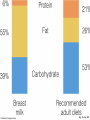
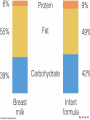
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Pregnancy and
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
ESSAYS DUE AT 5:35 PM IN CLASS ON 21 NOVEMBER 2013 –NOTHING CLINICAL AND NOTHING RELATING TO PATHOLOGY NO DEFICIENCIES OR TOXICITIES Final exam-120 multiple choice-120 marks from vitamins to end of course -4 short answer questions-15 points each for a total of 60 points covers whole course -3 hours- 180 marks •PLEASE SEE EXAM REGULATIONS ON: faculty.cbu.ca/ebarre Beta carotene-fat soluble Lecture 10- 14 November 2013 This lecture is based largely on Chapter 7, 12, 14, 15,16 in Understanding Normal and Clinical Nutrition by Rolfes et al. Lecture 10- 14 November 2013 Outline Water -role in metabolism -role in metabolic regulation Outline of lecture 10 Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Pregnancy and Lactation Infancy Early Childhood Adolescence Adulthood More Detailed Comments Water -role in metabolism -carries nutrients and waste products throughout the body -maintains structure of large molecules like proteins and glycogen Water -role in metabolism -participates in metabolic reactions- eg hydrolysis (eg protein catabolism), or product of metabolism (metabolic sink)(eg when hydrogen joins with oxygen as part of electron transport chain processes) -solvent (provides medium for reactions) -regulation of body temperature -maintains blood volume Water -class exercise -explain each role in metabolic regulation Break Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Pregnancy and Lactation Pregnancy foetal growth and development -folate supplementation -prevent neural tube defects -one month before conceptionwhy? Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Pregnancy and Lactation Pregnancy foetal growth and development folate supplementation -0.8 to 4 mg supplements -if have had previous neural tube baby then 4 mg supplements may be recommended - require a prescription as high folate intake may mask pernicious anemia of a vitamin B12 deficiency Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Pregnancy and Lactation Pregnancy critical periods -maternal anemia during critical growth period of placental growth alters pattern of blood vessel growth which may affect cardiovascular health of infant Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Pregnancy and Lactation Pregnancy critical periods -infant beta cell development-poor maternal nutrition during critical period of beta cell development (12 weeks gestation to 5 months post delivery) may cause diabetes particularly if person eats in overabundance in later life Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Pregnancy and Lactation Pregnancy weight prior to conception-underweight mother -underweight mother leads to greater chance of a low birthweight infant especially if mother is unable to gain sufficient weight during the pregnancy Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Pregnancy and Lactation Pregnancy weight prior to conception-underweight mother -as well rates of preterm births and infant deaths are higher for underweight women Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Pregnancy and Lactation Pregnancy weight prior to conception-overweight mother overweight mother leads to greater chance of her experiencing gestational diabetes, hypertension and post-partum infections and of having a stillborn and/or other labour and delivery complications Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Pregnancy and Lactation Pregnancy weight prior to conception-overweight mother -as well infants tend to be larger and have greater risk of poor health(including neural tube defects) and death than do normal weight infants -never try to lose weight during pregnancy- lose appropriately preconception or post-delivery Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Pregnancy and Lactation Pregnancy weight gain during pregnancy underweight correct weight overweight obese 28-40 lbs 25-35 lbs 15-25 lbs 15 lbs minimum Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Pregnancy and Lactation Pregnancy energy and nutrient needs during pregnancy energy add 100 kcal per day trimester 1 add 300 kcal per trimesters 2 and 3 pregnant teenagers, underweight and physically active women may require more Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Pregnancy and Lactation Pregnancy energy and nutrient needs during pregnancy nutrient needs fig 14-10 Fig. 14-10, p. 489 Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Pregnancy and Lactation Pregnancy energy and nutrient needs during pregnancy nutrient needs carbohydate- ideally 250 or more grams per day and no less than 100 grams per day Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Pregnancy and Lactation Pregnancy energy and nutrient needs during pregnancy nutrient needs protein add 5 grams per day trimester 1 add 20 grams per day trimester 2 add 25 grams per day trimester 3 Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Pregnancy and Lactation Pregnancy energy and nutrient needs during pregnancy nutrient needs protein most people have enough protein to begin with in their diet to meet these protein requirements Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Pregnancy and Lactation Pregnancy energy and nutrient needs during pregnancy nutrient needs protein do NOT use high protein supplements during pregnancy-chance of low birthweights, pre-term births and still borns Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Pregnancy and Lactation Pregnancy energy and nutrient needs during pregnancy nutrient needs essential fatty acids linoleic and alpha-linolenic- brain growth and development, visual acuity fish oil supplements are not recommended -possibility of toxins and effect on pregnancy is not known Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Pregnancy and Lactation Pregnancy energy and nutrient needs during pregnancy nutrient needs -folate, B12, iron and zinc as well as vitamin D and calcium require particular attention Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Pregnancy and