* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Immunoassays
Pharmaceutical marketing wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
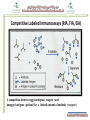
Director of Poison Control & Medical Forensic Chemistry Center, Techniques used in Toxicology Immunoassays Chromatographic Spectroscopic (TLC-LC–GC-IC ) ( MS-A.A-FTIR-UV) Immunoassays chromatographic methods were employed, which had good specificity and sensitivity but were too labor intensive. The advent of immunochemical assays, along with automation, meant faster, less labor intensive and more reliable for TDM and screening tests (not confirmatory). Immunoassays principle are depends on the reaction of an antigen (analyte) and an antibody All immunoassays require the use of labeled material in order to measure the amount of antigen or antibody. Labeled Immunoassays Antigen or antibody is labeled ( tagged ) with a substance that can be detected later on and allows for the detection of an antibody – antigen reaction Types of tags Radioactive isotopes Enzymes Fluorescent molecules Luminescent labels Types of reactions Competitive binding Noncompetitive binding Separation Techniques Heterogeneous assay Bound and free antibody must be separated before label is measured Example: ELISA (Enzyme Linked Immunosorbant Assay) Homogeneous assay Bound and free antibody do not need to be separated prior to measurement phase. Example: EMIT (Enzyme Multiplied Immunoassay Technique ) Competitive Labeled Immunoassays (RIA, FIA, EIA) A competition between tagged antigens ( reagent ) and untagged antigens ( patient )for a limited amount of antibody ( reagent ) Immunoassays EMIT: The EMIT (Enzyme Multiplied Immunoassay Technique) Homogeneous (Bound and free antibody do not need to be separated prior to measurement phase) The EMIT (is qualitative and semi-quantitative technology) is based on competition for the target analyte antibody binding sites. Analyte in the sample competes with the drug in the enzyme reagent that is labeled with G6PDH. Active enzyme G6PDH converts the coenzyme (NAD) in the antibody reagent to NADH, resulting in a kinetic absorbance change that is measured photometrically. Viva & Viva-E & Viva Twin Made by Siemens Bench top Relatively small Measures multiple therapeutic drugs quantitatively Also measures major drugs of abuse DOA) Requires little maintenance Flexible (Easy to use) Applies EMIT method for all measurements Sensitivity is not sufficient; many interference and falls positive (Disadvantages !!!) FPIA: Fluorescence Polarization Immunoassay This method uses a fluorescent molecule as the label instead of an enzyme, making it more sensitive. In FPIA, the patient sample is incubated with a known quantity of the fluorescent-labeled drug and an antibody specific for the drug. As in EMIT, the labeled and unlabeled drugs compete for the binding sites of the antibody. Polarized light is emitted in certain angles depending on whether the fluorescent-labeled drug is bound to antibodies or not. Since this is a competitive assay, the greater the amount of drug in the sample, the lower the amount of fluorescence. AxSYM Made by Abbott Big instrument Measures multiple therapeutic drugs quantitatively Also measures major drugs of abuse DOA) Easy to use Requires daily maintenance Great sensitivity FPIA is the main technique for most TDM measurements Relatively slow Requires continuous manual loading of RVs when running many samples. High cost of Kit (Disadvantages !!!) Chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay (CMIA) Chemiluminescence: This is a chemical reaction that emits energy in the form of light. When used in combination with immunoassay technology, the light produced by the reaction indicates the amount of analyte in a sample label is a molecule that will react as a part of the assay, so a change in signal can be measured in the urine after added reagent solution. CMIA is non-competitive sandwich assay technology to measure analytes. The amount of signal is directly proportional to the amount of analyte present in the sample CMIA is non-competitive sandwich assay technology (Pre-Tigger Solution) (Tigger Solution) Activiation ARCHITECT ci4100 Made by Abbott Very big instrument Measures multiple therapeutic drugs quantitatively Also measures major drugs of abuse DOA (Sensitivity problem for some tests) Very fast Take