* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download index of refraction
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
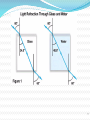
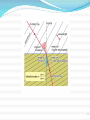
Lesson 5 Objective: You will be able to qualitatively and quantitatively describe the behavior of waves as they pass from one medium to another. Definition: Refraction occurs when a wave changes the direction in which it is moving. This is caused by a change in speed as the wave passes from one medium to another. Official definition: the bending of a ray of light as it passes obliquely between two mediums of different density Broken Pencil As light travels from the water into the air, its path changes because light travels at different speeds, and the pencil appears to be broken. How It works Why It Works The light ray bends as it moves from one medium (water) to another (air). We “see” the pencil at the end of a straight line. The light ray bending is refraction. Waves If waves slow as they go from one medium to another, they bend toward the normal. * * Index of Refraction n is the index of refraction and is a ratio of how much light bends when it enters a different medium. The n for a vacuum is exactly 1.0000... Every substance has a unique optical density. The index of refraction is used to describe the optical density of different materials. The n for air is 1.0003. Index of Refraction medium air water crown glass quartz flint glass diamond n(index of refraction) The greater the index the more light 1.00 bends or slows 1.33 down. This means that all indices will 1.50 - 1.52 be greater than 1.00. 1.54 Table on pg. 667 1.62 - 1.95 gives more 2.42 refractive indices for various mediums. Memory Trick MLA: more to less, away Light moving from a more dense medium (slower speed) into a less dense medium (faster speed) will bend away from the normal. The Law of Refraction Snell's Law sin 1 v1 1 n2 sin 2 v2 2 n1 Example Laser light ( = 6.33 x 10 –7 m) travels from air (n = 1.00) to glass (n = 1.50) at an angle of 47.3 to the normal. a) Calculate the velocity of laser light in the glass. 47.3 air glass b) Calculate the angle of refraction. c) Calculate the wavelength of the laser in the glass. * a) Calculate the velocity of laser light in the glass. n2 v1 v n v2 1 1 n1 v2 n2 8 m 3 . 00 10 1.00 m s 2.00 x 10 8 v2 s 1.50 b) Calculate the angle of refraction. sin 1 n2 sin 1 n1 sin 2 sin 2 n1 n2 sin 47.3 1.00 sin 2 1.50 2 29.3 c) Calculate the wavelength of the laser in the glass. 1 n2 n 2 1 1 2 n1 n2 2 6.33 10 7 m 1.00 1.50 2 4.22 10 7 m * Example #2 Light goes from air into water (n=1.33) with an angle of incidence of 54.1°. Determine the angle of refraction. Calculation: Example #3 Light goes from water (n = 1.33) into diamond (n = 2.42). The light ray in the diamond makes an angle of 72.8° w.r.t. the boundary between the two media. Determine the angle of the light ray w.r.t the normal in the water. Water to diamond: opposite of MLA, ray will bend toward the normal. Calculation: Homework: Workbook P.229 #9,10 P.205 #3,4,8,9,10,12