Lactation Pregnancy common nutrition related concerns of pregnancy -nausea, constipation, haemorrhoids, heartburn, food cravings and aversions, non food-cravings (pica) Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Pregnancy and Lactation Pregnancy malnutrition and pregnancy -malnutrition can lead to reduced fertility for males and females -malnutrition prior to pregnancyprevent placenta from developing properly with subsequent potential for physical and cognitive abnormalities on the part of the infant Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Pregnancy and Lactation Pregnancy infants birthweight -low- premature-can catch up -have easier time catching up in growth development if their post-delivery nutrition is good -less than gestational age- have tougher time catching up in growth development even if their post-delivery nutrition is good Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Pregnancy and Lactation Pregnancy mothers age -adolescence- immaturity may lead to poor food choices with subsequent foetal risk -weight gain of 35 lbs for normal weight female Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Pregnancy and Lactation Pregnancy practices incompatible with pregnancy alcohol and herbal supplements and nutraceuticals Break Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Pregnancy and Lactation Lactation Nutrition during lactation mother's nutrient needs energy additional 450 kcal per day consumedrest comes from fat stores built up during pregnancy figure 14-10 Fig. 14-10, p. 489 Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Infancy energy and nutrient needs energy infants require about 100 kcal/kg/day protein inadequate-consequences too much-stress kidneys and liver figure 15-2 Fig. 15-2, p. 517 Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Infancy breast milk lactose improves calcium absorption omega 3 fatty acids figure 15-3 Fig. 15-3, p. 518 Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Infancy infant formula nothing beats breast milk soya formulas-avoids allergy issue found with some non-soya formulas - good for lactose intolerance as there is no lactose in soya formulas avoid goats milk-low in folate table 15-2 figure 15-4 Table 15-2, p. 519 Fig. 15-4, p. 521 Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Infancy special needs of pre-term infants poor absorption of calcium and lipid, fat soluble vitamins, calcium, iron and zinc due to immature gut solution-pre-term breast milk eg higher protein concentration than full term breast milk Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Infancy introducing cow's milk not until 12 months of age poor iron content and it may cause intestinal bleeding cows milk is higher in calcium and lower in vitamin C-thus inhibiting iron absorption type 1 diabetes issue-this is controversial Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Infancy introducing solid foods no earlier than 6 months 6-12 months if not before end of first year there may be delayed growth Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Infancy introducing solid foods 6-12 months iron fortified cereals, meat or meat alternatives such as legumes -serve with vitamin C to improve iron absorption -vitamin C rich foods include citrus fruit juices and chopped berries Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Infancy introducing solid foods at one year-2-3.5 cups of milk maximum to avoid displacement of iron rich foods plus give iron fortified cereals, fruits and vegetables to meet iron requirements primary food in first 12 months ideally is breast milk Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Early Childhood energy and nutrient needs energy 1 year 1000 kcal/day 3 years-1300 kcal/day 10 years-2000 kcal/day Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Early Childhood energy and nutrient needs nutrient needs protein-needs dictated by needs to maintain nitrogen balance, protein quality and added needs of growth vitamins and minerals-met by 6 principles of dietary planning(adequacy, moderation, balance, variety, energy control and avoiding empty kcal foods) Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Early Childhood hunger and malnutrition in children glucose and iron are critical to brain functioning and subsequently to the child's behaviour adverse reactions to foods must meet nutrient needs of child childhood obesity excess energy intake relative to energy expenditure Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Early Childhood mealtimes at home -6 principles of good dietary planning nutrition at school -pack lunches Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Adolescence energy and nutrient needs energy-2000-4000 kcal/day activity levels males need more than females Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Adolescence nutrients vitamin D and calcium iron chronic diseases atherosclerosis type 2 diabetes hypertension Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Adulthood as we age in adulthood we reduce our metabolic rate- therefore need to reduce caloric intake while meeting the 6 principles of good dietary planning that adequately address changing nutrient intake requirements Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Adulthood water- avoid dehydration-mobility and desire to consume water are issues here protein- 0.8 g/kg/day carbohydrate- increased fibre to offset constipation- also need more fluid Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Adulthood vitamin B12, vitamin D, calcium as well as iron are among the nutrients of primary concern vitamin B12 -bacterial overgrowth-in stomach results in vitamin B12 consumption by bacteria vitamin D and calcium -a concern due to reduced dairy intake as we age as well as the risk of osteoporosis Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Adulthood vitamin B12, vitamin D, calcium as well as iron are among the nutrients of primary concern iron- deficiency risk if low food energy intakes-mobility and desire to consume food are issues here Nutrition metabolism throughout the life cycle Adulthood nutrient-brain relationships-table 16-2 Table 16-2, p. 574