many unlimited number of samples (good) Requires external water supply !!! Requires complex daily maintenance Complex software (Requires careful and long training process) Chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay (CMIA) is the main technique for most TDM measurements Others Immunoassays RIA: Radioimmunometric assays Not commonly used any longer due to waste disposal issues use radioactivity to detect the presence of the analyte. A gamma counter is then used to measure the amount of radioactivity in the sample as counts per minute (CPM). QC and standards must be performed with each run, leading to extra labor and cost. ACMIA: Affinity Chrome-Mediated Immunoassay. ACMIA is a technique to measure drug concentrations in which free and drug-bound antibody enzyme conjugates are separated using magnetic (chrome) particles. PETINIA: Particle Enhanced Turbidimetric Inhibition Immunoassay This method uses the creation of light scattering particles to measure drug levels. The latex particle-bound drug binds to the drug-specific antibody, forming insoluble light-scattering aggregates. This causes an increase in the turbidity of the reaction mixture. CEDIA: Cloned enzyme donor immunoassay (CEDIA) methodology is a novel approach which uses the DNA technology to produce homogenous enzyme immunoassays for drugs The Biochip The Biochip is the foundation of Biochip Array Technology. • A single 9x9mm biochip acts as the reaction vessel, replacing multiple cuvettes. • Randox biochips are pre-fabricated with an array of discrete test regions (DTR’s) • Randox biochips currently hold up to 25 tests - 23 tests and 2 internal controls. • One biochip is used per patient sample. • Biochip manufacturing processes are accredited to UKAS and ISO13485. Evidence Biochip Carrier DRUG DETCTION PERIODS Sampling Type of Samples received: CRUDES, BIOLOGICALS and SEIZED TOOLS Samples comes from hospitals forensic medicine administration and from different government sectors such as: -Ministry of Interior ( General Directorate of Narcotics Control and Police offices ) -Customs (Sea & Land ports) -Other Government sectors CRUDE SAMPLES Received from different sectors Samples of seized crude materials such: - Khat - Cannabis - Captagon tablets - Alcohols - Any seized materials and tools etc.. Sampling Specifications: Sealed and secure Privacy (no personal data) Enough (Fixed amount for each drug) e.g 5 grams khat Comes with a letter from requesting sector Received only from AUTHORIZED person BIOLOGICAL SAMPLES Include body fluids (i.e. blood, urine, gastric lavage, etc.) and tissue samples (Biopsies and Autopsies) - Hospitals samples: TDM , (ET) , Employees screening and police suspected cases - Forensic medicine administration samples BIOLOGICAL SAMPLES (FORENSIC) Purpose: Employee screening , police suspected cases, forensic medicine (FM). Urine sample is the main sample for Narcotics analysis Blood sample is the main sample for alcohol analysis For FM, all body fluids (urine, blood, Vitreous humor) and any other body parts or excretions can be received. NOTE: Crude samples can be received in some occasions to help in the detection of the death cause !! BIOLOGICAL SAMPLES (FORENSIC) cont. Sampling specifications for employee screening: 2 urine samples Request form Labeled correctly Biohazard bag and cold container Authorized person Sampling specifications for police cases: 2 urine samples for narcotics and 2 blood samples for alcohol All papers completed (request from police, request from hospital, sample collection witness form) Labeled correctly Finger prints of the suspect on the samples and request No delay Biohazard bag and cold container Authorized person BIOLOGICAL SAMPLES (FORENSIC) cont. • Sampling specifications for FM: • Any human or crude samples can be received • Request form completed by forensic doctor (dead person information, description of the body during sampling, any related information) • Labeled correctly • No delay • Biohazard container for tissue transportation and cold container • Authorized person Five “Rights” Right Right Right Right Right Sample drug dose route time (in case of Emergency Toxicology & TDM) Conclusion • • • • • • Immunoassay excluded negative samples. Immunoassay evolves continuously. Result obtained within short-time (minute). Easy to use. No require for extraction procedure. No hazard chemicals used.