 1 -Prob. 2 (if needed) 9.5 Measuring Short (Using Multiple Representation s to Solve Problems) 9.6 Variables and More Variables (The Many Uses of Variables in Mathematics) 9.7 Quantities that Change (Independent and Dependent Variables) inequality to determine whether it is a solution. (6.EEI.5) ● I can solve one-step equations. (6.EEI.7) OMIT LESSON (can be used for additional practice to supplement 9.4 if needed) OMIT LESSON OMIT LESSON OMIT LESSON ● I can translate between graphs, tables, and equations. (6.EEI.9) ● I can determine the independent and dependent variable in a relationship. (6.EEI.9) ● I can analyze the relationship between the dependent and independent variables by comparing the table, graph, and equation. (6.EEI.9) Adequate Problems: -Prob. 1 -Prob. 2 -Prob. 3 (if needed) **Make sure to have students discuss how y changes as a result of x based on the graph. Key Academic Vocabulary Key academic vocabulary comes directly from the standards. Students should be immersed in this language through instruction and assessment. These terms are not to be taught as a vocabulary “list” but used on a daily basis so students are literate in the content area of Mathematics. base, exponent, evaluate, sum, difference, term, product, factor, quotient, coefficient, arithmetic expression, algebraic expression, substitute, evaluate, equivalent expressions, commutative property, distributive property, equation, inequality, solve, solution, variable, constant, algebraic equation, independent variable, dependent variable, coordinate plane Additional Teaching Resources